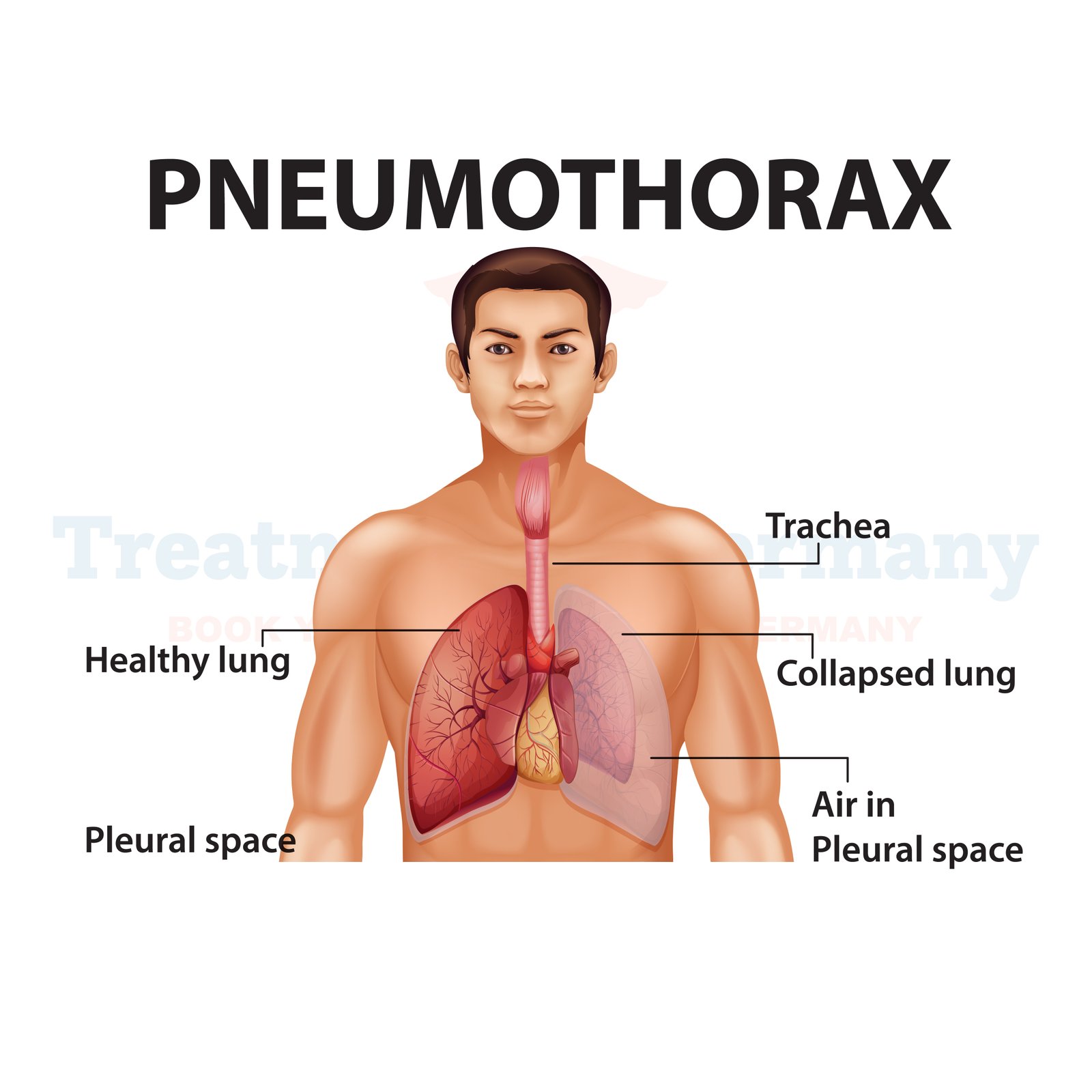
What is Pleural Effusion:
Pleural effusion refers to an abnormal buildup of fluid in the pleural space, the area between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and the chest cavity. Normally, a small amount of fluid is present in this space to help lubricate the surfaces and allow smooth movement during breathing. However, when excess fluid accumulates, it can lead to complications and discomfort.
Side effects of Pleural Effusion:
The symptoms of pleural effusion can vary depending on the amount of fluid present and the underlying cause. Common signs and symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially when lying down
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing
- Dry cough
- Fever and chills (if infection is present)
- Fatigue and weakness
In severe cases, Pleural Effusion can lead to respiratory distress and complications such as pneumonia or lung collapse if left untreated.
How is Pleural Effusion diagnosed?:
To diagnose pleural effusion, your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination and may order various tests, including:
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test can reveal the presence of fluid in the pleural space.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging can provide detailed images of the chest cavity and help determine the amount and location of fluid.
- CT scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan may be used to further evaluate the lungs and surrounding structures.
- Thoracentesis: In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the pleural space to drain fluid for analysis. This can help determine the cause of the effusion, such as infection, inflammation, or cancer.
Potential treatments of Pleural Effusion:
The treatment approach for pleural effusion depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Common treatment options may include:
- Thoracentesis: Draining the excess fluid from the pleural space can provide immediate relief of symptoms and help identify the cause of the effusion.
- Medications: Depending on the cause, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for infections, diuretics to reduce fluid buildup, or anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation.
- Pleurodesis: In cases where pleural effusion recurs frequently, a procedure called pleurodesis may be recommended. During this procedure, a chemical or irritant is injected into the pleural space to create inflammation and adhesion between the layers of the pleura, preventing further fluid buildup.
- Surgery: In some cases, especially if other treatments are ineffective or if there is an underlying structural issue, surgery may be necessary to drain the fluid or remove part of the pleura.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a
complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
