What is Polycythemia Vera:
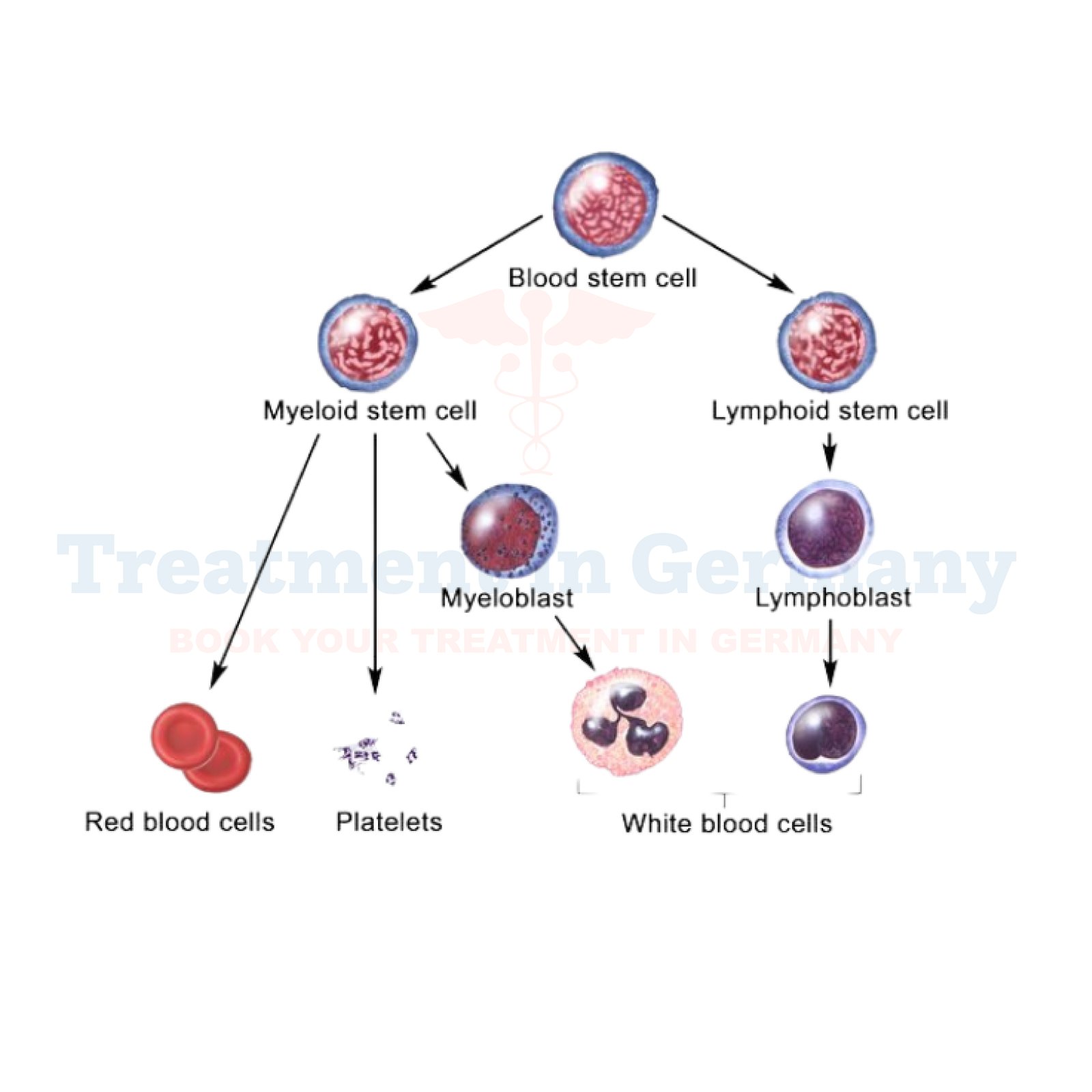
Polycythemia Vera is a rare blood disorder characterized by the overproduction of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
This excessive production thickens the blood, leading to various complications such as blood clots, stroke, or heart attack.
PV falls under the category of myeloproliferative neoplasms, where the bone marrow produces too many of one or more types of blood cells.
Side Effects of Polycythemia Vera:
Polycythemia Veracan manifest with a range of symptoms, including:
How is Polycythemia Vera Diagnosed:
Diagnosing Polycythemia Vera typically involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and possibly bone marrow tests. Your doctor may order a complete blood count (CBC) to check for elevated levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Additionally, genetic tests and imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI may be conducted to assess any organ damage caused by PV.
Potential Treatments of Polycythemia Vera:
The primary goals of PV treatment are to reduce the risk of blood clots and manage symptoms. Treatment options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
