What is Polymyalgia Rheumatica?
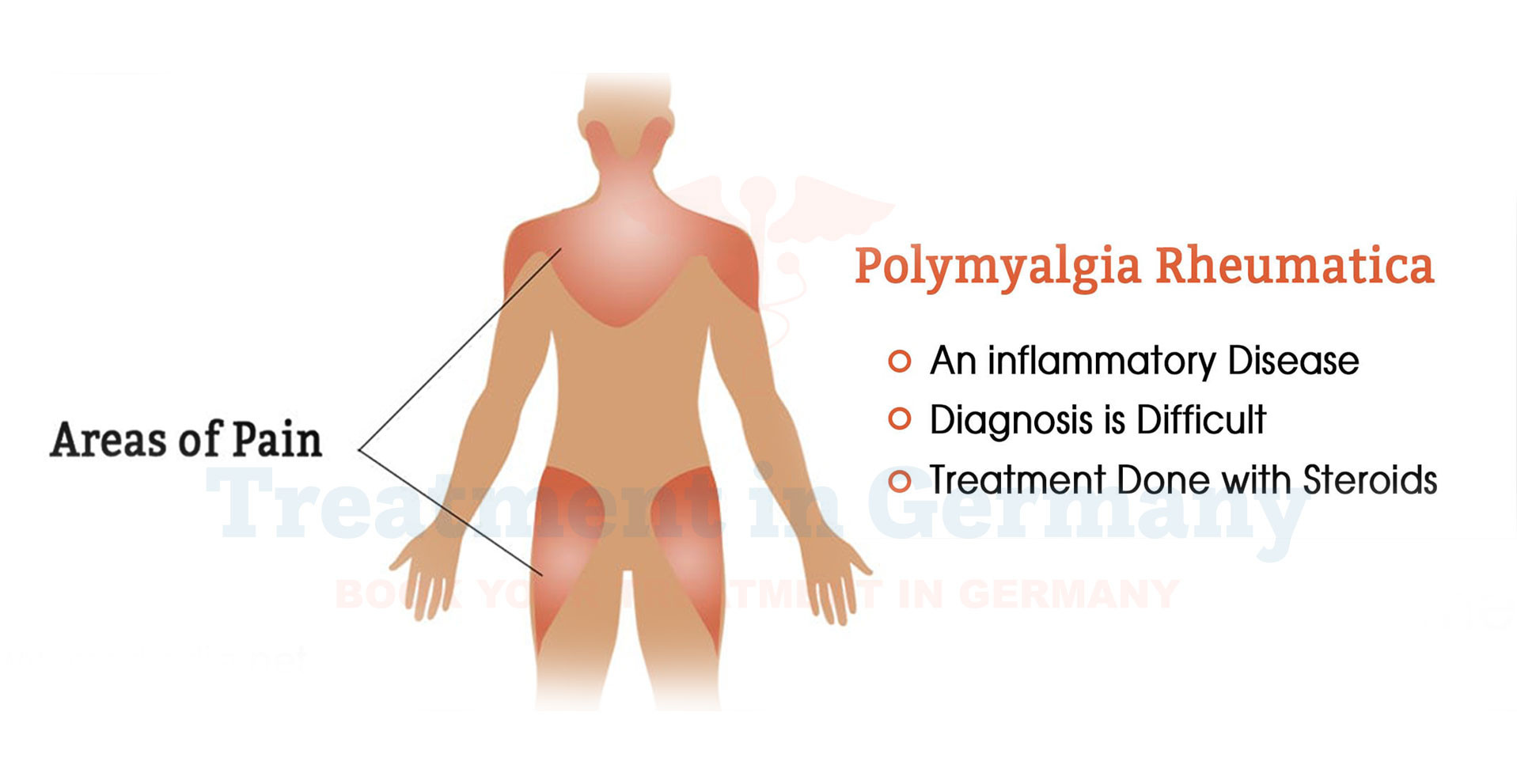
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects older adults, typically those over the age of 50.
It is characterized by muscle pain and stiffness, especially in the shoulders, neck, and hips.
The symptoms often develop rapidly and can lead to significant discomfort and impairment in daily activities. PMR is often associated with another condition called Giant Cell Arteritis, an inflammation of the blood vessels.
Side Effects of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
The side effects of Polymyalgia Rheumatica can be both physical and emotional:
- Physical Effects: Patients commonly experience severe pain and stiffness in the shoulders, hips, and neck. This can significantly impact mobility and daily function. Fatigue, weight loss, and sometimes low-grade fever may also accompany the condition.
- Emotional Effects: Chronic pain and reduced mobility can lead to emotional stress, anxiety, or depression. It’s important for patients to seek support from mental health professionals if needed.
How is Polymyalgia Rheumatica Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Polymyalgia Rheumatica involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Clinical Evaluation: A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial. Your doctor will assess symptoms like muscle pain and stiffness, particularly in the shoulders and hips.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests are used to check for markers of inflammation, such as elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Imaging: Sometimes, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI may be used to evaluate inflammation in the affected muscles and joints.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: The diagnosis is often one of exclusion, meaning other possible conditions that could cause similar symptoms are ruled out.
Potential Treatment of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Treatment for Polymyalgia Rheumatica typically involves medication and lifestyle adjustments:
- Medications: The primary treatment for PMR is corticosteroids, such as prednisone. These medications help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. The dosage is usually adjusted based on the patient’s response and side effects.
- Pain Relief: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can be beneficial to maintain flexibility and strength, which may be affected by the condition.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help improve overall well-being and support recovery.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
