Understanding Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome
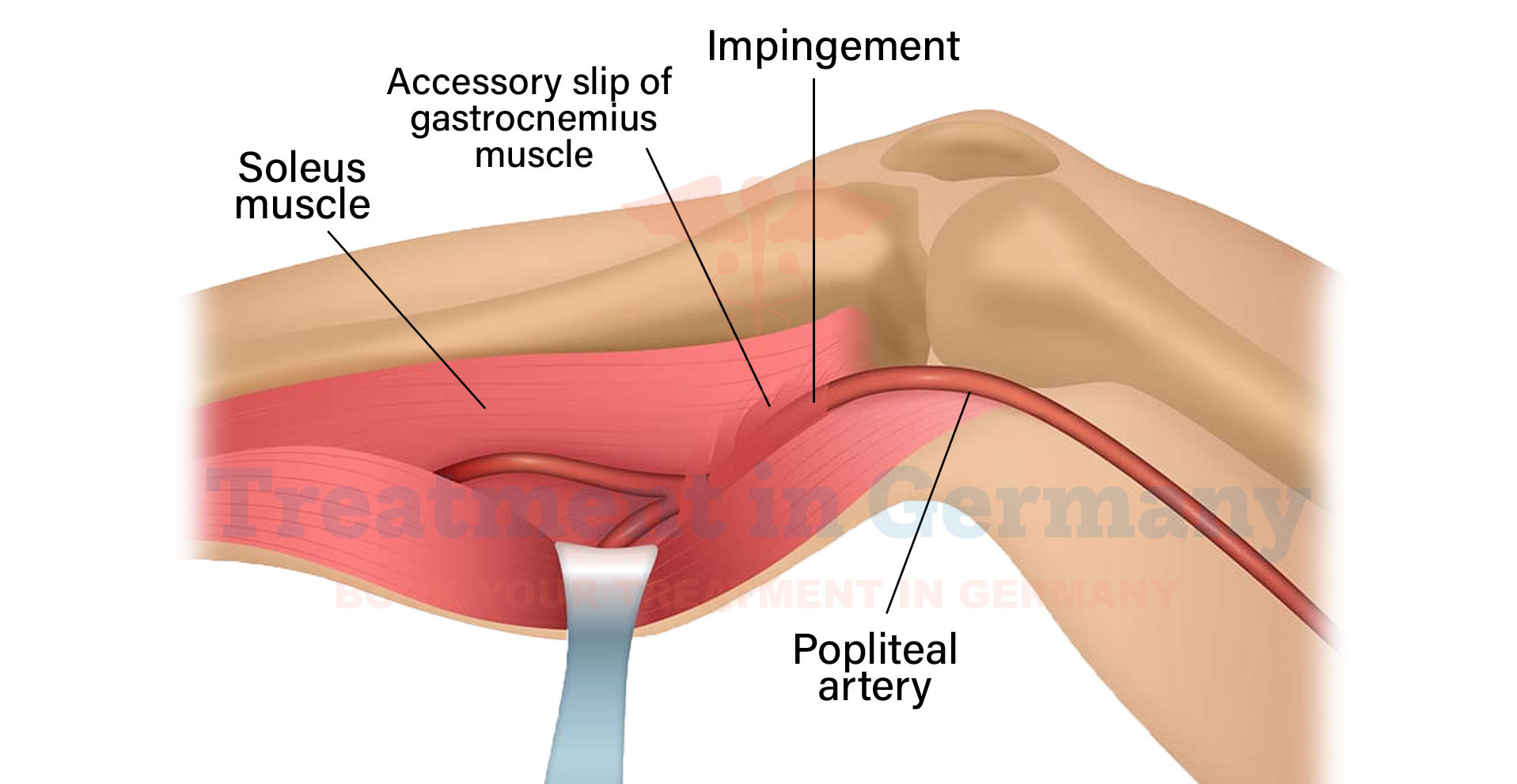
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome (PAES) is a rare condition where the popliteal artery, the major blood vessel behind the knee, becomes compressed or trapped by surrounding structures such as muscles or tendons.
This compression restricts blood flow to the lower leg, leading to symptoms that can range from mild discomfort to severe ischemia (lack of blood supply) and potential limb-threatening complications.
Side Effects of Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome
The symptoms of Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome can vary widely depending on the degree of compression and the duration of the condition. Common signs include:
- Intermittent Claudication: Pain, cramping, or fatigue in the calf or foot during physical activity.
- Coldness or numbness: Reduced circulation can lead to sensations of coldness or numbness in the affected limb.
- Muscle Atrophy: Chronic lack of blood flow can cause muscle wasting over time.
- Pallor or Cyanosis: Skin discoloration due to poor circulation, appearing pale or blue.
In severe cases where blood flow is severely compromised, there is a risk of acute limb ischemia, which requires immediate medical attention to prevent tissue damage or loss.
How is Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specialized imaging studies. The following diagnostic methods are commonly used:
- Doppler Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in the arteries and can detect abnormalities in the popliteal artery.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) or Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): These imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of blood vessels and can help identify the exact location and severity of arterial compression.
- Arteriography: A more invasive procedure where contrast dye is injected into the arteries to visualize blood flow, providing precise information for surgical planning if needed.
Potential Treatment of Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome
Treatment options for Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome depend on the severity of symptoms and the extent of arterial compression. They may include:
- Conservative Management: Initially, managing symptoms with rest, modification of physical activities, and medications to improve blood flow and reduce pain.
- Surgical Intervention: If conservative measures are ineffective or if there is significant arterial damage, surgical correction may be necessary. This typically involves releasing the entrapped artery and repositioning it to alleviate compression.
- Physical Therapy: Post-surgical rehabilitation to restore strength and function in the affected limb.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
