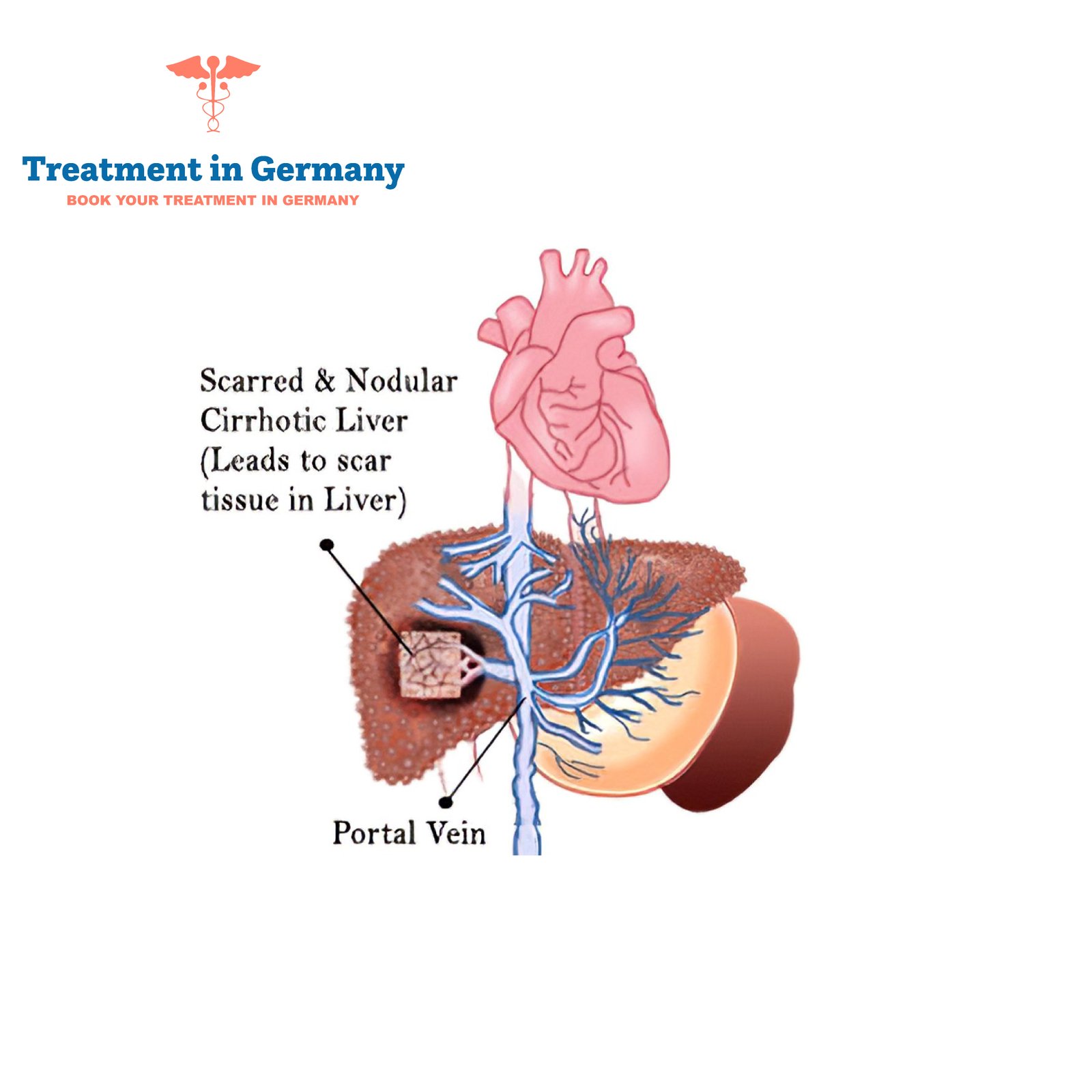
What is Portal Hypertension:
Portal hypertension is a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the portal vein, which is the major vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. This increased pressure can lead to various complications and affect the normal functioning of the liver and other organs.
Side effects of Portal Hypertension:
Portal hypertension can lead to several serious complications, including:
How is Portal Hypertension diagnosed?
Diagnosing portal hypertension typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
1. Imaging tests: such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the liver, portal vein, and any signs of obstruction or abnormalities.
2. Endoscopy:A procedure where a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the esophagus and stomach for the presence of varices or other abnormalities.
3. Liver function tests: Blood tests to assess liver function and detect any abnormalities in liver enzymes or other markers of liver health.
4. Hemodynamic measurements: Invasive procedures such as hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) measurement to directly assess the pressure in the portal vein and evaluate the severity of portal hypertension.
Potential treatments of Portal Hypertension:
Treatment for portal hypertension aims to manage its complications, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further progression of the condition. Depending on the severity and underlying cause of portal hypertension, treatment options may include:
1. Medications: such as beta-blockers to reduce portal pressure and prevent bleeding from varices, diuretics to manage ascites, and antibiotics to prevent infections in individuals with advanced liver disease.
2. Endoscopic therapy: Procedures such as banding or sclerotherapy to treat varices and reduce the risk of bleeding.
3. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): A minimally invasive procedure where a shunt is placed to redirect blood flow and reduce pressure in the portal vein.
4. Liver transplantation: For individuals with severe liver damage or complications of portal hypertension, liver transplantation may be considered as a definitive treatment option.
5. Lifestyle modifications: Including dietary changes, avoidance of alcohol and certain medications, and regular exercise to support liver health and manage symptoms.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
