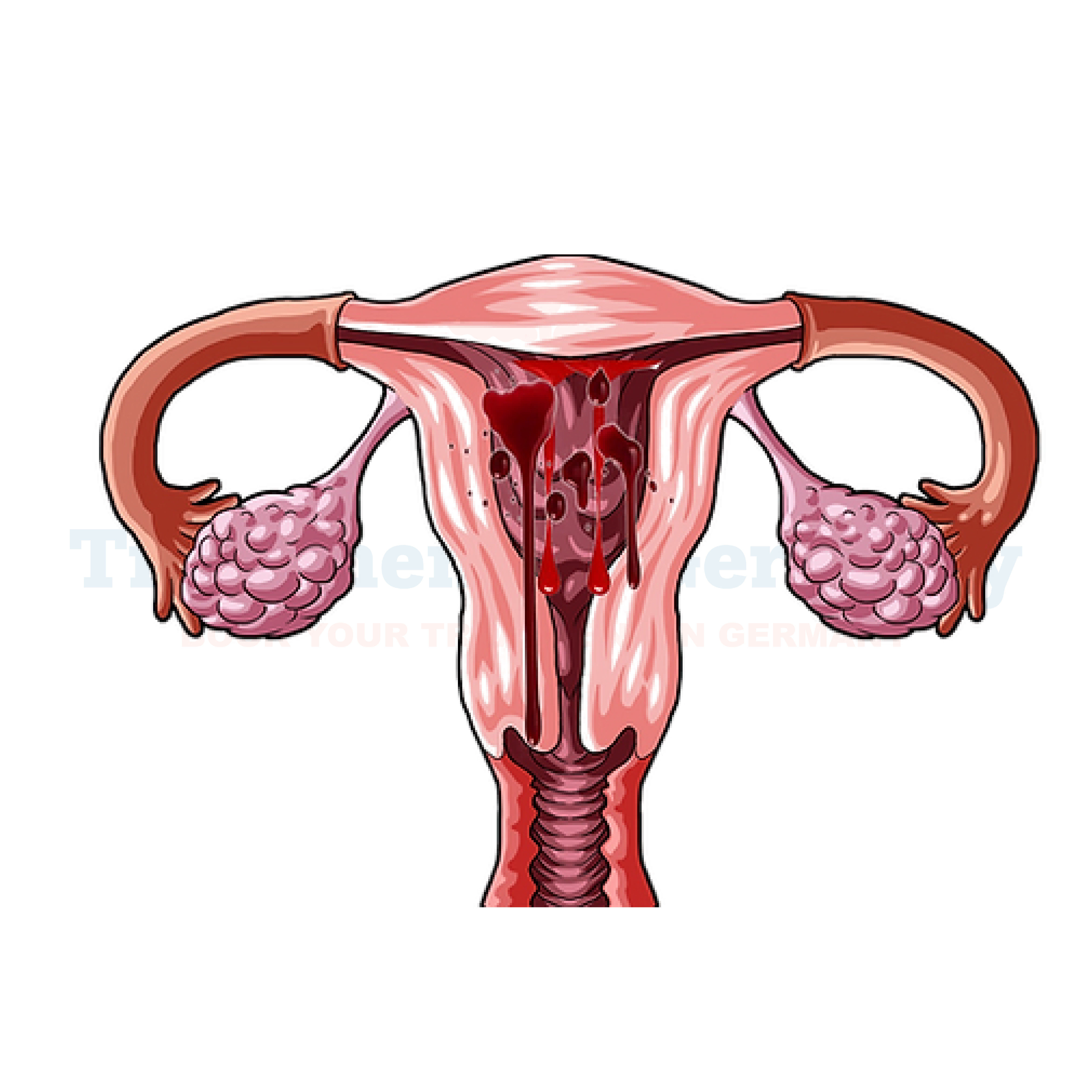
What is Postmenopausal Bleeding?
Postmenopausal bleeding refers to any vaginal bleeding that occurs after a woman has gone through menopause, which is defined as the absence of menstrual periods for 12 consecutive months. While it's not uncommon for women to experience occasional spotting or light bleeding in the years leading up to menopause (perimenopause), any bleeding that happens after menopause should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Side Effects of Postmenopausal Bleeding
Postmenopausal bleeding can be indicative of various underlying conditions, some of which may be benign, while others could be more serious. While it's natural to feel concerned when experiencing such symptoms, it's important to remember that not all cases of postmenopausal bleeding are associated with serious health issues. However, it's crucial to seek medical attention to rule out any potential causes that may require treatment.
How is Postmenopausal Bleeding Diagnosed?
Diagnosing the cause of postmenopausal bleeding typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. This may include:
By thoroughly evaluating your symptoms and conducting appropriate tests, your healthcare provider can determine the underlying cause of the postmenopausal bleeding and recommend an appropriate course of action.
Potential Treatments of Postmenopausal Bleeding
The treatment for postmenopausal bleeding depends on the underlying cause. Some potential treatment options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
