What is Primary Biliary Cholangitis?
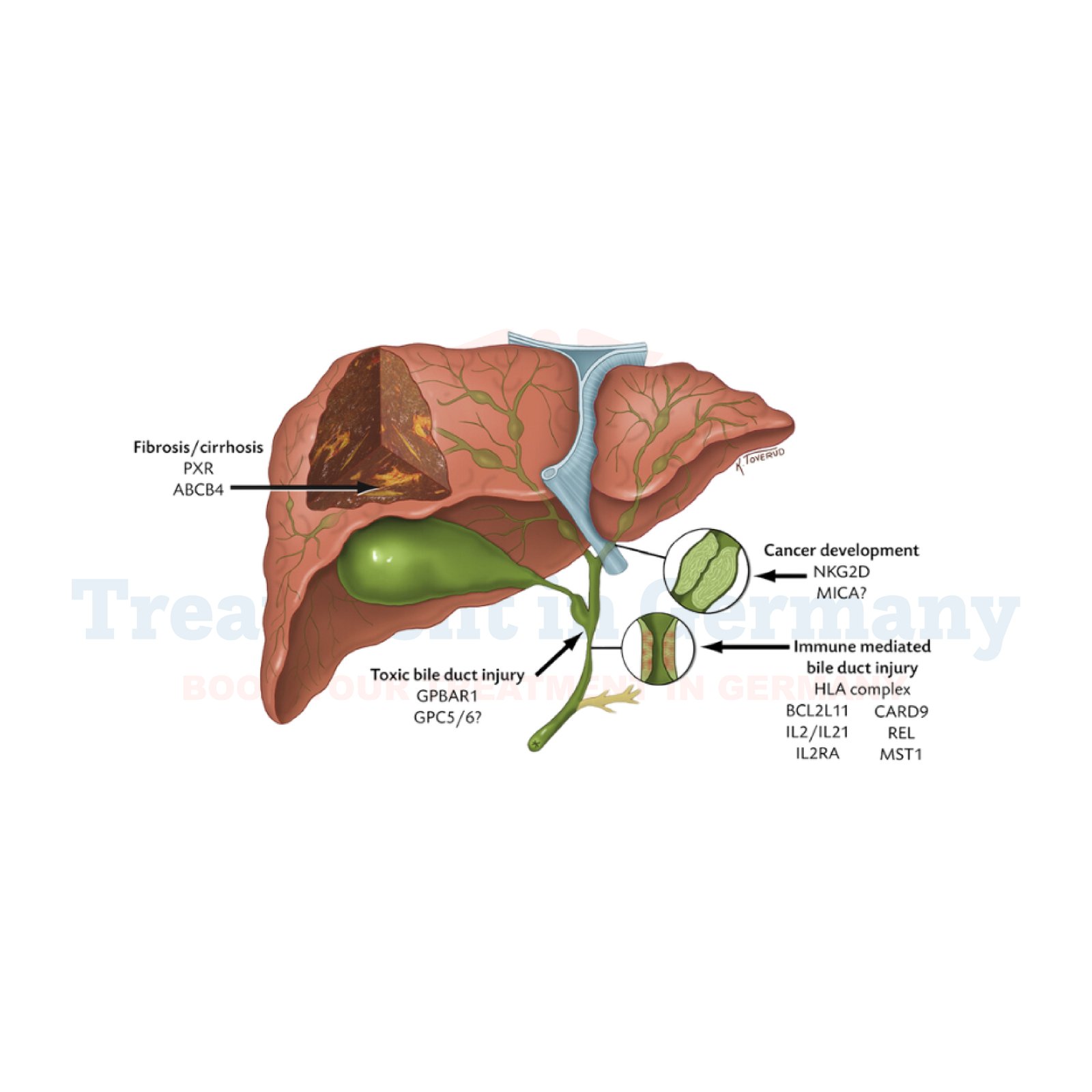
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease characterized by the inflammation and destruction of the bile ducts in the liver. These bile ducts are responsible for carrying bile, a digestive fluid, from the liver to the small intestine. When these ducts become damaged, bile builds up in the liver, leading to liver damage and scarring (cirrhosis) over time.
Side Effects of Primary Biliary Cholangitis:
The symptoms of PBC can vary from person to person and may include fatigue, itching, dry eyes and mouth, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and bone fractures due to decreased absorption of nutrients like vitamin D. If left untreated, PBC can progress to liver failure, which may require a liver transplant.
How is Primary Biliary Cholangitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing PBC typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, blood tests to check liver function and for specific antibodies associated with PBC (such as anti-mitochondrial antibodies), imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes a liver biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of liver damage.
Potential Treatments of Primary Biliary Cholangitis:
While there is no cure for PBC, treatment aims to slow disease progression, manage symptoms, and prevent complications. Commonly prescribed medications for PBC include Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), which helps improve liver function and slow the progression of the disease.
In cases where UDCA is not effective, other medications such as obeticholic acid may be prescribed. Additionally, managing symptoms like itching may involve medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
