What is Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET)?
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET) is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that originates from primitive nerve cells. PNETs are a subset of neuroblastomas and are classified as small, round blue cell tumors.
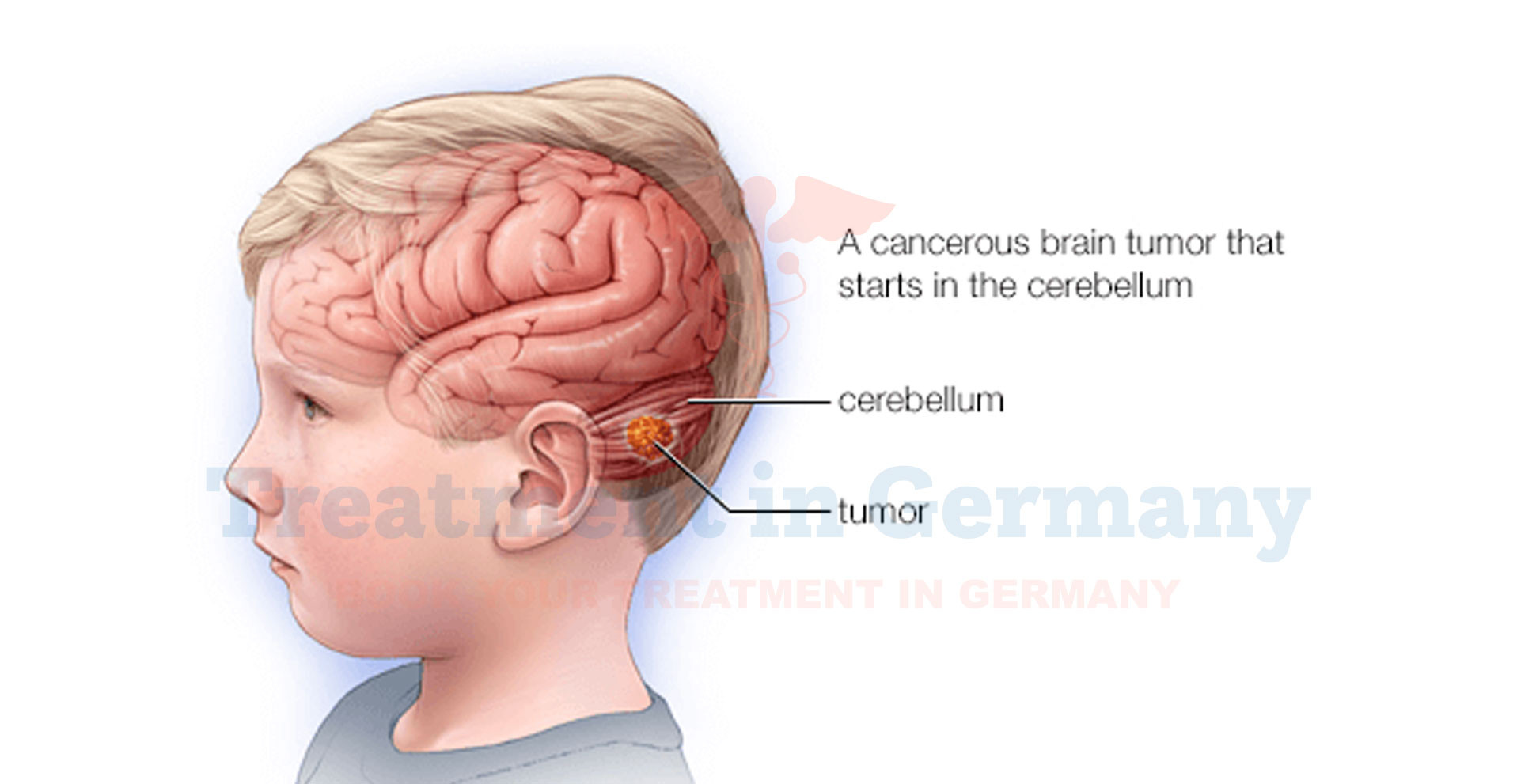
They most commonly occur in the brain and spinal cord but can also appear in other parts of the body.
PNETs are typically found in children, although they can occur in adults. The disease is characterized by the abnormal growth of nerve cells that have not yet matured properly.
Side Effects of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET)
The side effects of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor can vary depending on the tumor’s location and size. Common side effects include:
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, seizures, and changes in vision or coordination are often due to pressure on or invasion of surrounding brain structures.
- Cognitive and Behavioral Changes: Patients may experience difficulties with memory, concentration, and behavior due to the tumor’s impact on brain function.
- Physical Symptoms: Depending on the tumor's location, there may be nausea, vomiting, and problems with movement or balance.
- Fatigue and Weakness: General weakness and fatigue are common as the body battles the tumor and responds to treatments.
How is Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor involves several steps to accurately identify and understand the extent of the tumor:
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans are essential to visualize the tumor’s location, size, and impact on surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of the tumor tissue for microscopic examination. This helps confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of PNET.
- Lumbar Puncture: In some cases, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be performed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid for tumor cells.
- Molecular and Genetic Testing: These tests can provide additional information about the tumor’s characteristics and guide treatment options.
Potential Treatment of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET)
Treatment for Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor often requires a multi-disciplinary approach involving various medical specialists. The primary treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: The first step in treatment is often surgical removal of the tumor, if feasible. Surgery aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: This uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used after surgery to eliminate any remaining tumor cells.
- Chemotherapy: This involves using drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is particularly useful for treating PNETs that have spread beyond the primary site.
- Targeted Therapy: This newer approach targets specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as genetic mutations, to more precisely attack the tumor with fewer side effects.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may offer access to cutting-edge therapies and treatments not yet widely available.
.👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
