What is Pseudogout (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease)?
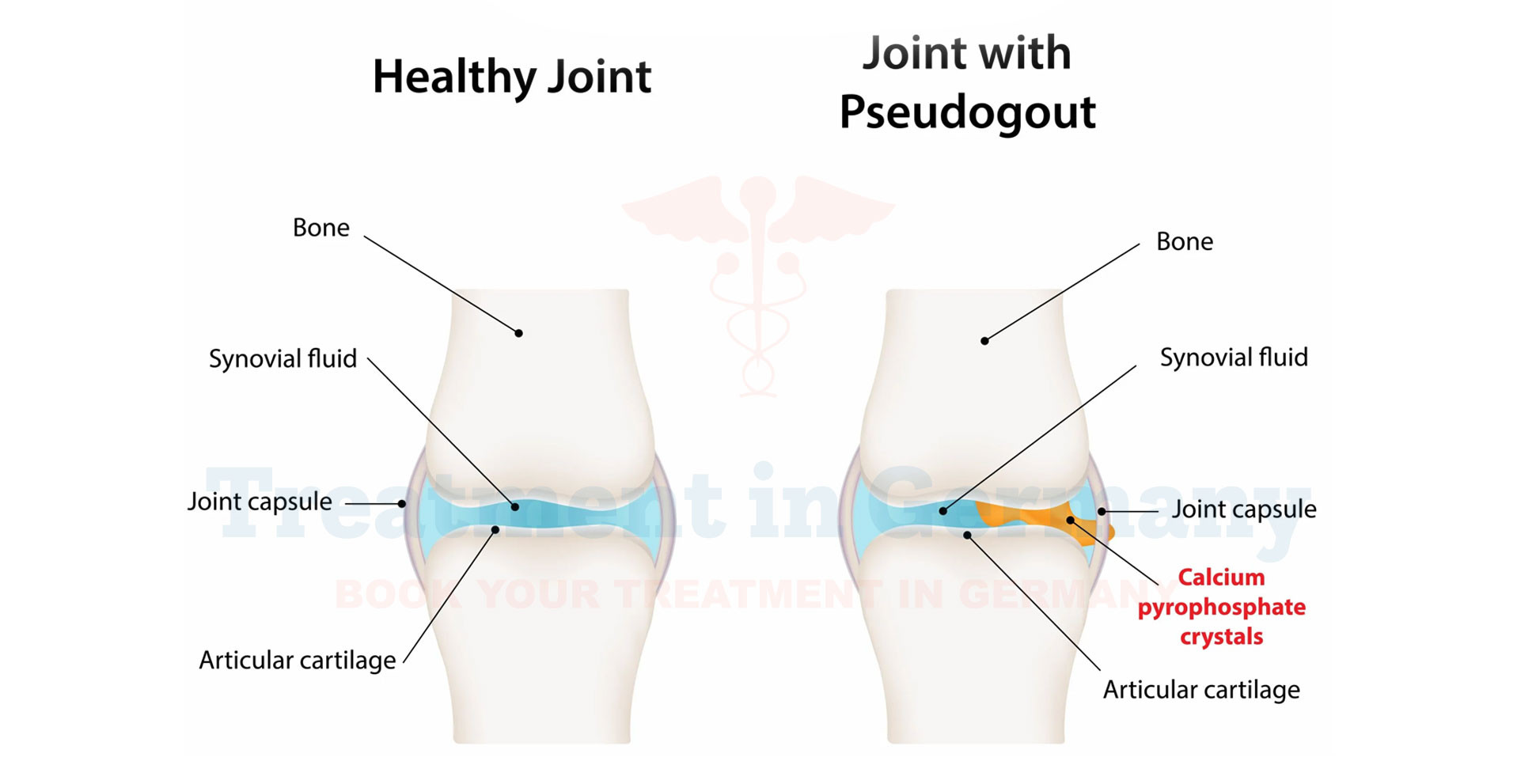
Pseudogout, also known as Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (CPPD), is a type of arthritis caused by the accumulation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joints.
This condition can lead to inflammation and sudden, severe pain, similar to gout but distinguished by its specific crystalline deposits.
CPPD commonly affects the knees, wrists, and other large joints, causing them to swell and become tender. The exact cause of these crystal deposits is not fully understood, but aging and genetic factors are believed to play significant roles.
Side Effects of Pseudogout (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease)
The primary symptoms of pseudogout are joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms can occur suddenly and are often mistaken for other conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
Over time, recurrent episodes of pseudogout can lead to joint damage and deformities if not properly managed. Chronic inflammation may also contribute to reduced joint function and mobility, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
How is Pseudogout (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease) Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of pseudogout involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination to assess symptoms and joint function. Key diagnostic procedures include:
Potential Treatment of Pseudogout (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease)
Treatment for pseudogout focuses on managing symptoms and preventing future attacks. Options include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
