What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects both the skin and the joints. It often develops in people who have psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches.
PsA can lead to inflammation in the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. The condition can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may face significant challenges in their daily lives.
Side Effects of Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis can have a range of side effects, which can impact various aspects of life. Common symptoms include:
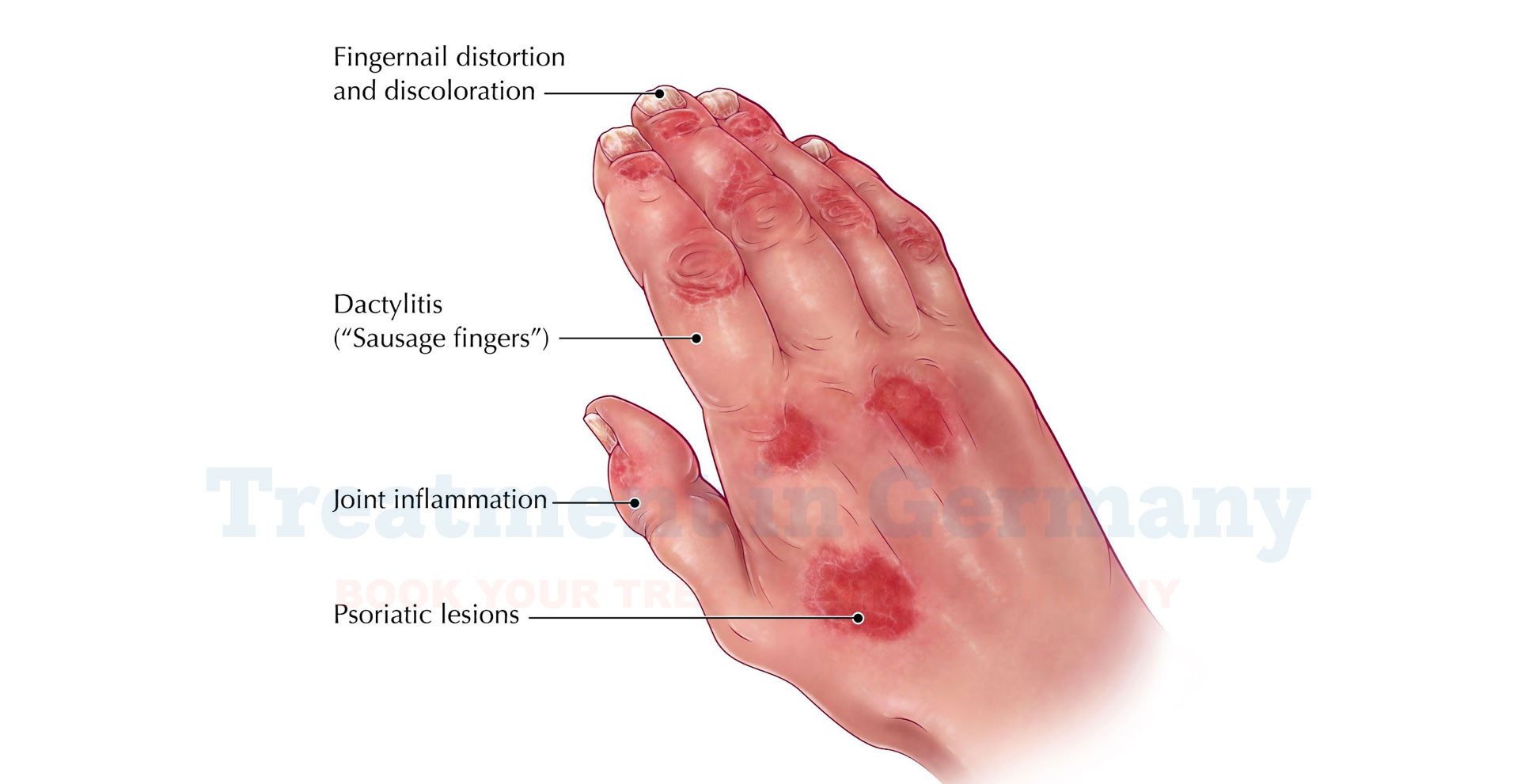
- Joint Pain and Swelling: The most noticeable effect is joint inflammation, which can cause pain and stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation can lead to persistent tiredness and a general feeling of fatigue.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Over time, affected joints may become less flexible, impacting daily activities and mobility.
- Nail Changes: PsA may cause changes in the appearance of nails, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed.
- Skin Issues: If you have psoriasis, you might experience flare-ups or worsening of skin symptoms alongside joint problems.
How is Psoriatic Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Psoriatic Arthritis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and diagnostic tests:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their duration, and any family history of autoimmune conditions. They will also perform a physical examination to assess joint inflammation and other signs of PsA.
- Blood Tests: While there is no specific blood test for PsA, tests can help rule out other conditions. Common tests include:
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-reactive Protein (CRP): These markers indicate inflammation.
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF): To differentiate PsA from rheumatoid arthritis.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays or MRI scans may be used to assess joint damage and inflammation. These imaging techniques help visualize the extent of joint involvement and guide treatment decisions.
- Skin Examination: If you have psoriasis, your doctor will evaluate the severity and extent of skin lesions, which can support the diagnosis of PsA.
Potential Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis
Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis aims to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent joint damage. Options may include:
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate can slow the progression of the disease and manage symptoms.
- Biologics: These advanced medications target specific immune system components and can be effective for moderate to severe PsA.
- Topical Treatments: If you have psoriasis, topical treatments may be used to manage skin symptoms alongside joint treatments.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and therapies can improve joint function, enhance mobility, and strengthen muscles around the affected joints.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can support overall health and reduce strain on joints.
- Surgery: In severe cases where joint damage is significant, surgical options may be considered to repair or replace damaged joints.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
