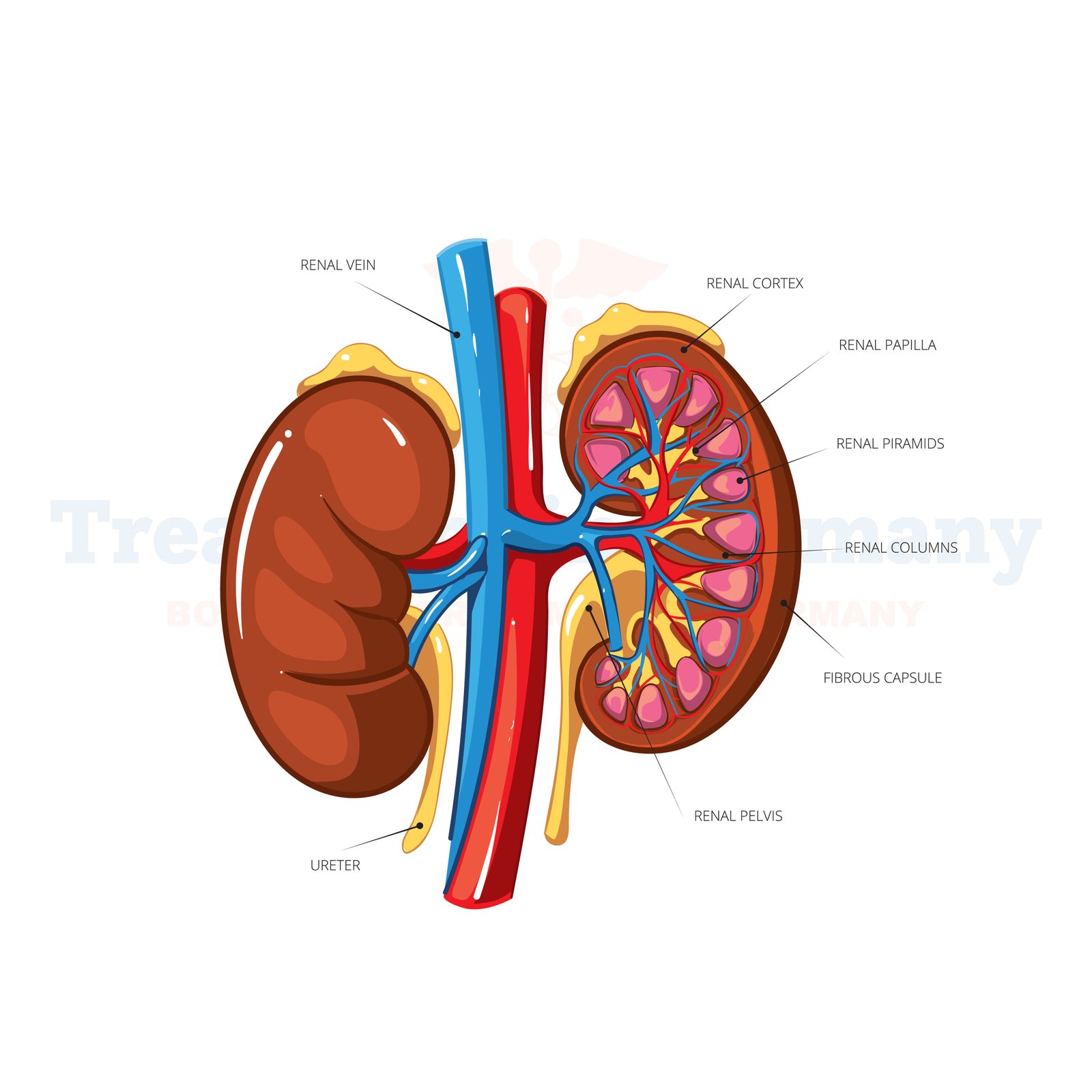
What is Renal Artery Stenosis?
Renal artery stenosis refers to the narrowing of one or both of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys. This narrowing typically occurs due to the buildup of plaque inside the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
As a result, blood flow to the kidneys is restricted, leading to various health complications.
Side Effects of Renal Artery Stenosis
The narrowing of the renal arteries can have several adverse effects on kidney function and overall health. Common side effects include:
How is Renal Artery Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing renal artery stenosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and risk factors for vascular diseases. A physical exam may also be conducted to check for signs of hypertension and kidney abnormalities.
2. Imaging Tests: Various imaging tests, such as Doppler ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), computed tomography angiography (CTA), or renal arteriography, may be performed to visualize the renal arteries and assess blood flow.
3. Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to evaluate kidney function, electrolyte levels, and the presence of substances indicative of kidney damage.
Potential Treatments of Renal Artery Stenosis?
Treatment options for renal artery stenosis aim to improve blood flow to the kidneys, manage hypertension, and preserve kidney function. Depending on the severity of the condition and individual health factors, treatment may include:
1. Medications: Medications such as antihypertensives, diuretics, and cholesterol-lowering drugs may be prescribed to control blood pressure, reduce fluid retention, and manage underlying conditions like atherosclerosis.
2. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress, can help improve overall cardiovascular health and reduce the progression of renal artery stenosis.
3. Interventional Procedures: In cases where medication and lifestyle changes are insufficient, interventional procedures such as angioplasty with or without stent placement may be performed to widen the narrowed renal artery and restore blood flow.
4. Surgery: In severe or complicated cases of renal artery stenosis, surgical intervention such as renal artery bypass surgery may be necessary to reroute blood flow around the blocked or narrowed artery.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
