Understanding Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA)
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) is a rare medical condition that affects the kidneys' ability to effectively remove acid from the blood, leading to an imbalance of acids and electrolytes in the body.
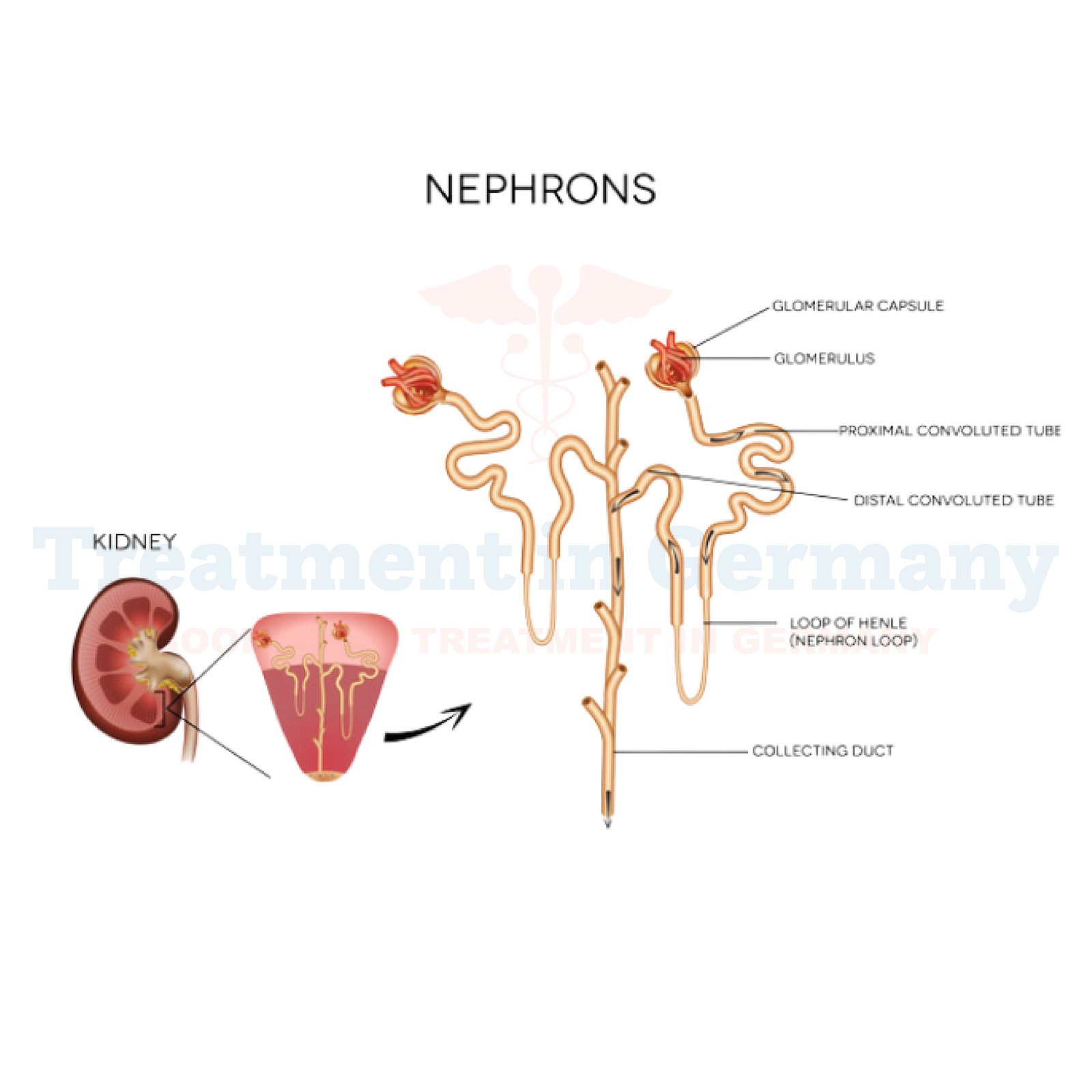
This disorder primarily involves the renal tubules, which are tiny tubes in the kidneys responsible for filtering waste and maintaining the body's acid-base balance.
Side Effects of Renal Tubular Acidosis
The symptoms of Renal Tubular Acidosis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs may include fatigue, weakness, muscle pain or cramps, bone abnormalities, urinary tract infections, and impaired growth in children. In severe cases, RTA can lead to electrolyte imbalances, kidney stones, and even kidney failure if left untreated.
Diagnosing Renal Tubular Acidosis
Diagnosing Renal Tubular Acidosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and specialized tests. Doctors may conduct blood and urine tests to measure levels of electrolytes and acid in the body.
Additionally, imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans may be performed to evaluate the kidneys for structural abnormalities.
Potential Treatments of Renal Tubular Acidosis
The treatment of RTA aims to correct the acid-base imbalance and manage associated symptoms. Depending on the type of RTA and its underlying cause, treatment options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
