Understanding Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI)
Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI) are a group of conditions that occur due to repetitive movements, forceful exertions, vibrations, or sustained awkward positions.
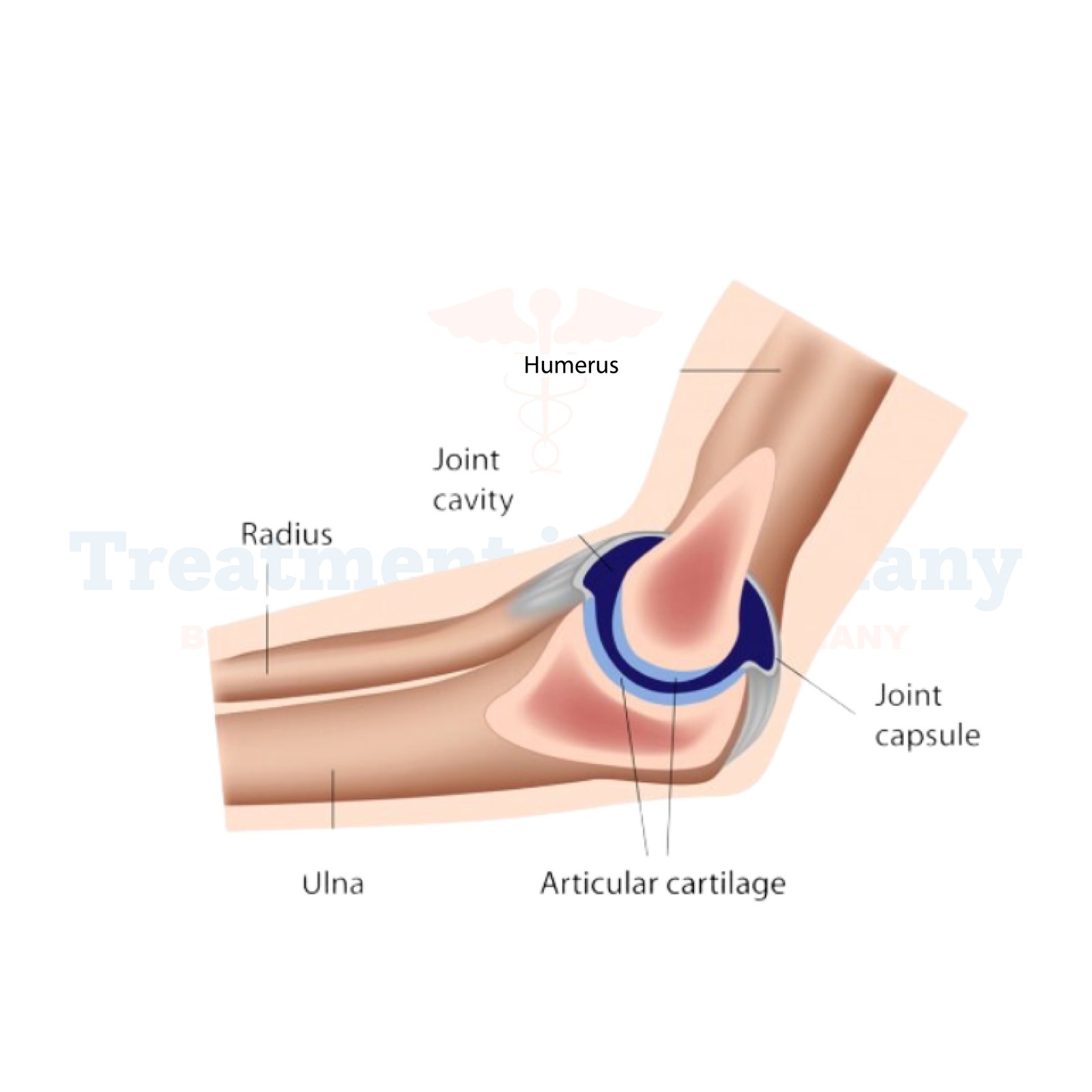
These injuries primarily affect muscles, tendons, nerves, and joints in areas such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, and neck.
Side Effects of Repetitive Strain Injuries
The symptoms of Repetitive Strain Injuries can vary widely but often include:
- Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the affected area, which may worsen with activity.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and stiffness in joints.
- Weakness: Decreased strength and coordination in the affected muscles.
- Numbness or tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or burning, indicating nerve involvement.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the affected tendons or joints.
- Loss of function: Difficulty performing everyday tasks due to pain and discomfort.
Diagnosis of Repetitive Strain Injuries
Diagnosing Repetitive Strain Injuries involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional, which may include:
- Medical history: Understanding the patient's work habits, hobbies, and symptoms.
- Physical examination: Evaluating the affected area for signs of tenderness, swelling, weakness, or restricted movement.
- Diagnostic tests: X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, or nerve conduction studies may be used to rule out other conditions or to confirm the extent of tissue damage.
Potential Treatments for Repetitive Strain Injuries
Treatment options for Repetitive Strain Injuries focus on relieving symptoms, promoting healing, and preventing further injury. Depending on the severity and specific condition, treatments may include:
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and incorporating rest breaks during repetitive tasks.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and posture, along with techniques to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ergonomic modifications: Adjusting workstations, tools, and techniques to reduce strain and improve posture.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, or pain relievers may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Splints or braces: Supporting and immobilizing the affected area to promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be considered to repair damaged tissues or release compressed nerves.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
