Germany is one of the countries that pride themselves on advanced medical treatments, care. People also travel to the country seeking innovative techniques and systematic treatment. This article will give additional information concerning salivary gland cancer treatment inGermany, from diagnosis to rehabilitation.
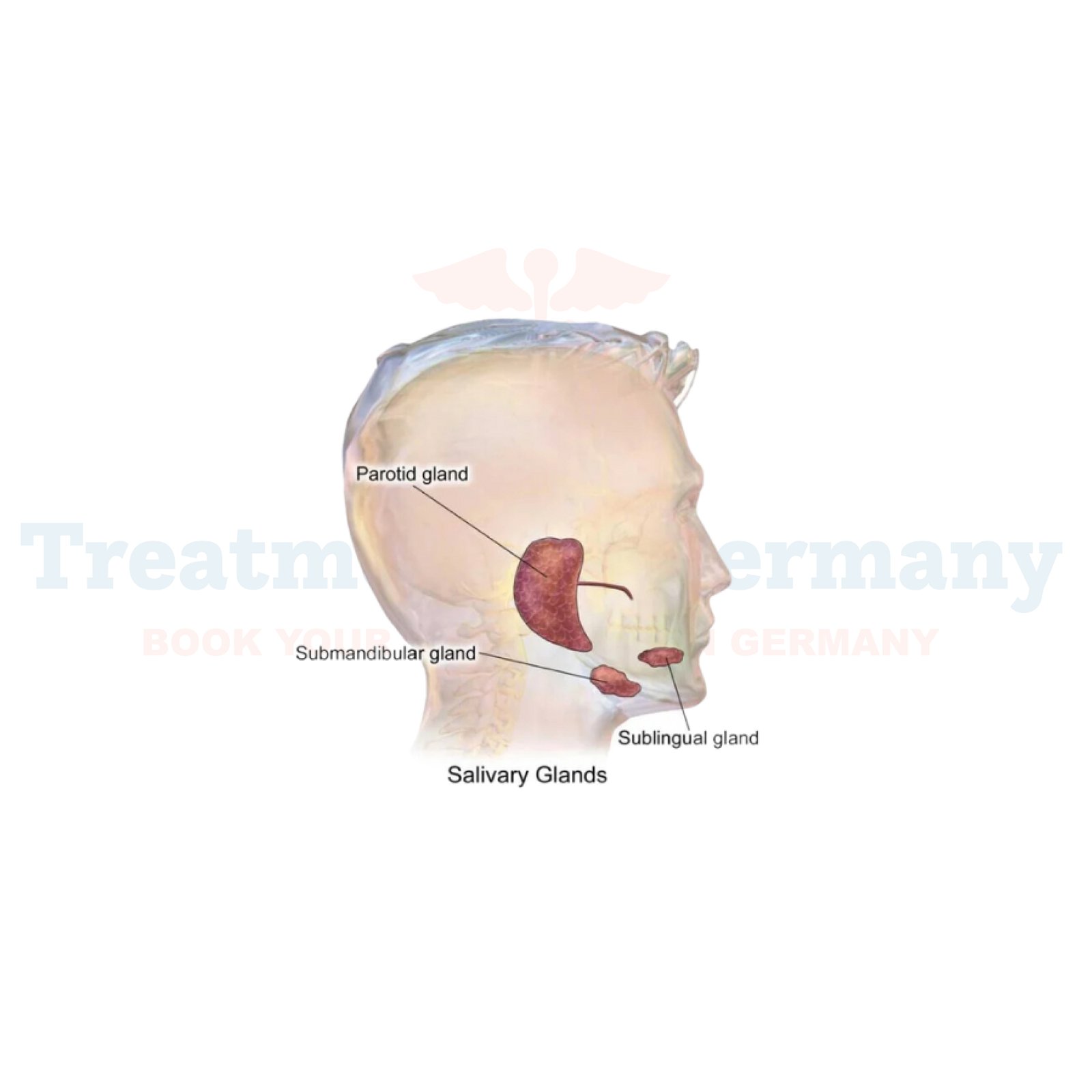
Salivary gland cancer defines the process of development of malignant tumors in the salivary gland, which is very important for producing saliva that allows the digestive system to function.
It affects three major salivary glands: the salivary glands, submandibular salivary glands, and sublingual salivary glands, in addition to a few minor salivary glands.
Although most of these tumors are benign, some of them become cancerous and metastasize to other parts of the body, for example, the head and neck region. This cancer can also occur at old ages and assigned male at birth (AMAB) is at a higher risk.
Salivary Gland Cancer Types
There exist different forms of salivary gland
cancer, and each has a different impact on the body. The most common forms
include:
Each of the diverse tumors behaves differently, and treatment depends on the nature of the tumor.
Diagnosis in Germany
Diagnosis is extremely central to cancer
treatment. Present diagnostic tests are used by physicians in Germany.
Earliest Possible Diagnosis
Early detection allows for better cure results. In Germany, doctors ensure more penetrating tests like biopsy and CT scans wherein the cancer is identified before it spreads within the body.
Best Hospitals for
Salivary Gland Cancer Treatment in Germany
These are considered among the best in Germany, with excellent and quality facilities to treat salivary gland cancer.
These hospitals have specialized departments for head and neck cancers and are equipped with the latest technology to deliver individualized plans of treatment.
Innovative Treatment
Germany is known for its cutting edge
treatment modalities. Besides surgery, newer treatments are immunotherapy and targeted
therapies.
Surgery is the first line of treatment and the
main way that the tumor is removed.
Dendritic Cell Therapy
Dendritic cell therapy is a groundbreaking form of immunotherapy aimed at activating the patient’s immune system to identify and attack salivary gland cancer cells.
Hyperthermia Therapy
Hyperthermia therapy is often used in conjunction with radiation or chemotherapy to enhance their effectiveness in treating salivary gland cancer.
Proton Beam Therapy
Proton beam therapy is a precise and advanced form of radiation therapy ideal for treating salivary gland cancer, particularly when tumors are located near sensitive structures.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecular changes or genetic mutations in salivary gland cancer cells.
Rehabilitation after Treatment of Salivary Gland Cancer
Following therapy, rehabilitation is a crucial
step toward complete recovery. German hospitals implement general plans:
Psychological Counseling
The patients are provided with psychological counseling to alleviate the emotional impact of the cancer treatment. Most hospitals provide long-term mental health counseling. The patients are encouraged to fend off anxiety and depression.
The German Expense of Salivary Gland Cancer Treatment
The treatments given to salivary gland cancer patients in Germany are of great quality and efficiency, and it depends on the seriousness of the case and what is the surgery going to cost, not to mention the additional treatments such as radiotherapy or proton therapy added to it.
Leading German Hospita ls for Treatment of Salivary Gland Cancer
The best hospital for salivary gland cancer
treatment in Germany includes:
Why Prefer Germany for treatment of Salivary Gland Cancer?
Germany ranks as one of the best destinations for salivary gland surgery due to its excellent healthcare system, very experienced surgeons, and up-to-date medical technology.
In Germany, innovative treatments are provided to patients, which are unavailable in many other countries.
Important Benefits of Cancer Treatment in Germany
There are numerous advantages of cancer
treatment in Germany:
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the most frequent symptoms of salivary gland cancer?
Salivary gland cancer often manifests itself as a painless swelling in the neck or jaw, and there is also numbness or pain in the face; other symptoms may include dysphagia or an inability to move facial muscles.
How is salivary gland cancer diagnosed?
It typically begins with physical examination and images, for instance, CT scans and MRIs, to confirm the existence of cancerous cells through biopsy.
What are the treatment options for salivary gland cancer in Germany?
Some of the treatments offered in Germany range from surgery and radiation to advanced interventions such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, so that thorough care is guaranteed.
What is the cost of salivary gland cancer treatment in Germany?
The cost of treatment in Germany depends upon the procedure, whereas surgery generally accounts for the largest share of expenditure. Other forms of treatment, such as radiation or chemotherapy, may add to overall costs if the case has unique conditions.
Can salivary gland cancer be subjected to chemotherapy?
Yes. Chemotherapy is applied when the spread of the tumor has happened or in advance stages of the disease. Chemotherapy can be administered along with other therapies, radiation therapy in particular.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
