What is Single Ventricle Defects?
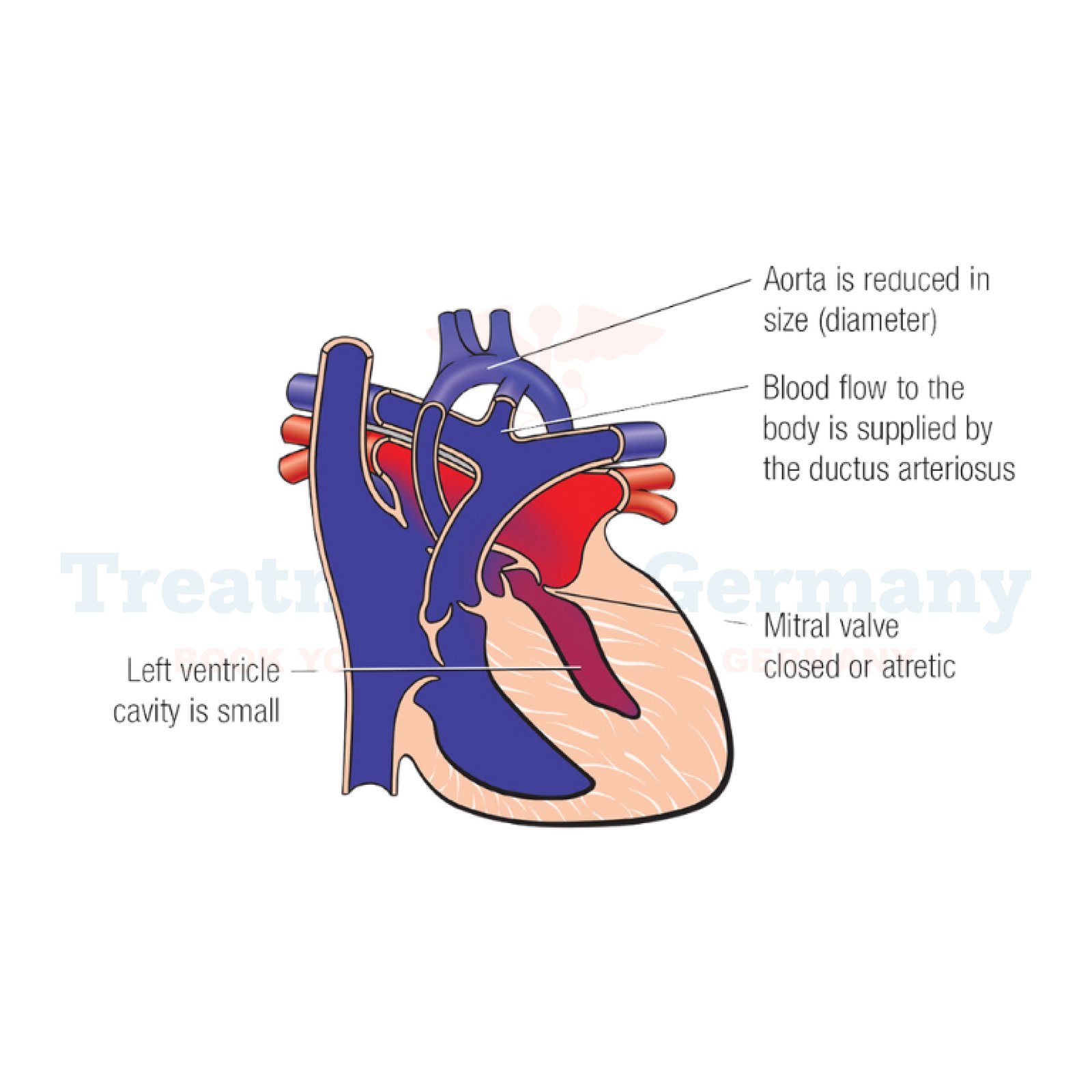
Single Ventricle Defects (SVD) is a congenital heart condition where one of the heart's two pumping chambers (ventricles) is either underdeveloped or missing entirely.
Normally, the heart has two ventricles - the left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, while the right ventricle pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. In SVD, the heart cannot function as efficiently because it lacks this dual pumping system.
Side Effects of Single Ventricle Defects
The symptoms and side effects of Single Ventricle Defects vary depending on the specific defect and its severity. Common symptoms include:
Untreated or poorly managed Single Ventricle Defects can lead to serious complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and reduced life expectancy.
How is Single Ventricle Defects Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough physical examination and may include various tests such as:
Potential Treatment of Single Ventricle Defects
Treatment for Single Ventricle Defects depends on several factors including the specific type of defect, its severity, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatment approaches may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
