What is Skin Cancer (Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)?
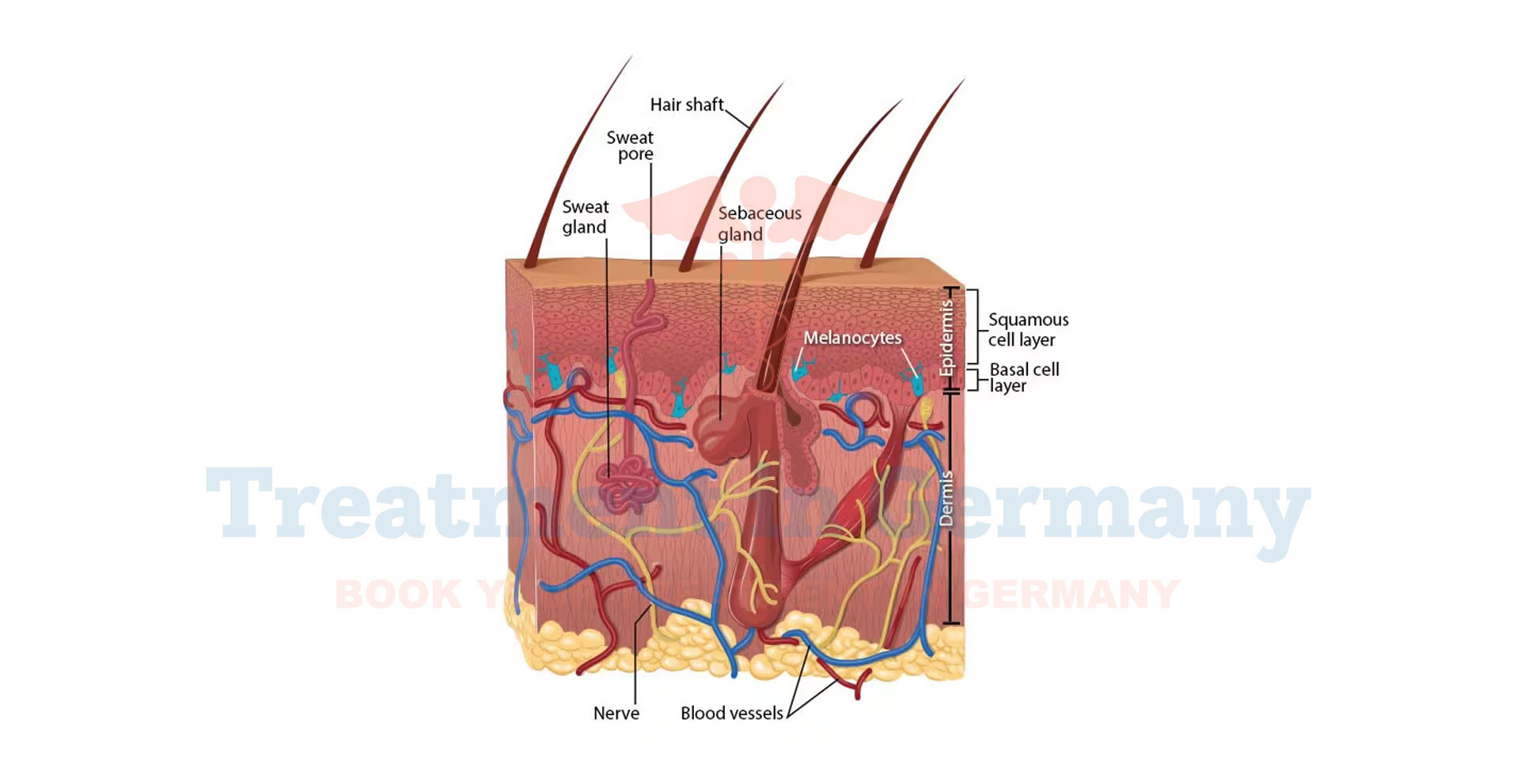
Skin cancer, including Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) and Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), are types of cancers that originate from the skin cells.
BCC usually develops in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face and neck, while SCC can arise from sun-exposed areas as well as scars or chronic wounds. Both types of skin cancer are typically slow-growing and can be successfully treated if detected early.
Side Effects of Skin Cancer (Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
The potential side effects of BCC and SCC can vary depending on the size, location, and depth of the tumor. Common side effects include:
If left untreated, these cancers can invade nearby tissues and, in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body.
How is Skin Cancer (Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma) Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of visual inspection, biopsy, and sometimes imaging tests:
Early detection through regular skin examinations is crucial for successful treatment.
Potential Treatment of Skin Cancer (Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
Treatment options depend on the type, size, location, and depth of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatment modalities include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
