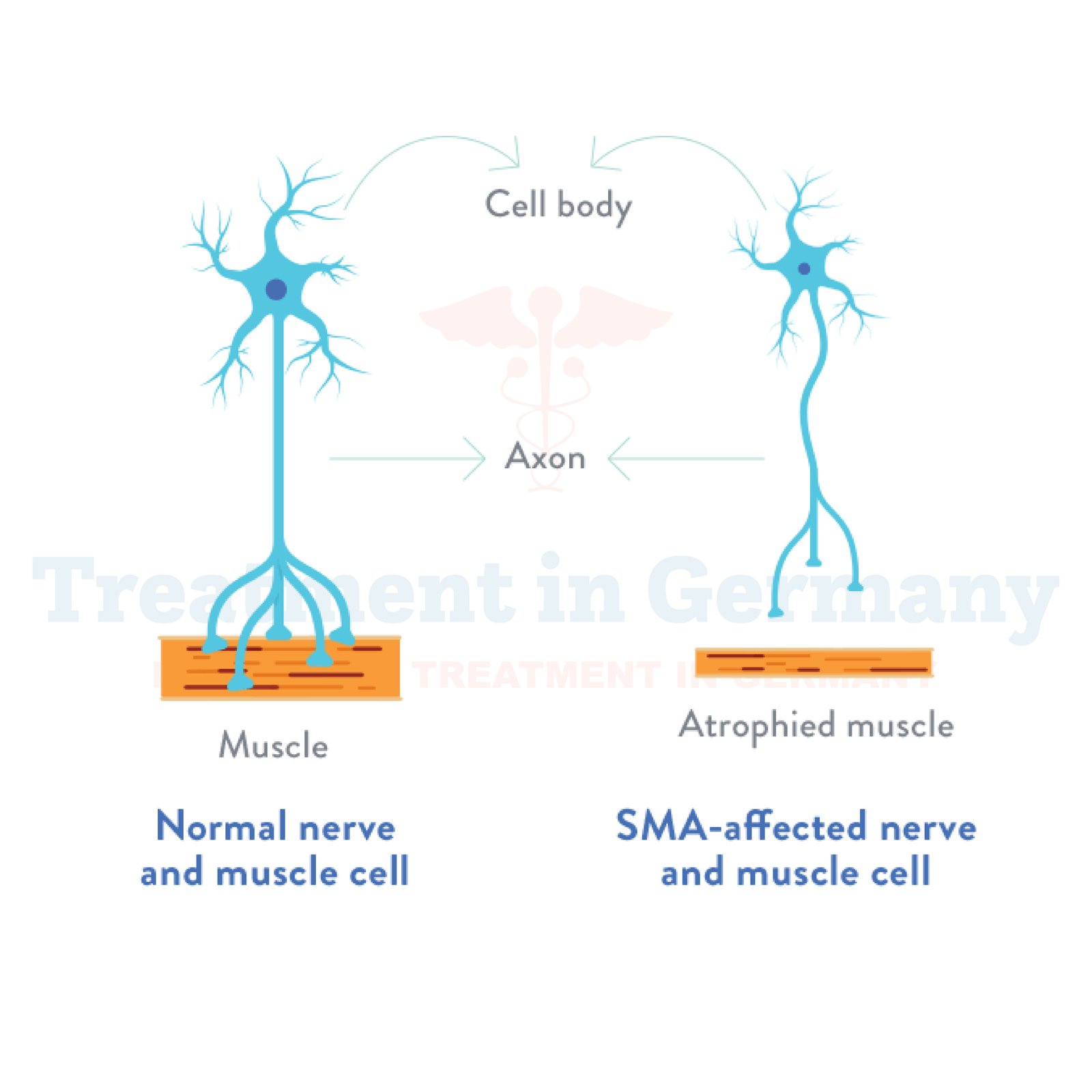
Understanding Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the motor neurons in the spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and atrophy. It primarily manifests in infants and children but can also affect adults in varying degrees of severity.
Side Effects of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
The symptoms of Spinal Muscular Atrophy vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common side effects include:
- Muscle Weakness: Gradual weakening of muscles, leading to difficulty in crawling, walking, and eventually, standing.
- Respiratory Issues: Weakened respiratory muscles can cause breathing difficulties, especially in more severe cases.
- Swallowing Problems: Weakness in throat and mouth muscles can lead to difficulty in swallowing and poor nutrition.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis) is common in SMA patients due to muscle imbalance.
How is Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Spinal Muscular Atrophy typically involves a combination of clinical examination, genetic testing, and electromyography (EMG). Key diagnostic steps include:
- Clinical Assessment: Evaluation of symptoms and physical examination by a neurologist or pediatrician.
- Genetic Testing: Identification of mutations in the SMN1 gene, which is responsible for producing a protein essential for motor neuron function.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity in muscles to assess their function and detect abnormalities.
Early diagnosis is crucial as it allows for timely intervention and management strategies.
Potential Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
While there is currently no cure for Spinal Muscular Atrophy , several treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Gene Therapy: Medications like onasemnogene abeparvovec (Zolgensma) are designed to replace the defective SMN1 gene.
- Spinraza (Nusinersen): This medication helps increase production of the SMN protein, slowing down the progression of SMA.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and therapies help maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and overall mobility.
- Respiratory Support: Devices such as breathing machines (ventilators) and respiratory therapies help manage breathing difficulties.
- Nutritional Support: Dietary planning and feeding assistance address swallowing difficulties and ensure adequate nutrition.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
