What is Spondyloarthritis?
Spondyloarthritis is a group of inflammatory rheumatic diseases that primarily affect the spine and the sacroiliac joints (the joints between the base of the spine and the pelvis).
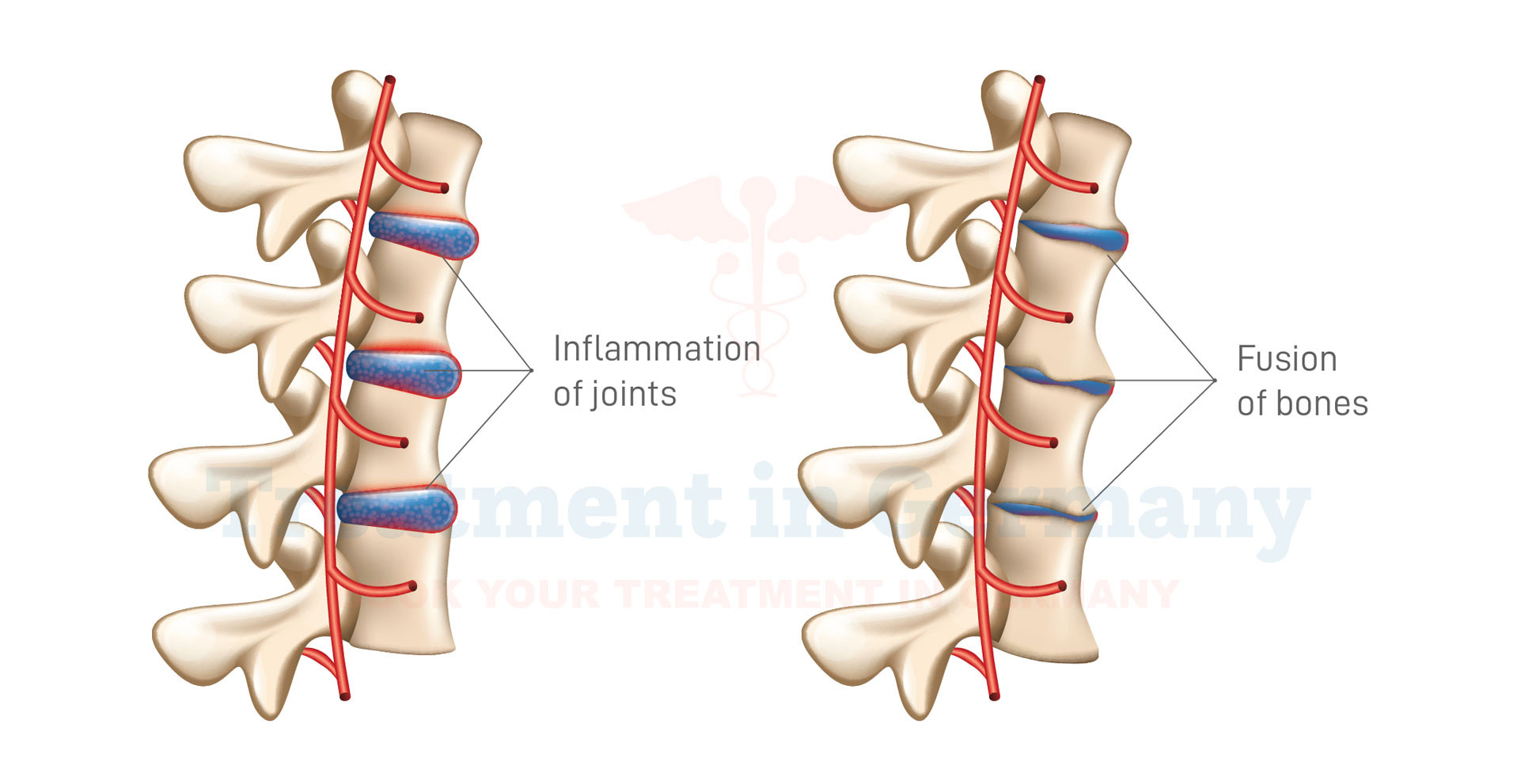
The most common form is ankylosing spondylitis, but other types include psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, and enteropathic arthritis. These conditions are characterized by chronic inflammation, which can lead to pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
Side Effects of Spondyloarthritis
The side effects of spondyloarthritis can significantly impact your quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Chronic Back Pain: Often worse in the morning and improves with movement.
- Stiffness: Particularly in the lower back and hips, which can limit mobility.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to ongoing inflammation.
- Joint Swelling: In some cases, other joints beyond the spine may also be affected.
- Reduced Flexibility: Over time, inflammation can cause the spine to fuse, reducing overall flexibility.
In addition to physical symptoms, spondyloarthritis may also contribute to emotional and psychological stress due to chronic pain and reduced mobility.
How is Spondyloarthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of spondyloarthritis involves several steps to accurately identify the condition and differentiate it from other possible causes of your symptoms. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, family history, and any other relevant health information.
- Physical Examination: This helps assess your range of motion, joint tenderness, and overall physical condition.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRI scans can reveal characteristic changes in the spine and joints.
- Blood Tests: These may identify markers such as the HLA-B27 antigen or other inflammatory indicators, which can support the diagnosis.
Potential Treatment of Spondyloarthritis
Treatment for spondyloarthritis focuses on managing symptoms, improving function, and slowing disease progression. In Germany, a comprehensive treatment plan may include:
Medications:
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): To reduce pain and inflammation.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Especially if other joints are involved.
- Biologic Agents: For more severe cases, these can target specific immune system pathways involved in inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercises can help maintain and improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and manage pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight can support overall well-being and joint health.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery might be considered to address severe joint damage or complications.
- Alternative Therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture or massage may offer additional relief.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
