What is Synovial Sarcoma?
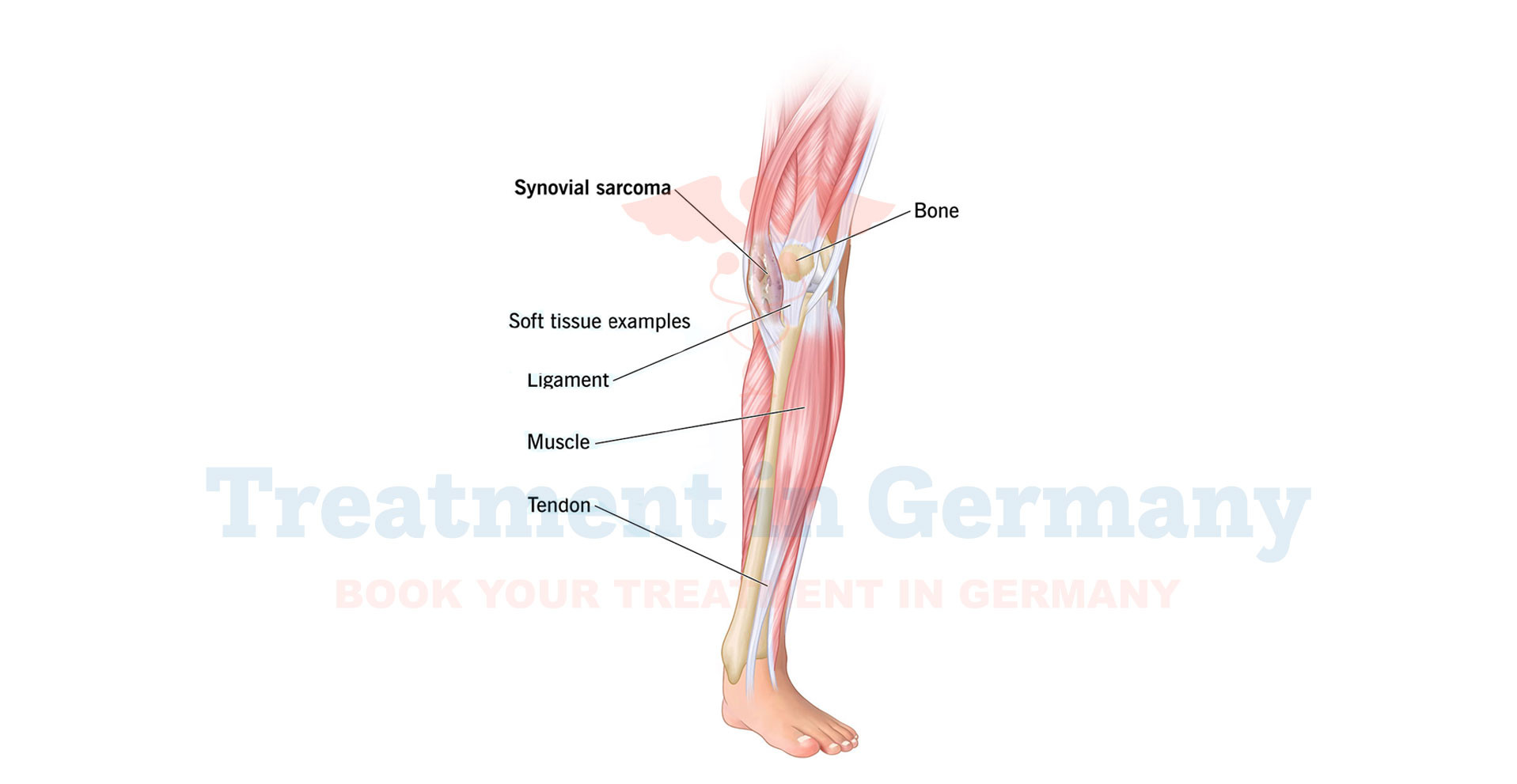
Synovial Sarcoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that primarily affects soft tissues around the joints, such as the synovial membrane, which lines the joints.
Despite its name, synovial sarcoma does not typically originate from synovial tissues but rather from cells in soft tissues near the joints. This type of cancer often presents in young adults and adolescents but can occur at any age.
Side Effects of Synovial Sarcoma
The side effects of Synovial Sarcoma can vary widely depending on the location and stage of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and Swelling: The most frequent symptoms are localized pain and swelling in the affected area, which can be persistent or worsening over time.
- Limited Mobility: Tumors near joints can impair the range of motion and flexibility.
- Fatigue: As with many cancers, fatigue and general weakness can be significant issues.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss may occur due to the body's response to the cancer or side effects from treatments.
- Other Symptoms: In some cases, if the cancer metastasizes (spreads to other parts of the body), it may lead to additional symptoms related to those areas.
How is Synovial Sarcoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Synovial Sarcoma involves several steps to confirm the presence of the cancer and determine its extent:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The process typically starts with a thorough review of the patient's medical history and a physical examination to assess symptoms.
- Imaging Studies: To visualize the tumor and assess its size and location, doctors use imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans.
- Biopsy: A definitive diagnosis is made through a biopsy, where a sample of the tumor tissue is extracted and examined under a microscope. This is crucial for identifying the cancer type and confirming its diagnosis.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic tests may be conducted to identify specific mutations associated with Synovial Sarcoma, which can provide additional information for treatment planning.
Potential Treatment of Synovial Sarcoma
Treatment for Synovial Sarcoma in Germany is typically multidisciplinary, involving a team of specialists to provide comprehensive care. The primary treatment options include:
- Surgery: The mainstay of treatment is usually surgical removal of the tumor. The goal is to excise the tumor completely while preserving as much surrounding healthy tissue as possible.
- Radiotherapy: This is often used in conjunction with surgery to target and kill any remaining cancer cells, especially if the tumor is large or has spread to nearby tissues.
- Chemotherapy: For cases where the cancer has metastasized or is at high risk of recurrence, chemotherapy may be recommended to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted Therapy: Advances in medicine have led to the development of targeted therapies that specifically address the genetic mutations and pathways involved in Synovial Sarcoma.
- Clinical Trials: Patients may have the option to participate in clinical trials exploring new treatments or combinations of therapies. These trials can offer access to cutting-edge treatments not yet widely available.
- Rehabilitation and Supportive Care: Post-treatment, rehabilitation and supportive care play a crucial role in helping patients recover and improve their quality of life. This may include physical therapy, pain management, and psychological support.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
