What is Tetralogy of Fallot:
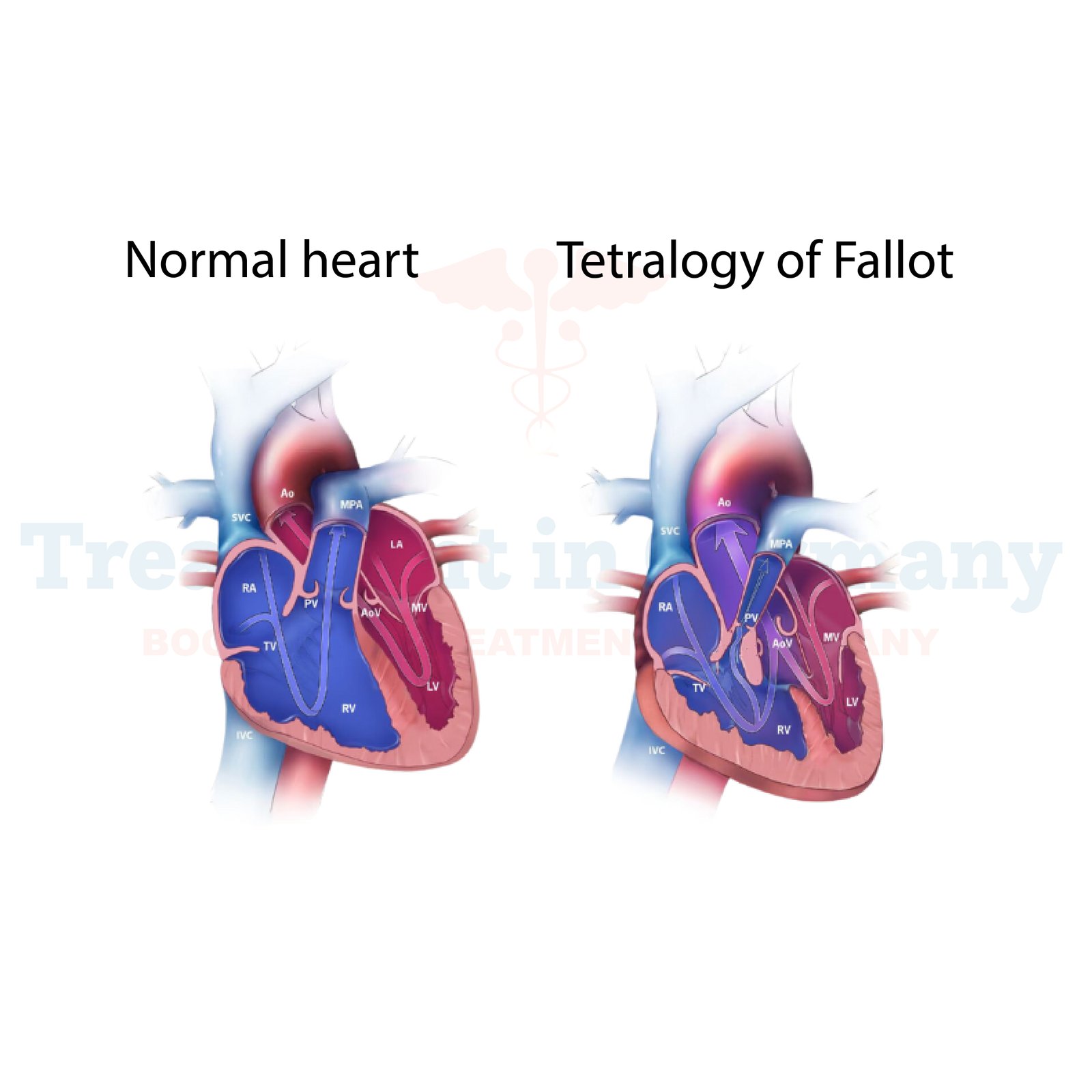
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect characterized by a combination of four heart abnormalities present at birth. These abnormalities include:
1. Pulmonary Stenosis: Narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the pulmonary artery, which restricts blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
2. Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): A hole in the wall (septum) between the heart's lower chambers (ventricles), allowing oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to mix with oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle.
3.Overriding Aorta: The aorta, the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood to the body, is shifted slightly to the right and lies directly over the VSD, receiving blood from both ventricles.
4. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy: Thickening of the muscular wall of the right ventricle due to its increased workload.
Side effects of Tetralogy of Fallot:
The symptoms and severity of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) vary from person to person, but common side effects may include:
How is Tetralogy of Fallot diagnosed?
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) may be diagnosed before birth through fetal echocardiography or shortly after birth through a physical examination and various diagnostic tests, including:
Potential treatments of Tetralogy of Fallot:
The treatment approach for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) depends on the severity of the condition and may include:
Medications: Medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and oxygen therapy may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve heart function.
Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with a cardiologist are essential to monitor heart health, track growth and development, and adjust treatment as needed. In some cases, additional procedures or surgeries may be necessary as the individual grows older.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
