What is Thalassemia:
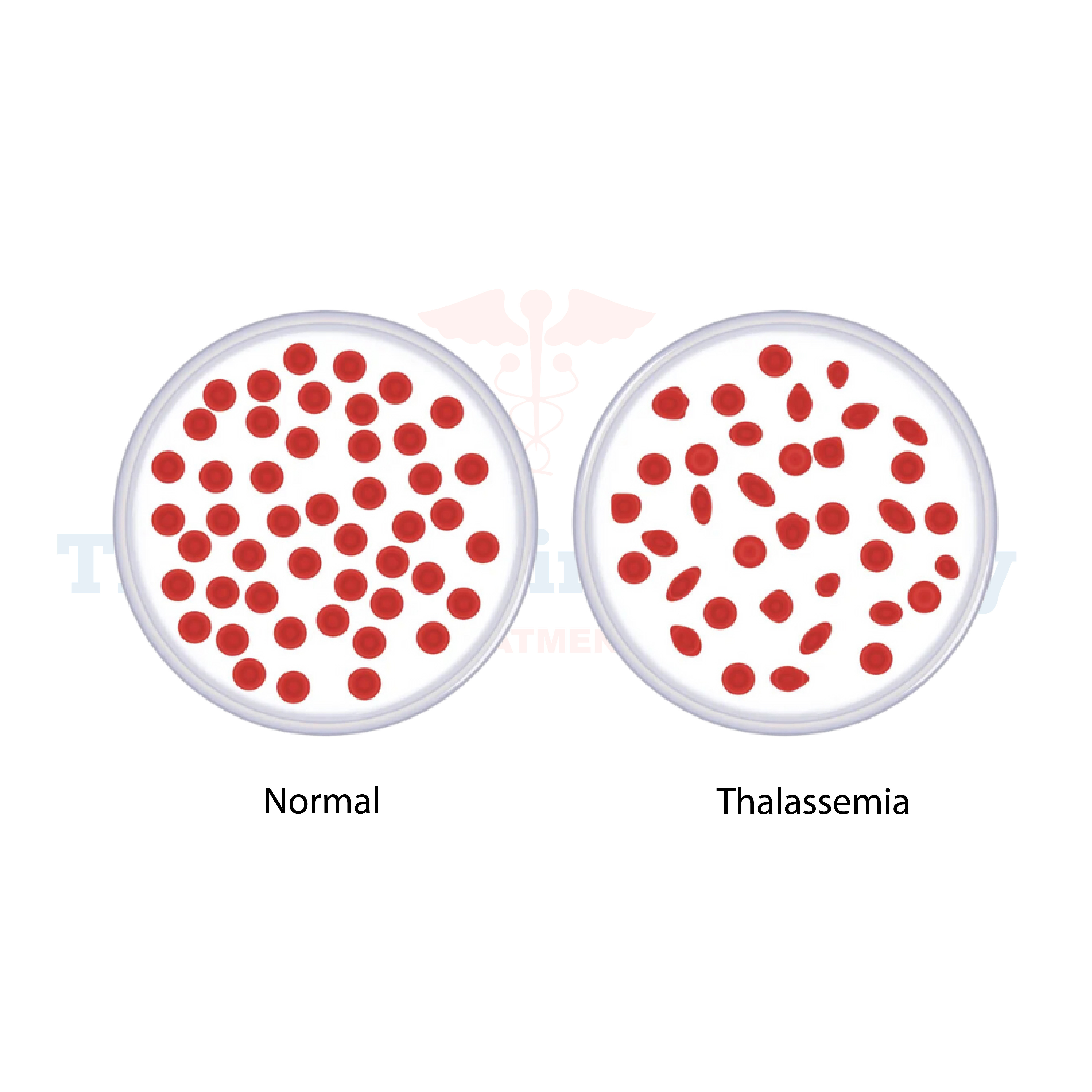
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder characterized by abnormal hemoglobin production, leading to inadequate oxygen transport throughout the body. Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs. Individuals with thalassemia have either reduced or abnormal hemoglobin, causing anemia and other complications.
Side effects of Thalassemia:
The severity of thalassemia symptoms varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common side effects include:
How is Thalassemia diagnosed?:
Diagnosing thalassemia involves several steps, including:
Potential treatments of Thalassemia:
While there is no cure for thalassemia, treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
