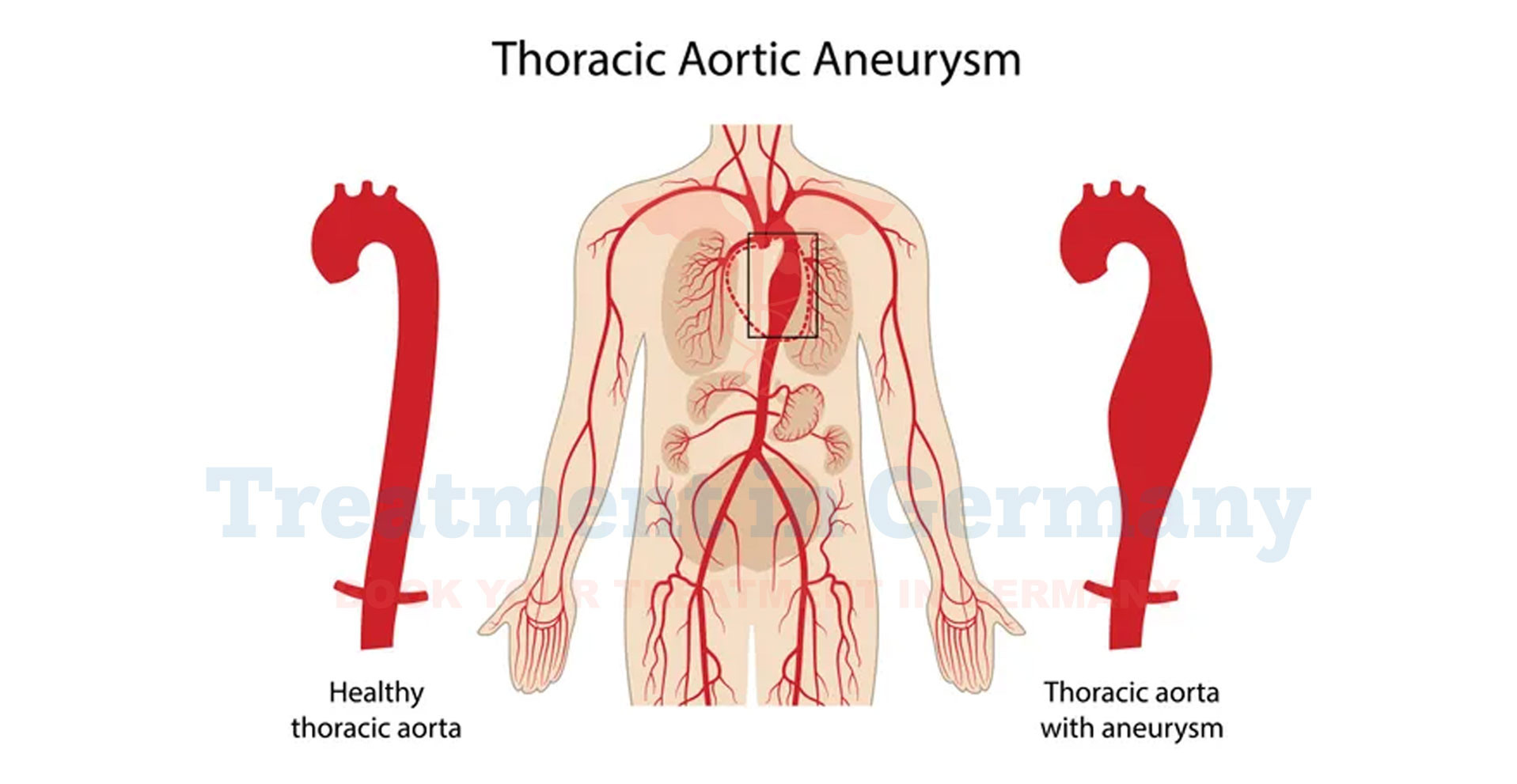
What is a Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is a condition where a section of the aorta, the main artery carrying blood from the heart to the rest of the body, becomes enlarged or bulges in the chest area.
This enlargement occurs due to a weakening of the artery wall. The aorta is divided into different segments, and when the aneurysm occurs in the thoracic portion (the part of the aorta that runs through the chest), it’s specifically termed a thoracic aortic aneurysm.
Side Effects of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
The side effects and symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm can vary greatly depending on the aneurysm's size and rate of growth. Some common side effects include:
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest area, which can be mild or severe.
- Back Pain: Pain may also radiate to the back.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing or feeling breathless.
- Coughing: Persistent cough, especially if the aneurysm is pressing on the airways.
- Hoarseness: Voice changes or hoarseness due to pressure on the nerves.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Difficulty swallowing or a sensation of pressure in the throat.
In severe cases, if the aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding and require immediate medical attention.
How is Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a thoracic aortic aneurysm often involves several steps, including:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical exam to check for signs of an aneurysm.
- Imaging Tests: Various imaging tests can help visualize the aorta and determine the size and extent of the aneurysm. Common tests include:
- Chest X-ray: To identify any abnormal bulging or widening of the aorta.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the aorta.
- MRI Scan: Offers high-resolution images to assess the aneurysm's size and structure.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart and aorta.
Potential Treatment of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
Treatment options for a thoracic aortic aneurysm depend on its size, growth rate, and overall health of the patient. Potential treatments include:
- Lifestyle Changes: For small aneurysms or those not causing symptoms, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes such as managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to control blood pressure and reduce stress on the aortic wall.
- Surgical Repair: For larger or symptomatic aneurysms, surgery may be necessary. Options include:
- Open Surgery: Involves removing the damaged section of the aorta and replacing it with a synthetic graft.
- Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR): A minimally invasive procedure where a stent-graft is inserted into the aorta through a catheter.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
