What is Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)?
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is a condition characterized by the compression of nerves and blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, which is the space between your collarbone and first rib.
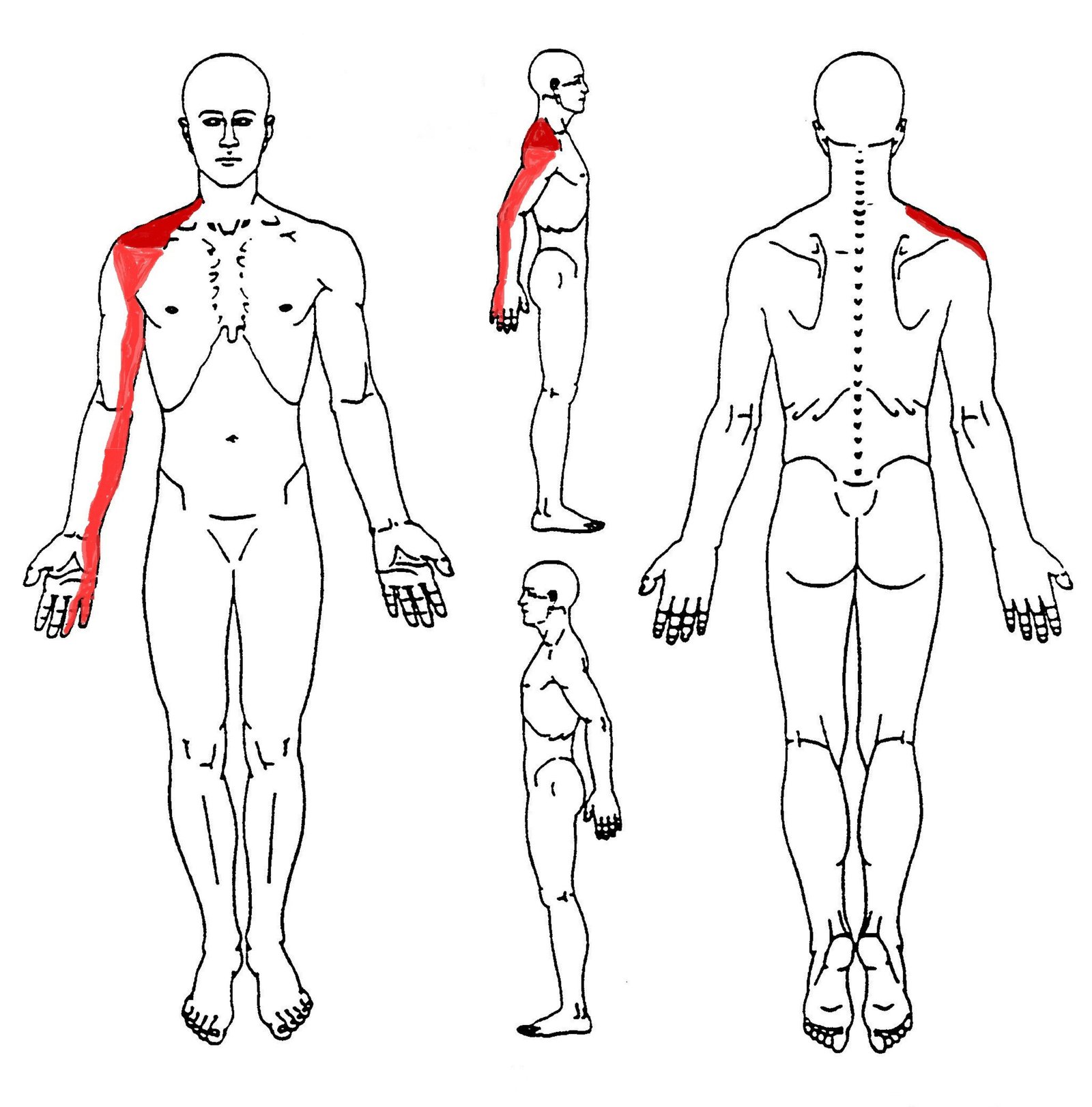
This compression can result in pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the neck, shoulder, arm, and hand.
Side effects of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
The symptoms of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome can vary widely among individuals but commonly include:
These symptoms can significantly impact one's quality of life, making it essential to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
How is Thoracic Outlet Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosing Thoracic Outlet Syndrome often involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, which may include:
1. Medical History: Your doctor will review your medical history and ask about your symptoms, including when they started and what exacerbates or alleviates them.
2. Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination will be conducted to assess your range of motion, muscle strength, and any signs of nerve or blood vessel compression.
3. Diagnostic Tests: Additional tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, CT scans, or nerve conduction studies may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and identify the underlying cause of compression.
Potential treatments of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
Treatment for TOS aims to relieve symptoms, improve function, and address the underlying cause of compression. Depending on the severity and type of TOS, treatment options may include:
1. Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches to improve posture, strengthen muscles, and relieve pressure on the nerves and blood vessels.
2. Medications: Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort and inflammation.
3. Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be recommended to release compressed structures and restore normal function.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Ergonomic adjustments, such as improving workstation setup and avoiding repetitive motions, can help reduce strain on the affected area.
5. Alternative Therapies: Techniques like acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care may offer symptomatic relief for some individuals.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
