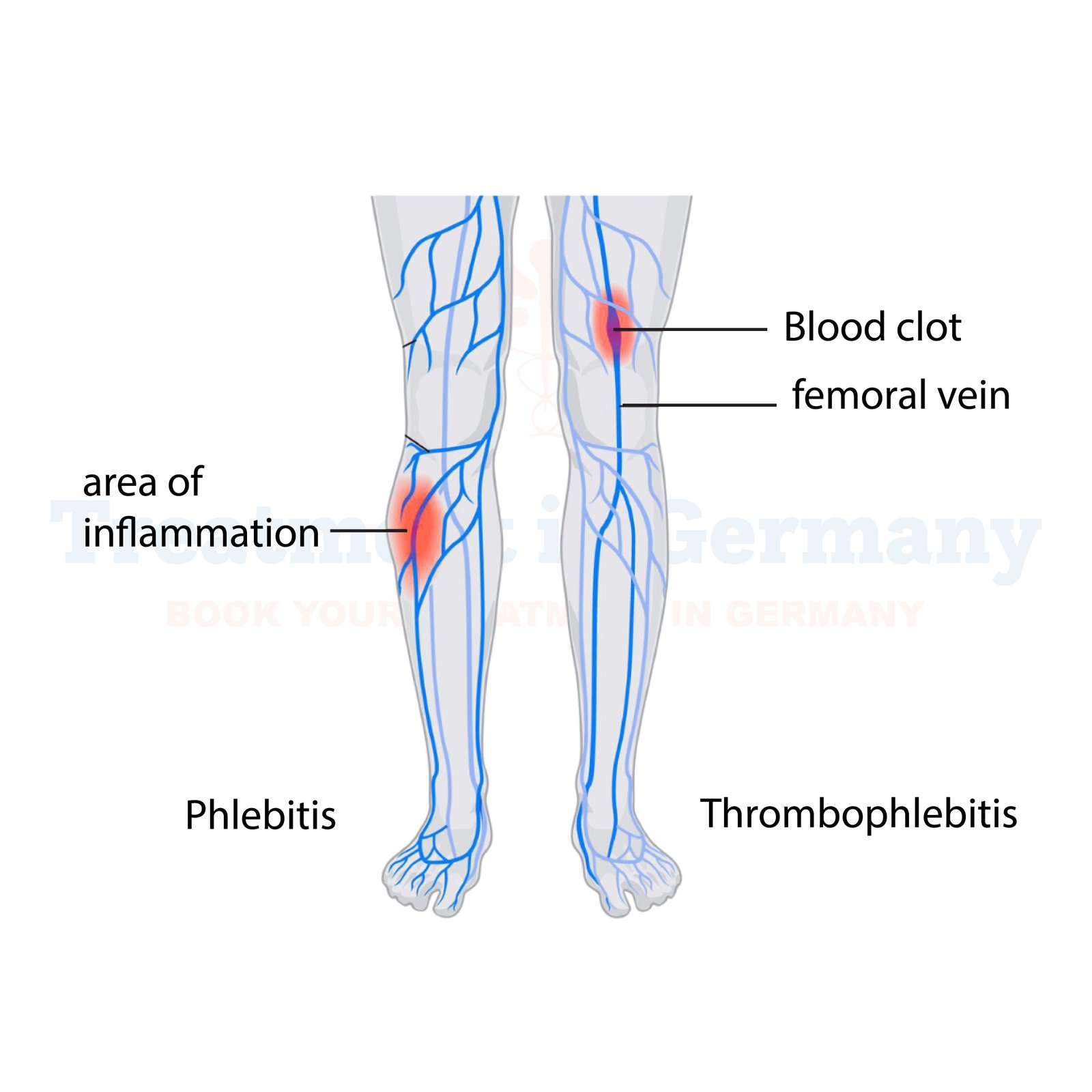
What is Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis, also known as superficial thrombophlebitis or phlebitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation and blood clot formation in a vein, usually near the surface of the skin. This condition commonly affects the legs but can occur in other parts of the body as well. When a blood clot forms in a vein, it can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
Side Effects of Thrombophlebitis:
The symptoms of thrombophlebitis can vary depending on the severity and location of the blood clot. Common side effects include:
In severe cases, thrombophlebitis can lead to complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or even pulmonary embolism if the blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs.
How is Thrombophlebitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing thrombophlebitis typically involves a physical examination and medical history review by a healthcare professional. Additional tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the condition. These tests may include:
1. Ultrasound imaging to visualize the blood flow and detect blood clots.
2. Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation and clotting disorders.
3. Venography, a procedure where a dye is injected into the veins followed by X-rays to identify blood clots.
Potential Treatments of Thrombophlebitis:
Treatment for thrombophlebitis aims to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of blood clot recurrence. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
1. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin may help alleviate discomfort and inflammation.
2. Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings or bandages can promote blood flow and reduce swelling.
3. Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area may help improve blood circulation and relieve pain.
4. Medication: In some cases, anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) may be prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming or to dissolve existing clots.
5. Surgery: In rare instances, surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot or repair damaged veins.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
