Understanding Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
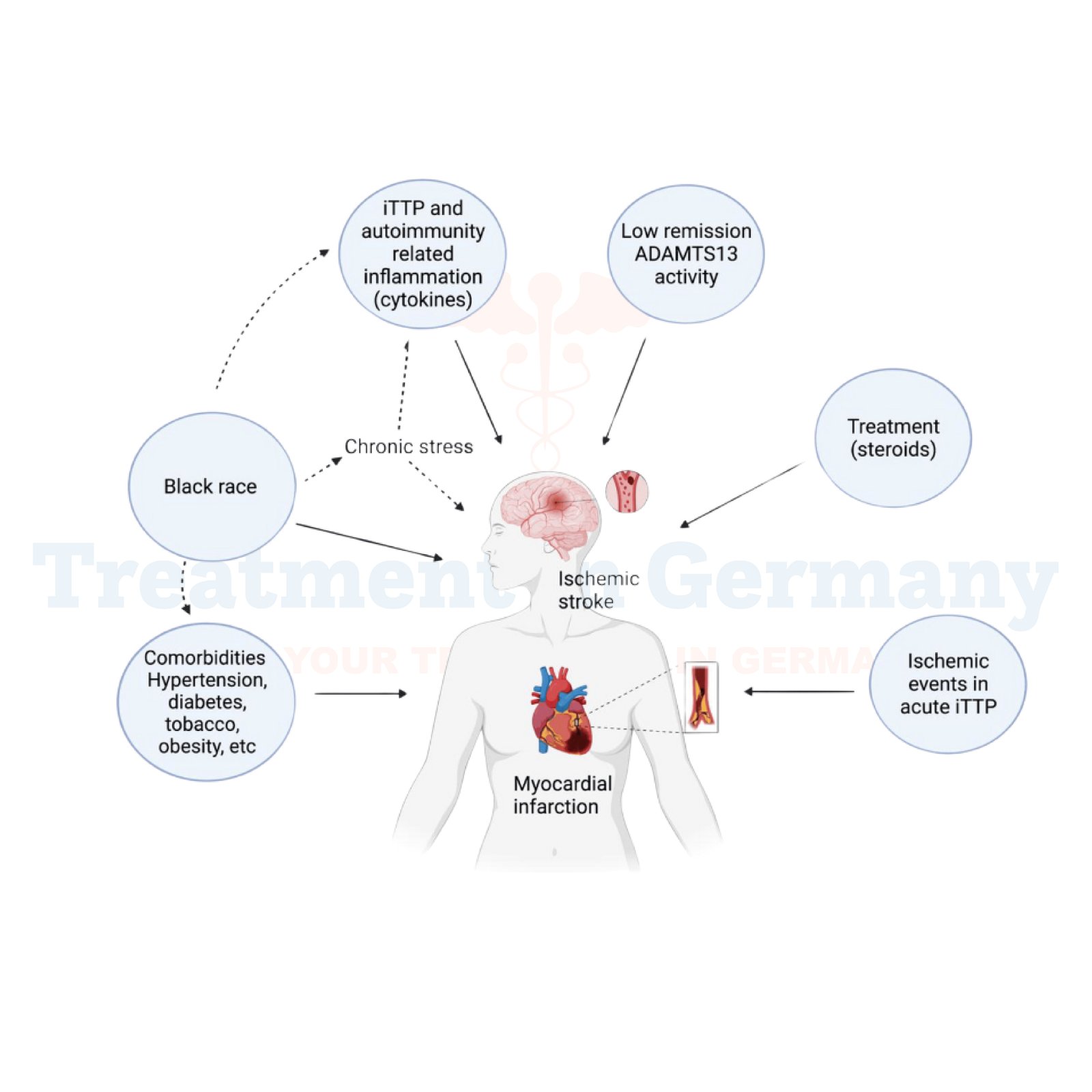
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is a rare and serious blood disorder characterized by blood clotting in small blood vessels throughout the body.
This condition leads to a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia) and can cause damage to multiple organs due to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Side Effects of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
The effects of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura can vary widely depending on the severity and rapidity of onset. Common symptoms include:
- Bruising and Purpura: Easy bruising and small red or purple spots on the skin (petechiae).
- Fatigue and Weakness: Due to anemia caused by red blood cell destruction.
- Neurological Symptoms: Such as confusion, seizures, and headaches, which can occur as a result of decreased blood flow and oxygen to the brain.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Which may lead to decreased urine output or blood in the urine.
How Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is Diagnosed
Diagnosing Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes specialized procedures. Diagnostic steps may include:
- Blood Tests: To assess platelet count, red blood cell count, and levels of enzymes and substances indicative of organ damage.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: To examine blood cells under a microscope for characteristic changes.
- ADAMTS13 Activity Test: Measures the activity of ADAMTS13 enzyme, which is typically reduced in TTP.
- Imaging Studies: Such as CT scans or MRI to evaluate organ damage or involvement.
Potential Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
Prompt treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura is crucial to prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. Treatment options may include:
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): This is the primary treatment for TTP, where the patient's plasma (containing antibodies causing TTP) is removed and replaced with donor plasma that contains the missing ADAMTS13 enzyme.
- Corticosteroids: These may be used in combination with plasma exchange to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Medications like rituximab may be used to target specific immune cells involved in TTP.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
