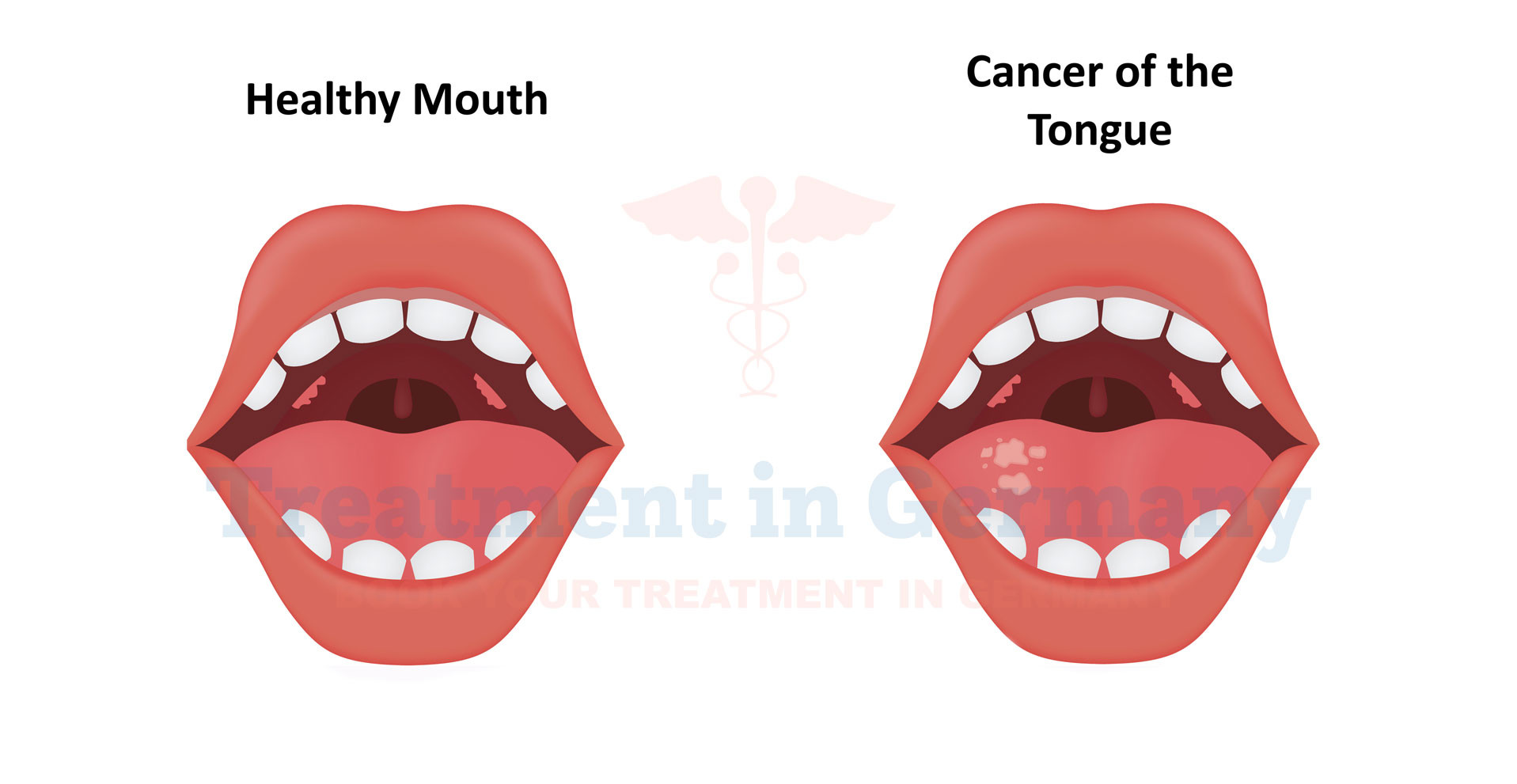
Understanding Tongue Cancer
Tongue cancer refers to malignant growths that develop on the tongue's surface or in its tissues. It can affect either the front (oral tongue) or the back (base) of the tongue.
These cancers typically arise from the squamous cells lining the tongue and can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Side Effects of Tongue Cancer
The symptoms and side effects of tongue cancer may include:
- Persistent soreness or pain on the tongue
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- A lump or thickening on the tongue
- Persistent ear pain on one side
- Hoarseness or changes in the voice
- Persistent sore throat or feeling that something is caught in the throat
- Unexplained weight loss
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing these symptoms effectively.
Diagnosis of Tongue Cancer
Diagnosing tongue cancer typically involves the following steps:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the tongue and mouth by a doctor or dentist.
- Biopsy: Removal of a small sample of tissue from the tongue for examination under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
- Imaging Tests: Such as CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans to determine the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Potential Treatment of Tongue Cancer
Treatment options for tongue cancer depend on the stage of cancer, its location, and the patient's overall health. They may include:
- Surgery: Removal of the cancerous tumor and possibly nearby lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
