What is Tonsil Cancer?
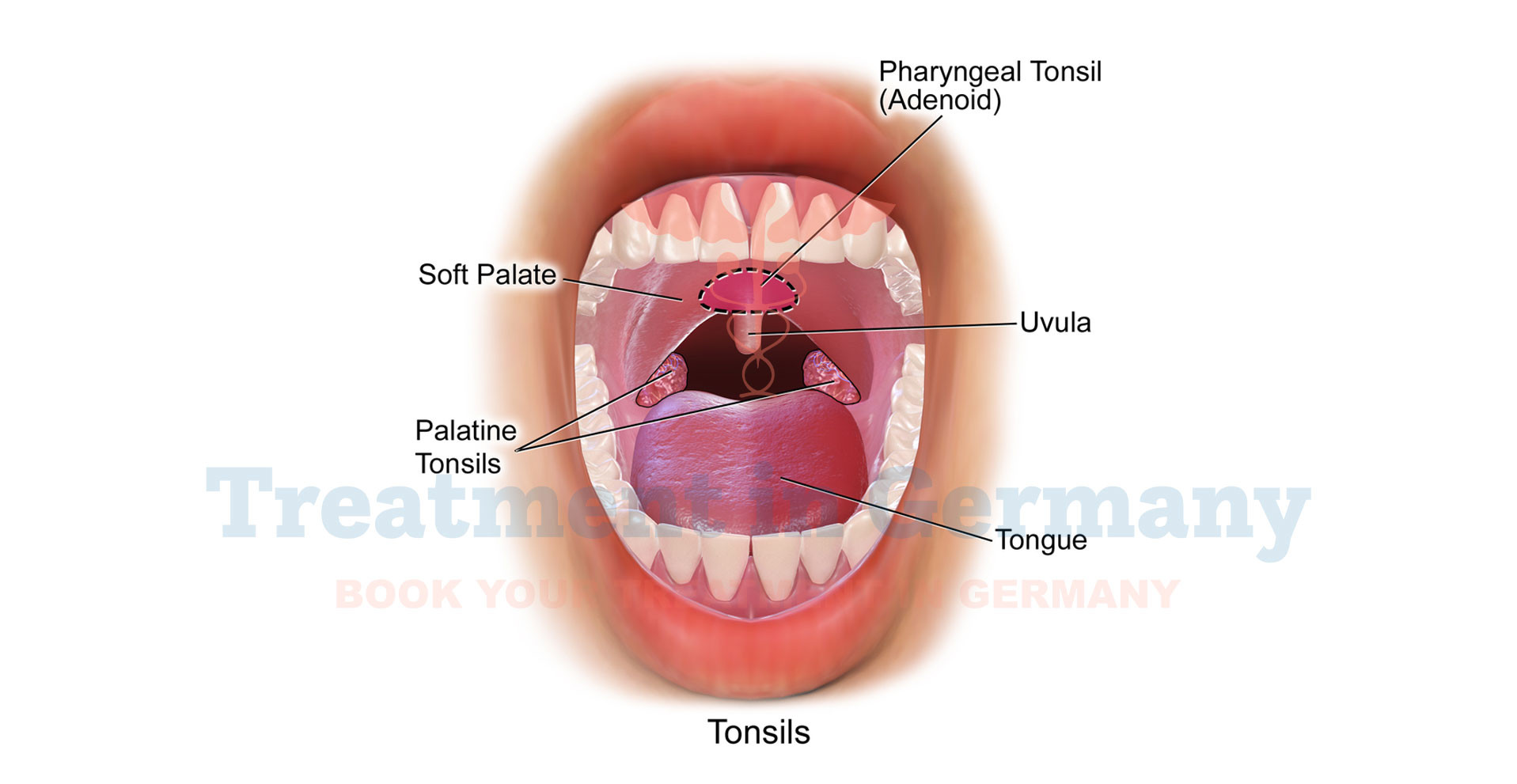
Tonsil cancer, also known as squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil, is a type of cancer that originates in the tissues of one or both of the tonsils located at the back of the throat.
These cancers usually develop from the surface cells (squamous cells) of the tonsils and can affect various parts of the tonsils, including the base or the folds.
Side Effects of Tonsil Cancer
The symptoms and side effects of tonsil cancer can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. Common signs may include:
- Sore throat: Persistent pain or discomfort in the throat that does not improve with usual treatments.
- Difficulty swallowing: Painful or challenging swallowing, especially solid foods.
- Ear pain: Discomfort in the ears, which can be referred pain from the throat.
- Persistent cough: Coughing that does not resolve and may worsen over time.
- Swelling in the neck: Enlarged lymph nodes that can be felt as lumps in the neck.
How is Tonsil Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing tonsil cancer typically involves a series of tests and procedures to confirm the presence of cancer and determine its extent. These may include:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the throat and neck by a specialist.
- Biopsy: Removal of a small tissue sample from the tonsil for laboratory analysis.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans to visualize the tumor and assess if cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is used to examine the throat and obtain tissue samples if needed.
Potential Treatments of Tonsil Cancer
Treatment options for tonsil cancer depend on the stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and other factors such as the location and size of the tumor. Common treatments may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the affected tonsil (tonsillectomy) or more extensive surgery to remove surrounding tissues if cancer has spread.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays targeted at the cancerous cells to destroy them.
- Chemotherapy: Medications used to kill cancer cells or slow their growth; sometimes used in combination with radiation therapy.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that specifically target certain molecules involved in cancer growth.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
