Understanding Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR)
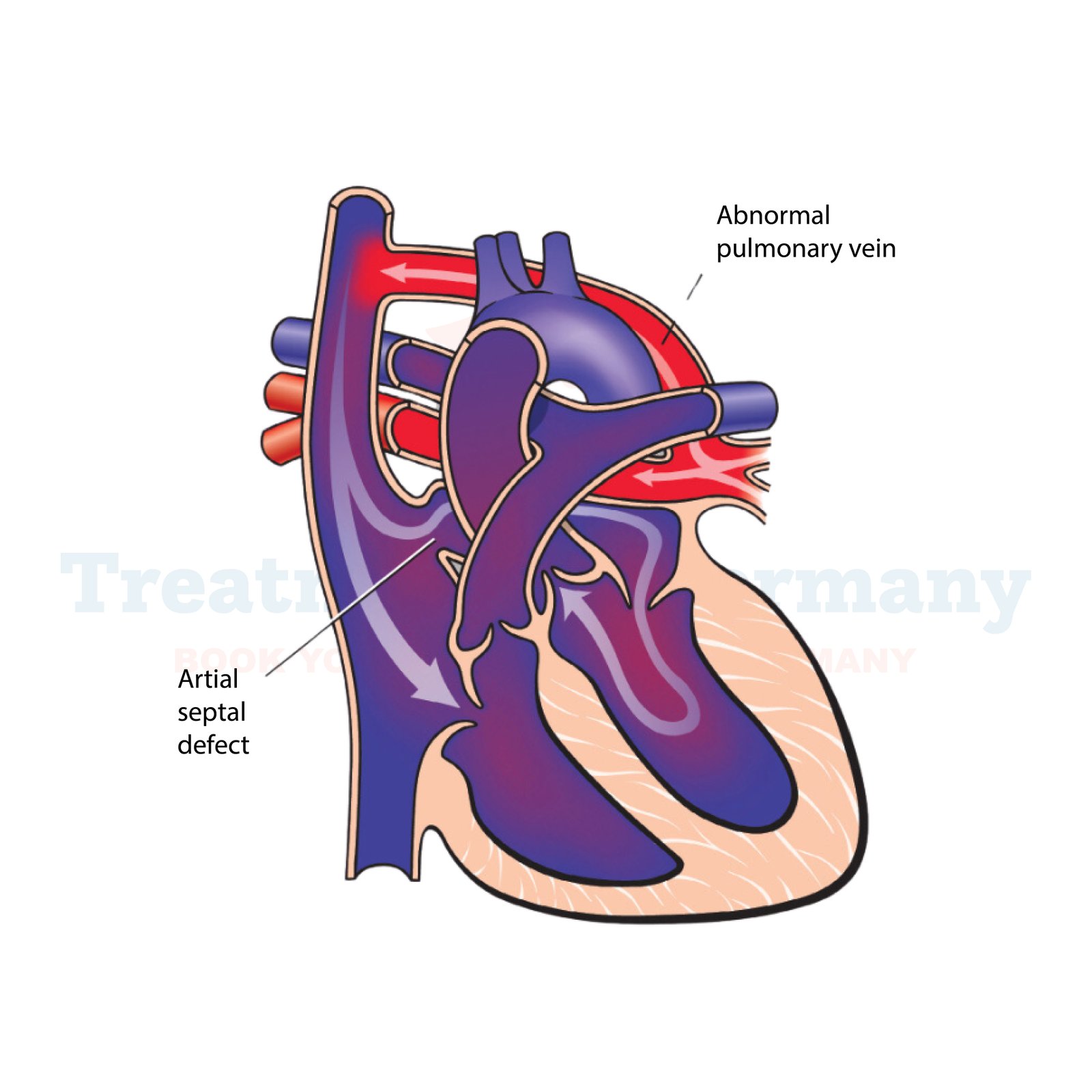
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) is a congenital heart defect where the pulmonary veins, which normally carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart, are abnormally connected.
In Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return , these veins do not connect to the left atrium as they should, but instead connect to either the right atrium or to another vein or heart chamber.
This causes a mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the body.
Side Effects of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR)
The side effects of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return can vary depending on the specific type and severity of the defect. Common symptoms may include:
How is Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return typically involves several tests and procedures:
Potential Treatment of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR)
Treatment for TAPVR typically involves surgery shortly after birth to correct the abnormal connection of the pulmonary veins. The goal of surgery is to reroute the pulmonary veins to the left atrium where they should naturally drain.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
