Tourette syndrome Treatment in Germany
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurological disorder characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements and vocalizations known as tics. It typically manifests in childhood and varies in severity among individuals. Although the exact cause remains unknown, TS is believed to result from genetic and environmental factors affecting the brain's neurotransmitters. While there is no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Germany is renowned for its innovative treatment approaches, top-tier specialists, and cutting-edge medical facilities, making it an excellent destination for Tourette syndrome management.
Understanding Tourette syndrome
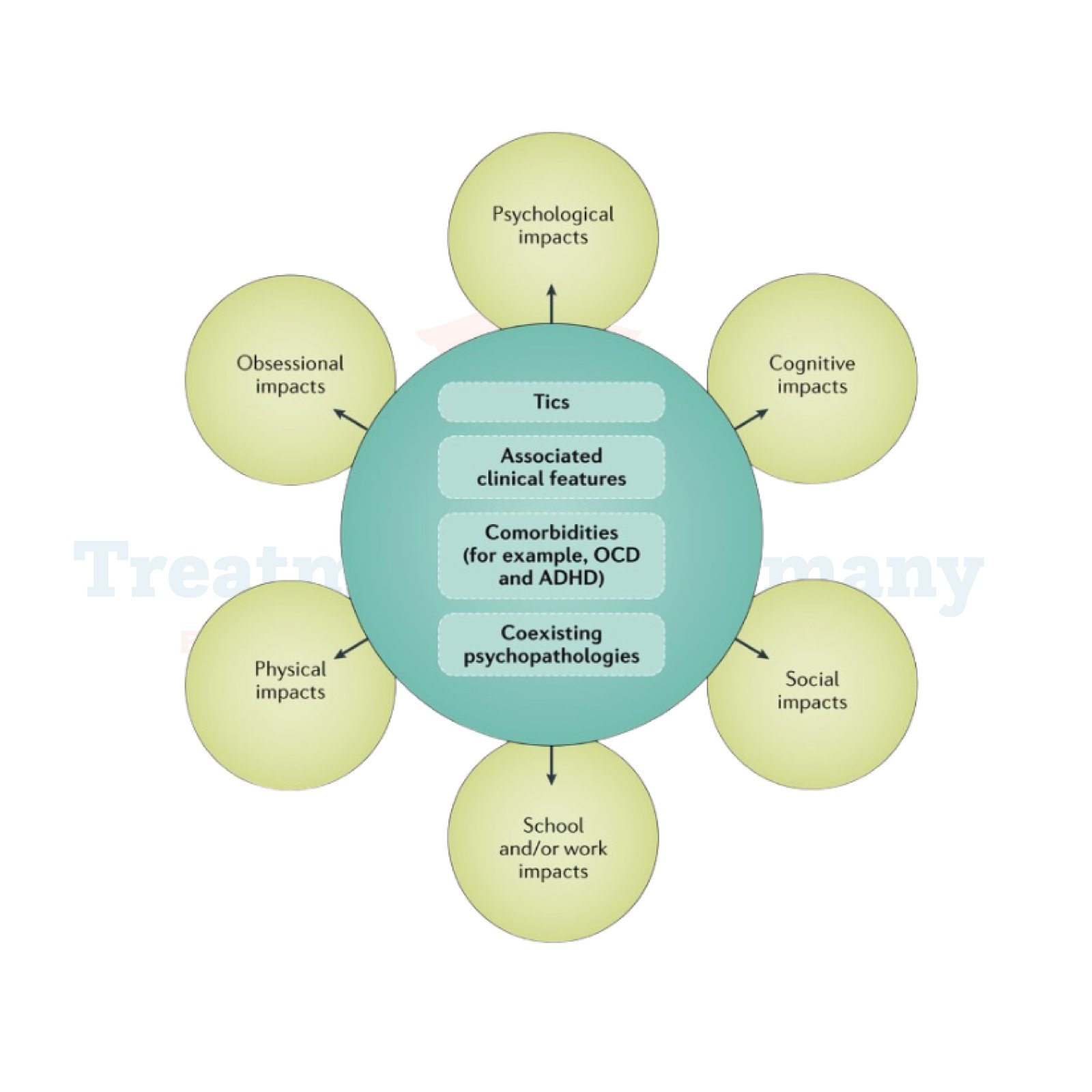
Tourette syndrome is part of a spectrum of tic disorders and can range from mild to severe. The disorder affects the nervous system and is often associated with other conditions, such as Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and anxiety disorders.
Types of Tourette syndrome
- Transient Tic Disorder – Short-term tics lasting less than a year.
- Chronic Tic Disorder – Motor or vocal tics that persist for over a year.
- Tourette syndrome (TS) – A combination of motor and vocal tics lasting over a year, often severe enough to impact daily life.
Risk Factors for Tourette syndrome
While the exact cause is unknown, several factors contribute to the development of TS:
- Genetics – TS often runs in families, suggesting a hereditary component.
- Neurochemical Imbalance – Disruptions in dopamine and serotonin levels may influence tic severity.
- Prenatal and Perinatal Factors – Maternal stress, smoking, and low birth weight can increase risk.
- Autoimmune Response – Some cases of TS are linked to post-infectious autoimmune reactions affecting the brain.
Symptoms of Tourette syndrome
Tourette syndrome symptoms usually appear between ages 5 and 10 and may worsen during adolescence. The main symptoms include:
- Motor Tics – Involuntary movements such as blinking, head jerking, shoulder shrugging, and facial grimacing.
- Vocal Tics – Sounds like grunting, throat clearing, sniffing, or, in rare cases, involuntary use of inappropriate words (coprolalia).
- Cognitive and Behavioral Issues – Anxiety, impulsivity, difficulty concentrating, and obsessive-compulsive tendencies.
- Worsening Symptoms with Stress – Anxiety and fatigue can exacerbate tic severity.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
German hospitals utilize advanced diagnostic tools to assess Tourette syndrome and differentiate it from other neurological disorders:
- Neurological Examination – Evaluates motor function and tic patterns.
- Patient History Review – Identifies symptom progression and family history.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) Scans – Used to rule out other brain conditions.
- EEG (Electroencephalography) – Measures electrical activity in the brain to detect abnormalities.
- Blood Tests – Checks for autoimmune responses and metabolic disorders contributing to symptoms.
Innovative Therapies in Germany
Germany offers comprehensive, multidisciplinary approaches to treating Tourette syndrome. These include medication, behavioral therapy, and cutting-edge treatments such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) and regenerative medicine.
Medications for Symptom Management
While medication does not cure TS, it can help reduce tics and related behavioral issues:
- Dopamine-Blocking Medications – Such as haloperidol and aripiprazole, which regulate neurotransmitter activity.
- ADHD Medications – Stimulants like methylphenidate help improve focus while minimizing tic exacerbation.
- SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) – Manage anxiety and OCD-related symptoms.
- Muscle Relaxants – Reduce physical tics and muscle stiffness.
Behavioral and Psychological Therapies
Germany prioritizes non-pharmacological interventions for Tourette Syndrome, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps patients manage anxiety and compulsive behaviors.
- Habit Reversal Training (HRT) – Teaches individuals to recognize and replace tics with voluntary movements.
- Comprehensive Behavioral Intervention for Tics (CBIT) – A structured therapy program that reduces tic severity.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS is an innovative surgical treatment used in severe cases where other therapies fail. This procedure involves implanting electrodes in the brain to regulate abnormal neural activity. Germany’s leading neurological centers and neurosurgeons specialize in DBS for Tourette syndrome, making it a promising option for patients with disabling tics.
Regenerative Medicine and Advanced Treatments
- Stem Cell Therapy – Research is ongoing in Germany regarding the use of stem cells to repair neurological dysfunctions related to TS.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy – Used in experimental settings to modulate immune responses potentially linked to tic disorders.
- TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization) – A technique primarily used for tumor-related conditions but investigated for neurological applications.
- Complementary Therapies – Includes acupuncture, meditation, and dietary modifications to support overall well-being.
Solutions and Prevention Strategies
While there is no way to prevent Tourette syndrome, some strategies help reduce symptom severity and improve quality of life:
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment – Allows for better symptom management and intervention.
- Stress Management Techniques – Yoga, mindfulness, and relaxation exercises can help reduce tic frequency.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise – A well-balanced diet and regular physical activity support neurological health.
- Educational Support – Schools and workplaces should accommodate individuals with TS to create a supportive environment.
- Medication and Therapy Compliance – Adhering to prescribed treatment plans ensures optimal results.
Why is Treatment in Germany Preferable?
Germany stands out as a premier destination for Tourette Syndrome treatment due to:
- Expert Neurologists and Specialists – Highly trained professionals with extensive experience in tic disorders.
- State-of-the-Art Hospitals – Equipped with the latest technology, including MRI, CT, EEG, and Deep Brain Stimulation devices.
- Cutting-Edge Research and Clinical Trials – Ongoing studies on stem cell therapy and advanced neuromodulation techniques.
- Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach – Combines medical, behavioral, and alternative therapies for comprehensive care.
- Personalized Rehabilitation Programs – Tailored interventions to support patients in managing their symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
Tourette Syndrome is a complex neurological condition requiring a comprehensive treatment plan to manage symptoms effectively. Germany offers world-class medical expertise, cutting-edge treatments, and innovative research for Tourette Syndrome patients. Seeking treatment in Germany ensures access to top-tier hospitals, experienced doctors, and advanced rehabilitation programs, improving long-term outcomes and quality of life.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
