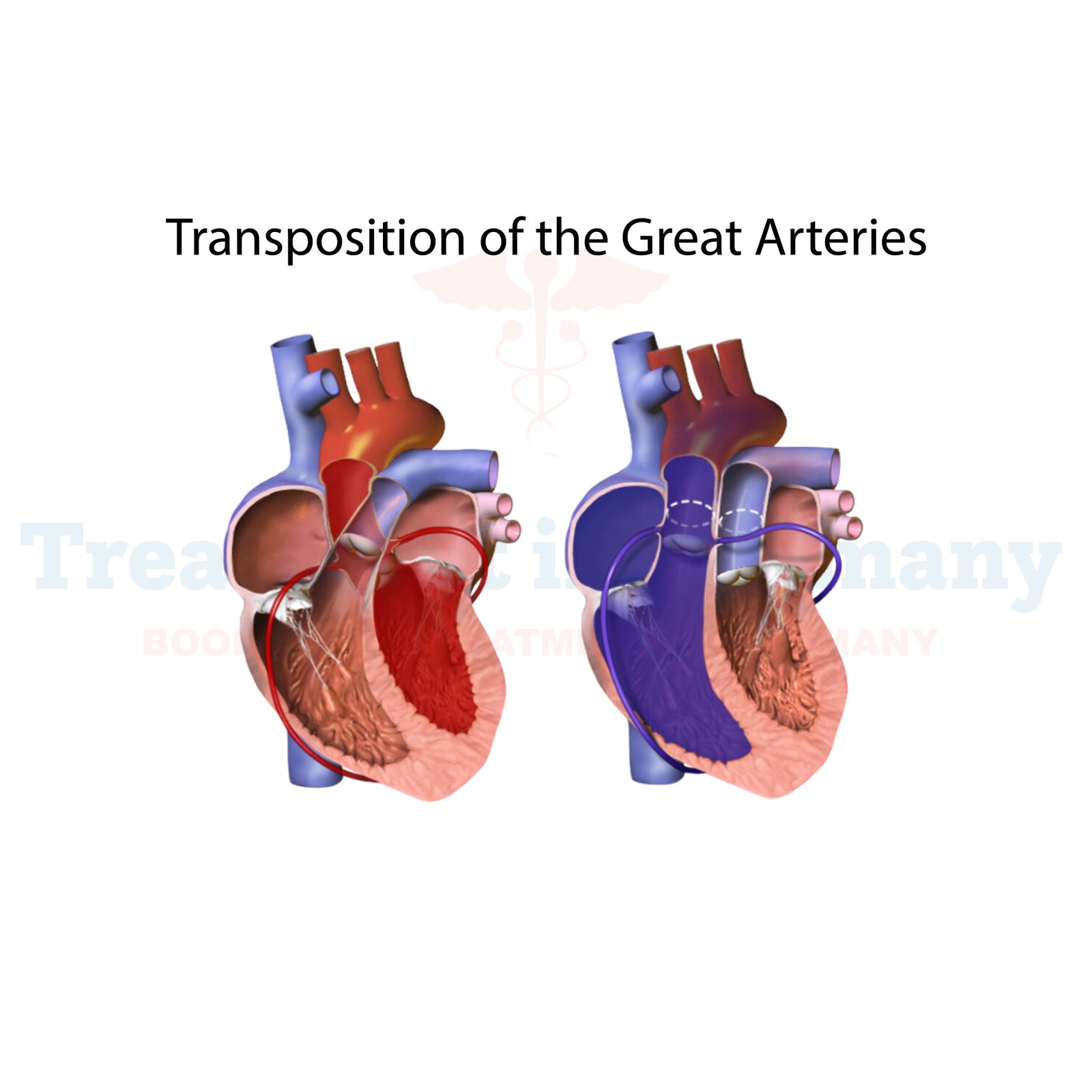
Understanding Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)
Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA) is a congenital heart defect where the two main arteries leaving the heart—the pulmonary artery and the aorta—are switched (transposed). This condition disrupts the normal circulation of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
Side Effects of Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)
How is Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA) Diagnosed?
Potential Treatments for Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
