What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
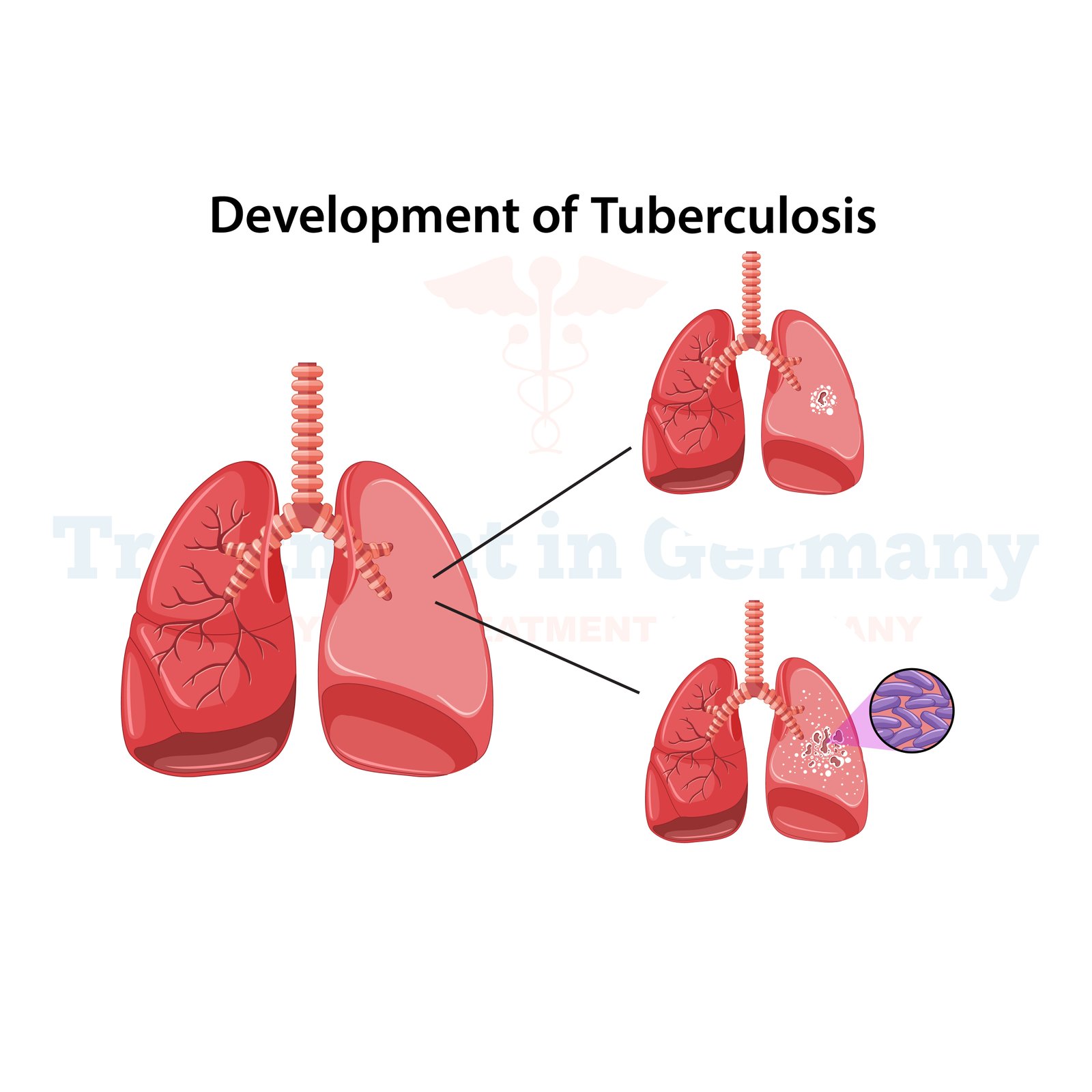
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also target other parts of the body like the kidneys, spine, or brain. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, making it highly contagious.
Side Effects of Tuberculosis (TB):
TB can cause a range of symptoms, including:
Left untreated, TB can lead to severe complications and even death. It's essential to seek medical attention if experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if living in or traveling to areas with a high TB prevalence.
How is Tuberculosis (TB) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Tuberculosis typically involves several steps, including:
In some cases, additional tests such as a CT scan or biopsy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Potential Treatments of Tuberculosis (TB):
Treating TB involves a combination of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains. The most commonly used medications include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
