What is Type 2 Diabetes?
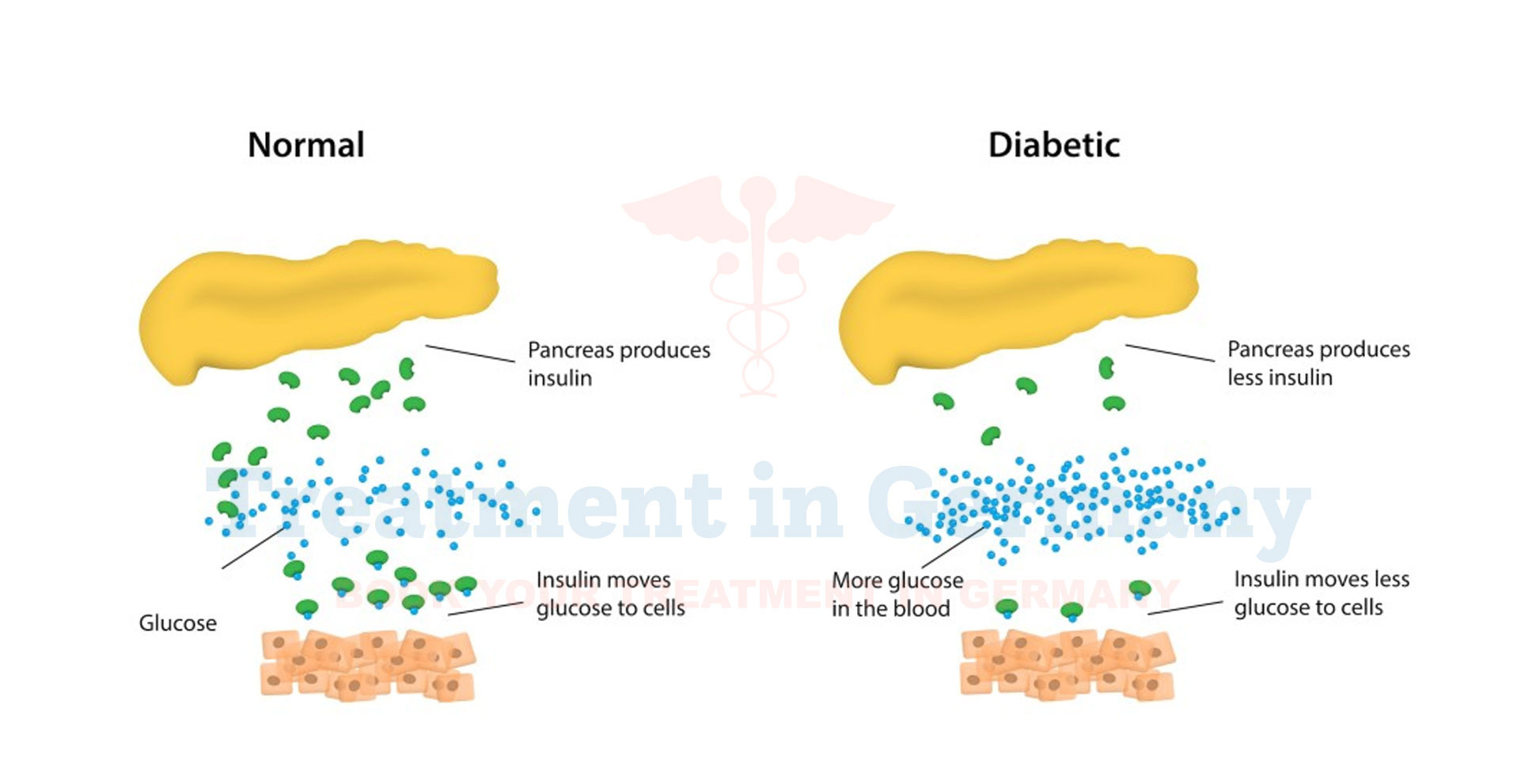
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body metabolizes sugar (glucose). It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels in the blood.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps glucose from food enter cells to be used for energy.
Side Effects of Type 2 Diabetes
Untreated or poorly managed Type 2 Diabetes can lead to various complications over time, including:
How is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure glucose levels. Common tests include:
Potential Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Treatment aims to manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Options may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
