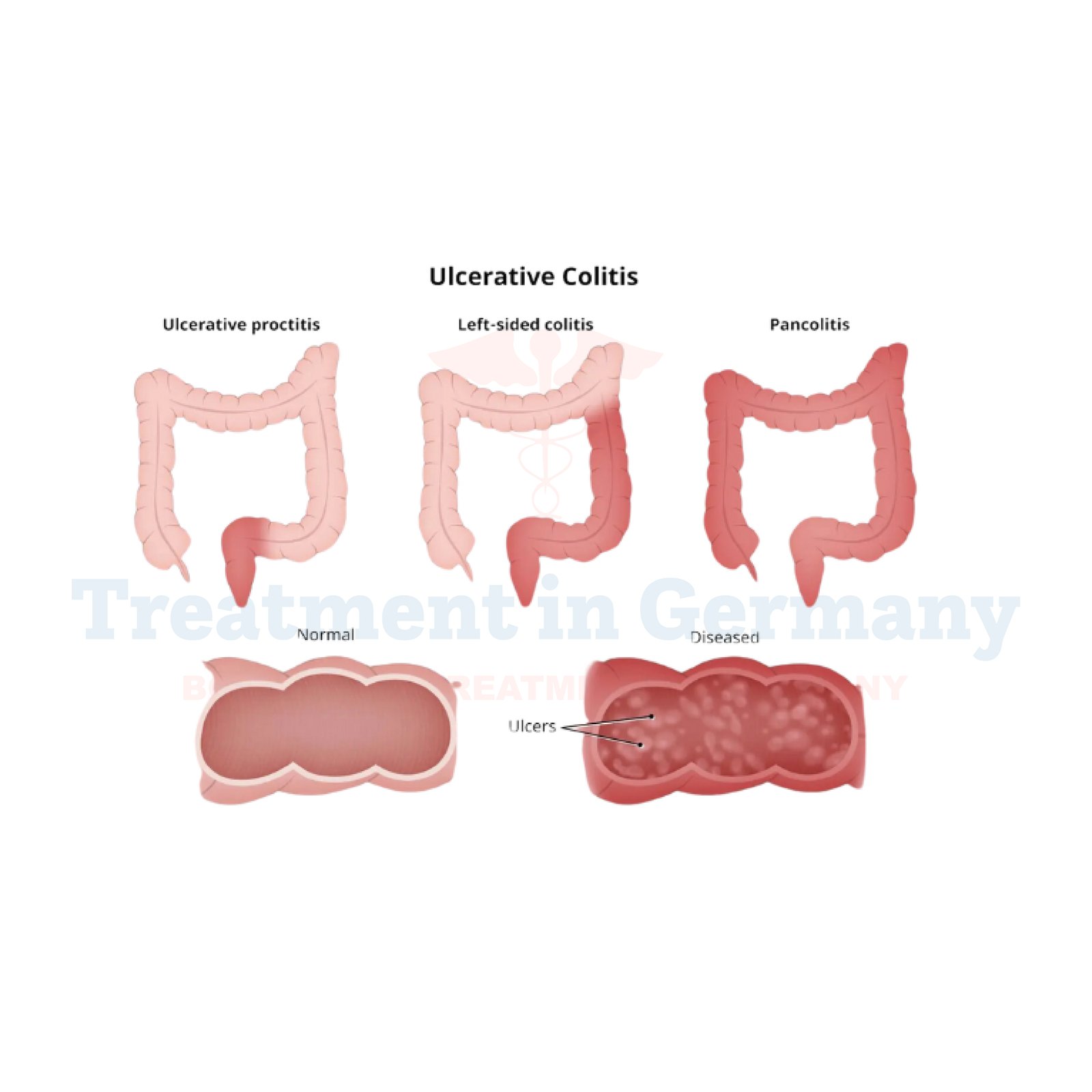
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis:
Ulcerative Colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It falls under the broader category of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and is characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the colon and rectum.
Side effects of Ulcerative Colitis:
The symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Persistent discomfort and cramping in the abdominal region are common symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis.
- Diarrhea: Patients often experience frequent and urgent bowel movements, which may be accompanied by blood or pus.
- Rectal bleeding: Inflammation and ulceration in the colon and rectum can lead to bleeding during bowel movements.
- Weight loss: Loss of appetite, coupled with diarrhea and malabsorption of nutrients, can result in weight loss.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and the body's efforts to combat it can lead to fatigue and a general feeling of weakness.
- Rectal urgency: A sudden and overwhelming need to have a bowel movement, which can be difficult to control.
- Anemia: Chronic bleeding from the inflamed tissue can lead to a decrease in red blood cells, resulting in anemia and its associated symptoms like weakness and dizziness.
How is Ulcerative Colitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing Ulcerative Colitis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests, including:
- Colonoscopy: This procedure allows a gastroenterologist to examine the colon and rectum using a flexible tube with a camera attached. Tissue samples (biopsies) can also be collected during colonoscopy for further analysis.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for signs of inflammation, anemia, and to rule out other conditions.
- Stool sample analysis: Examination of stool samples can help detect the presence of blood, mucus, or infectious agents.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to assess the extent of inflammation and to rule out complications such as bowel obstruction or perforation.
Potential treatments of Ulcerative Colitis:
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and achieve remission. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics are commonly prescribed to control inflammation and suppress the immune response.
- Lifestyle modifications: Dietary changes, stress management techniques, and regular exercise can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when medications fail to provide relief, surgical removal of the colon (colectomy) may be necessary. This procedure can effectively cure Ulcerative Colitis but requires careful consideration and discussion with a healthcare provider.
- Alternative therapies: Some patients may explore complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, probiotics, and herbal supplements. However, the effectiveness of these treatments varies, and their use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
