Advanced Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Treatment in Germany
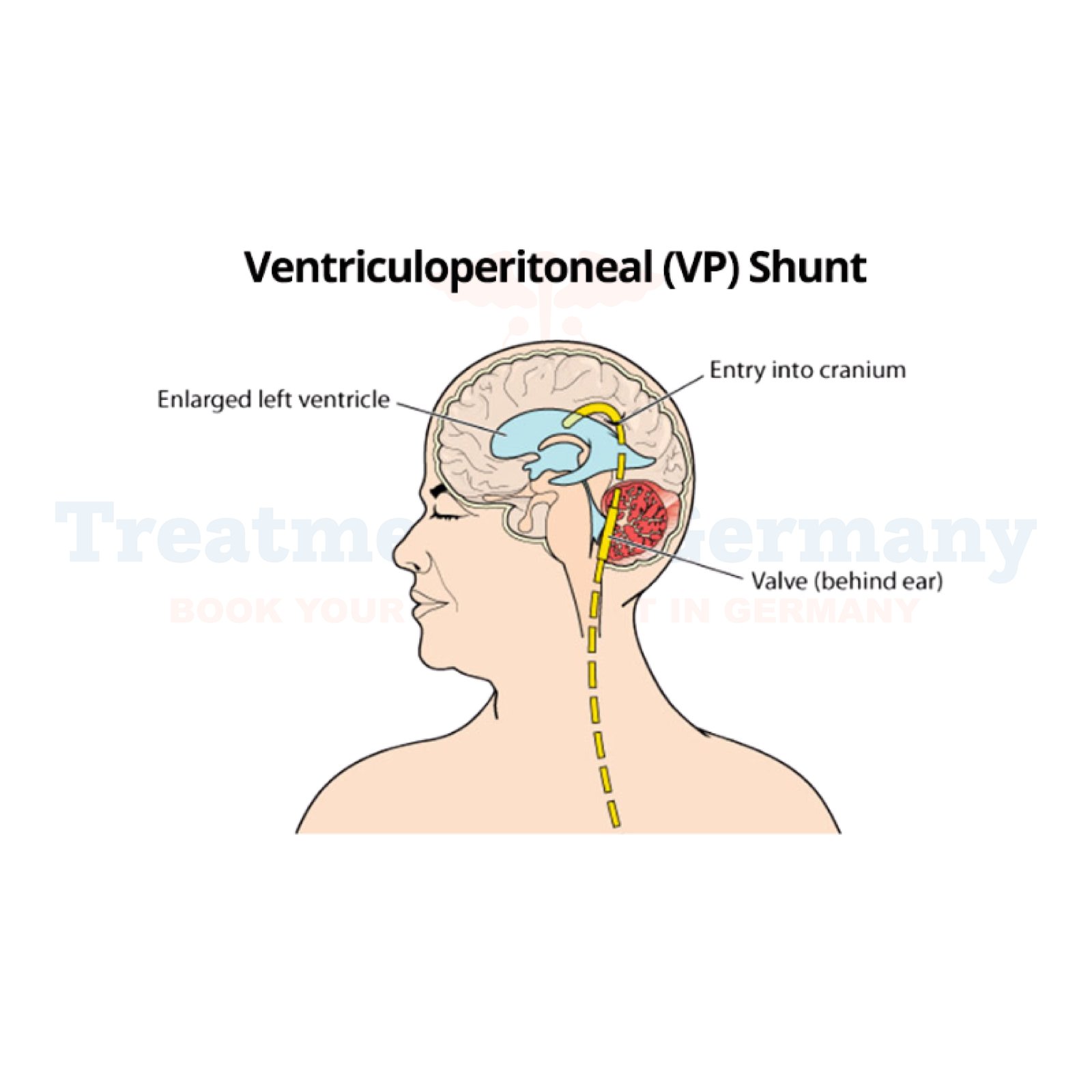
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement is a medical procedure that is used to treat hydrocephalus, a condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain's ventricles. A VP shunt is a device implanted surgically to redirect excess CSF from the brain's ventricles to the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen, where the fluid can be absorbed by the body. The therapy helps to relieve pressure on the brain, preventing damage and providing significant symptom relief.
Germany is renowned for its world-class healthcare system and cutting-edge neurosurgical facilities. Patients from around the globe travel to the country for expert diagnostic assessments and advanced surgical treatments, including highly precise VP shunt placement procedures. These interventions are performed using the latest imaging technologies and minimally invasive techniques, ensuring optimal outcomes and quicker recovery times.
Types of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can be classified into three main types according to its symptoms, severity and causes:
- Congenital Hydrocephalus: Present at birth and often linked to genetic conditions or developmental abnormalities in the central nervous system.
- Acquired Hydrocephalus: Develops after birth due to injury, infections, tumors, or bleeding in the brain.
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH): Often seen in older adults, caused by gradual fluid buildup and showing symptoms like difficulty walking, dementia-like behavior, or incontinence.
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus vary by age and type, but the most common signs patients can experience includes:
- Headache: Often caused by increased pressure in the brain due to fluid buildup.
- Nausea and Vomiting: A result of elevated intracranial pressure, frequently accompanying headaches.
- Blurred or Double Vision: Occurs as the swelling impacts the optic nerves, affecting eyesight.
- Balance Issues: Difficulty in walking or coordination due to pressure on areas of the brain controlling movement.
- Cognitive Impairments: Includes memory loss, confusion, or difficulty concentrating as brain function is disrupted.
- Unusual Enlargement of the Head (in infants): Visible swelling occurs due to skull bones not being fully fused, allowing the head to expand with pressure.
- Seizures: Episodes of abnormal brain activity resulting from increased cranial pressure or disturbance in brain function.
- Irritability (in children): A symptom of discomfort or pain due to rising pressure inside the skull.
Causes of Hydrocephalus
The cause of Hydrocephalus vary from patient to patient but it can be triggered by several factors, including:
- Congenital Defects: Hydrocephalus may result from congenital defects, such as neural tube defects or aqueductal stenosis.
- Head Trauma: Severe injuries to the head can disrupt the balance of cerebrospinal fluid, leading to its accumulation and pressure buildup.
- Brain Tumors: Tumors in the brain can block the pathways of cerebrospinal fluid, preventing its proper circulation and absorption.
- Central Nervous System Infections: Infections like meningitis can cause inflammation that disrupts the normal production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Hemorrhage: Bleeding in the brain, commonly occurring in premature infants or due to a stroke, may disturb the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Age Factor: Aging-related changes can be the cause in the case of normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis is vital for successful treatment. Physicians use advanced imaging technologies to plan effective interventions.
- Imaging Tests: Tests like MRI and CT scans help identify abnormalities.
- Lumbar Puncture: A lumbar puncture involves extracting cerebrospinal fluid for analysis.
- Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: This involves measuring the pressure within the brain.
- Neuropsychological Tests: Examine patient's cognitive function, memory, and overall mental state.
- Gait Analysis: Observation of walking patterns, as hydrocephalus can often impact balance.
Advanced VP Shunt Treatment in Germany
Germany has introduced advanced medical facilities and specialists in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Our experts provide cutting-edge ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement surgery with a focus on safety, precision, and comfort.
The Process Includes
- Thorough Diagnosis: We analyze your medical history and perform imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, to confirm the presence and cause of hydrocephalus.
- Customized Treatment Planning: Our neurologists and neurosurgeons tailor a treatment plan based on the severity and type of hydrocephalus.
- Surgical Expertise: The VP shunt procedure involves placing a thin, flexible tube with a pressure-sensitive valve into the brain’s ventricle system. The valve ensures the correct amount of fluid is redirected to the abdominal cavity for absorption.
- Follow-up Care: We focus on long-term recovery and support to minimize complications and ensure an optimal outcome.
Medications
- Corticosteroids: Limited use in specific cases to ease the pain.
- Diuretics: Reduce cerebrospinal fluid production.
- Acetazolamide: Help manage intracranial pressure
- New Medicines: Advanced Medications with less side effects.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany is renowned for its advanced healthcare system, cutting-edge medical technology, and highly skilled professionals. Here’s why Germany is well-known for quality healthcare:
- World-Class Surgeons: Consult experienced specialists and medical experts for neurosurgical procedures.
- Advanced Technologies: Integration of modern medical technologies and facilities for the patients.
- Comprehensive Patient Support: Receive ongoing support, from diagnosis to post-operative recovery and beyond.
- Innovative Treatment: Access to all kinds of diagnosis, research, treatment and therapy.
Prevention and Management
While some causes of hydrocephalus can't be prevented, proactive management can support long-term health. Strategies include:
- Medical Visits: Regular medical checkups to monitor neurological health.
- Proactive Treatment: Timely treatment of head injuries or infections.
- Consult Medical Support: Seeking expert advice if symptoms suggest hydrocephalus.
- Routine Check-ups: Post-treatment care and follow-up appointments after VP shunt placement.
Conclusion:
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement is a proven and effective surgical procedure for managing hydrocephalus and other conditions that cause an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. By redirecting excess fluid to the abdominal cavity, a VP shunt helps relieve pressure on the brain, alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Germany’s commitment to medical excellence ensures patients undergoing this procedure benefit from the latest innovations, highly skilled surgeons, and comprehensive post-operative care.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.
.webp)
.webp)
 (1).webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
.webp)
 (1).webp)
 (1).webp)
