What is Vertebral Artery Stenosis?
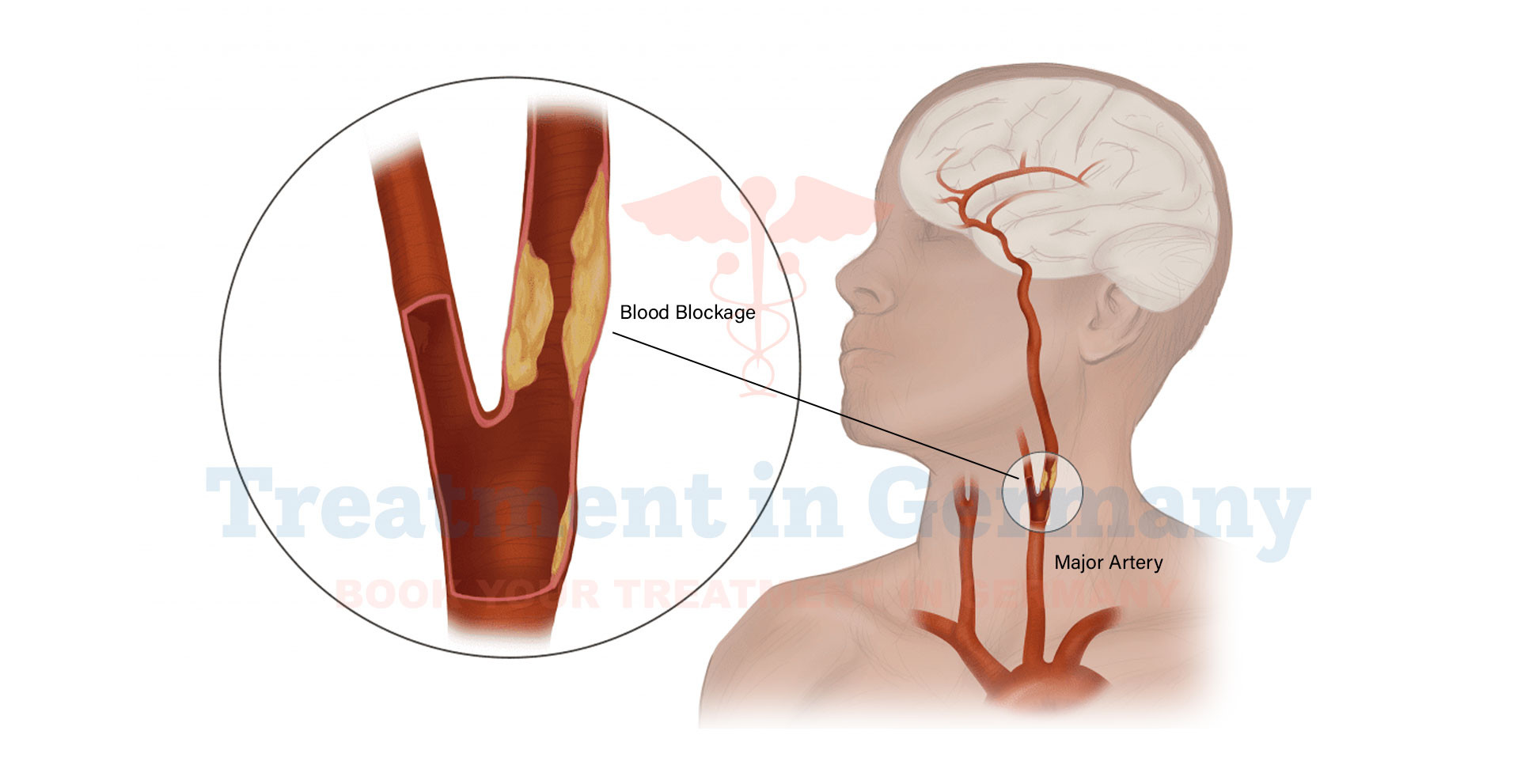
Vertebral artery stenosis is a condition where the vertebral artery, one of the major arteries supplying blood to the brain, becomes narrowed or constricted. This narrowing can reduce blood flow to the brain and spinal cord, potentially leading to serious complications.
The vertebral arteries are crucial for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the brain, particularly to the brainstem and cerebellum, which are essential for balance, coordination, and various automatic functions.
Side Effects of Vertebral Artery Stenosis
The side effects of vertebral artery stenosis can vary depending on the severity of the narrowing and the extent of reduced blood flow. Common symptoms may include:
- Dizziness or Vertigo: A sensation of spinning or loss of balance.
- Nausea: Feelings of sickness, often accompanied by dizziness.
- Headaches: Particularly in the back of the head.
- Visual Disturbances: Such as blurred vision or double vision.
- Difficulty with Coordination: Trouble with balance or fine motor skills.
- Fainting or Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, a reduction in blood flow can lead to episodes of fainting.
If left untreated, vertebral artery stenosis can lead to more severe complications, such as stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are often characterized by sudden, temporary symptoms like weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking.
How is Vertebral Artery Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing vertebral artery stenosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical exam to assess your neurological function and any potential signs of reduced blood flow.
- Ultrasound (Doppler Imaging): This non-invasive test uses sound waves to visualize the blood flow through the vertebral arteries and identify any narrowing or blockages.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): These imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of the blood vessels and can help identify areas of stenosis.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): This scan uses X-rays and a computer to create detailed images of the blood vessels, offering another method to visualize stenosis.
Potential Treatment of Vertebral Artery Stenosis
Treatment for vertebral artery stenosis depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of symptoms. Options may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, can help improve overall vascular health and potentially reduce the progression of stenosis.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to manage symptoms or address underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, or blood clots.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary. Options include:
- Endarterectomy: A surgical procedure to remove plaque from the artery and restore normal blood flow.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A procedure where a balloon is used to widen the narrowed artery, and a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
