What is Vulvodynia:
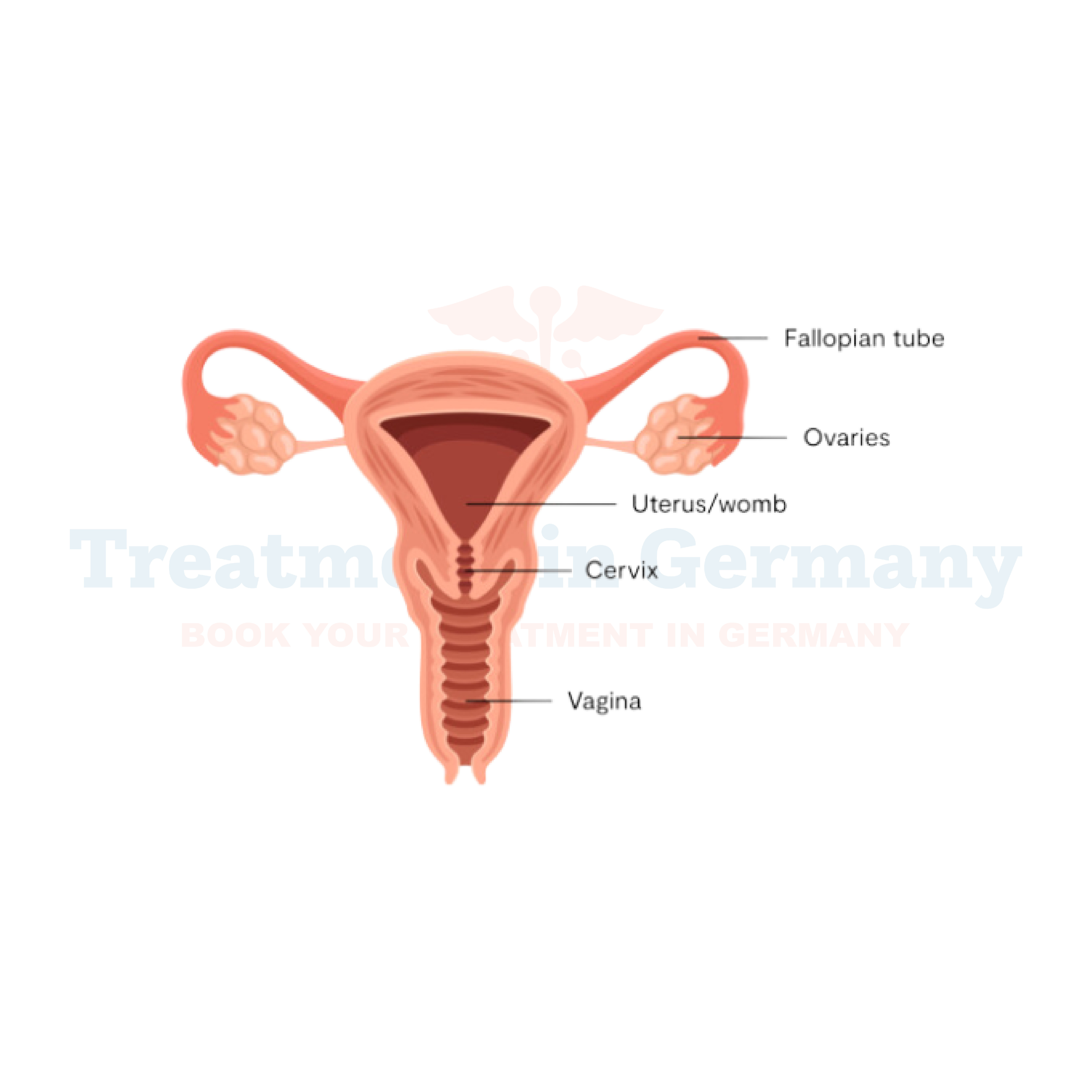
Vulvodynia is a chronic pain condition characterized by discomfort, burning, stinging, or sharp pain in the vulva - the external genital area of a woman's body.
This condition can significantly impact daily life, affecting activities like sitting, exercising, or sexual intercourse. While the exact cause of vulvodynia remains unclear, it's believed to involve various factors such as nerve damage, hormonal changes, muscle spasms, or inflammation.
Side effects of Vulvodynia:
The symptoms of vulvodynia can vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Persistent pain in the vulva, often described as burning, stinging, or rawness.
- Discomfort during intercourse (dyspareunia).
- Irritation or itching around the vaginal opening.
- Painful urination.
- Difficulty sitting for prolonged periods.
- Emotional distress, including anxiety or depression, due to the chronic nature of the condition.
How is Vulvodynia diagnosed?
Diagnosing vulvodynia typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests to rule out other possible causes of vulvar pain, such as infections or skin conditions.
Your healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to assess for any signs of inflammation or abnormalities in the vulvar tissue. Additionally, they may conduct tests to check for infections, allergies, or hormonal imbalances that could contribute to your symptoms.
Potential treatments of Vulvodynia:
While there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for vulvodynia, various options are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Some potential treatments include:
- Topical Medications: Your doctor may prescribe topical creams or ointments containing lidocaine, steroids, or other medications to help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Pelvic Floor Therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy involves exercises and techniques to relax and strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, which can help reduce pain and improve pelvic function.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or nerve pain medications, may be prescribed to help manage chronic pain associated with vulvodynia.
- Nerve Blocks: In some cases, nerve blocks or injections of local anesthetics or steroids may be recommended to help relieve pain by temporarily blocking nerve signals in the affected area.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle modifications such as wearing loose-fitting clothing, avoiding irritants like perfumed soaps or scented products, and practicing stress-reduction techniques can help reduce vulvar discomfort and improve overall well-being.
- Alternative Therapies: Some patients find relief from complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, biofeedback, or dietary supplements, although more research is needed to determine their effectiveness for vulvodynia.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
