Detect and locate infections accurately with the white blood cell (WBC) scan, a cutting-edge diagnostic tool used worldwide. Consider trusted medical expertise and state-of-the-art technology with treatment in Germany.
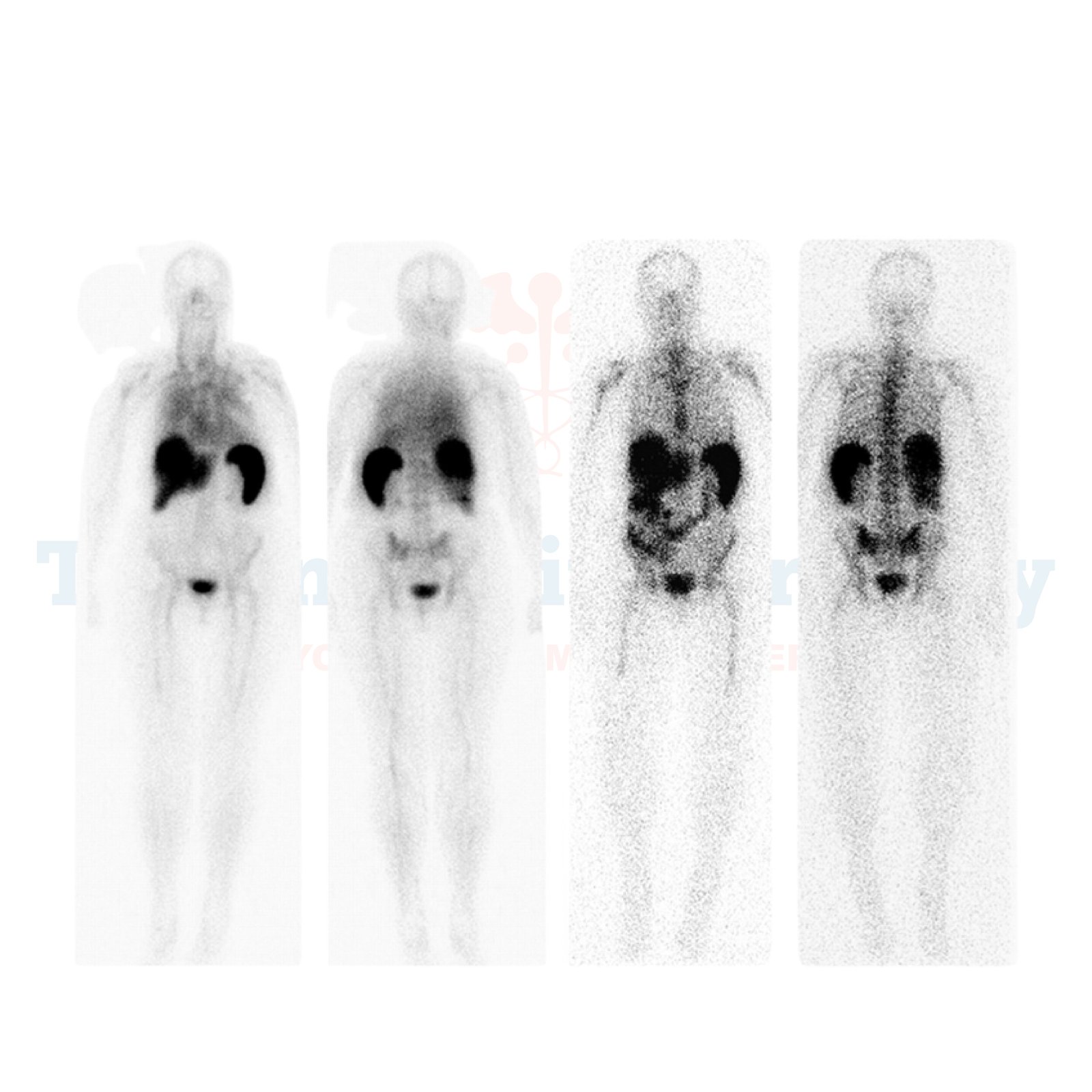
A white blood cell (WBC) scan, also referred to as a tagged WBC scan or an indium-111 WBC scan, is a specialized imaging test used to identify hidden infections or abscesses in the body. By tagging your white blood cells with a small amount of radioactive material, doctors can pinpoint areas of infection with exceptional precision, visualizing where your immune system is focusing its efforts.
Uses of White Blood Cell (WBC) Scans
White blood cell (WBC) scans are essential diagnostic tools often employed in complex medical cases. They help detect infections that may be challenging to locate through other methods. Below are some common uses of WBC scans.
How the White Blood Cell (WBC) Scan Works
A White Blood Cell (WBC) scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that helps identify areas of infection or inflammation in the body. The WBC scan follows a simple but effective process:
Benefits of White Blood Cell (WBC) Scans
By providing precise imaging of areas where white blood cells accumulate, these scans help healthcare providers identify underlying conditions and guide appropriate treatment plans. Below are some key benefits of WBC scans:
Side Effects of White Blood Cell (WBC) Scans
Like all medical procedures, WBC scans carry some potential but minimal risks:
Why Choose Treatment in Germany for a WBC Scan?
Germany is widely recognized as a global leader in healthcare for good reason:
Advanced Medical Technology
Germany offers cutting-edge diagnostic tools and world-class imaging technology, ensuring unparalleled precision.
Expert Medical Professionals
German hospitals and clinics ensure you'll be treated by specialists with years of experience in diagnostic imaging and infection management.
Comprehensive Care
Facilities in Germany are known for their patient-first approach, providing comprehensive care—from diagnosis to follow-ups.
Cost-Effective Treatment
Patients seeking treatment in Germany often find it to be a high-value investment in their health, combining affordability with top-tier medical care.
Conclusion
White blood cell (WBC) scans are a vital diagnostic tool for identifying and managing infections and inflammatory conditions. With minimal risks and accurate results, a WBC scan offers both patients and physicians clarity in treatment planning. With state-of-the-art imaging technology, highly skilled experts, and a patient-focused approach, Germany provides an ideal environment for precise diagnostics and superior care. This combination of advanced medical practices and comprehensive care makes Germany a trusted destination for health diagnostics, guaranteeing peace of mind and top-tier results for international patients.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
