What is Yersinia enterocolitica Infection?
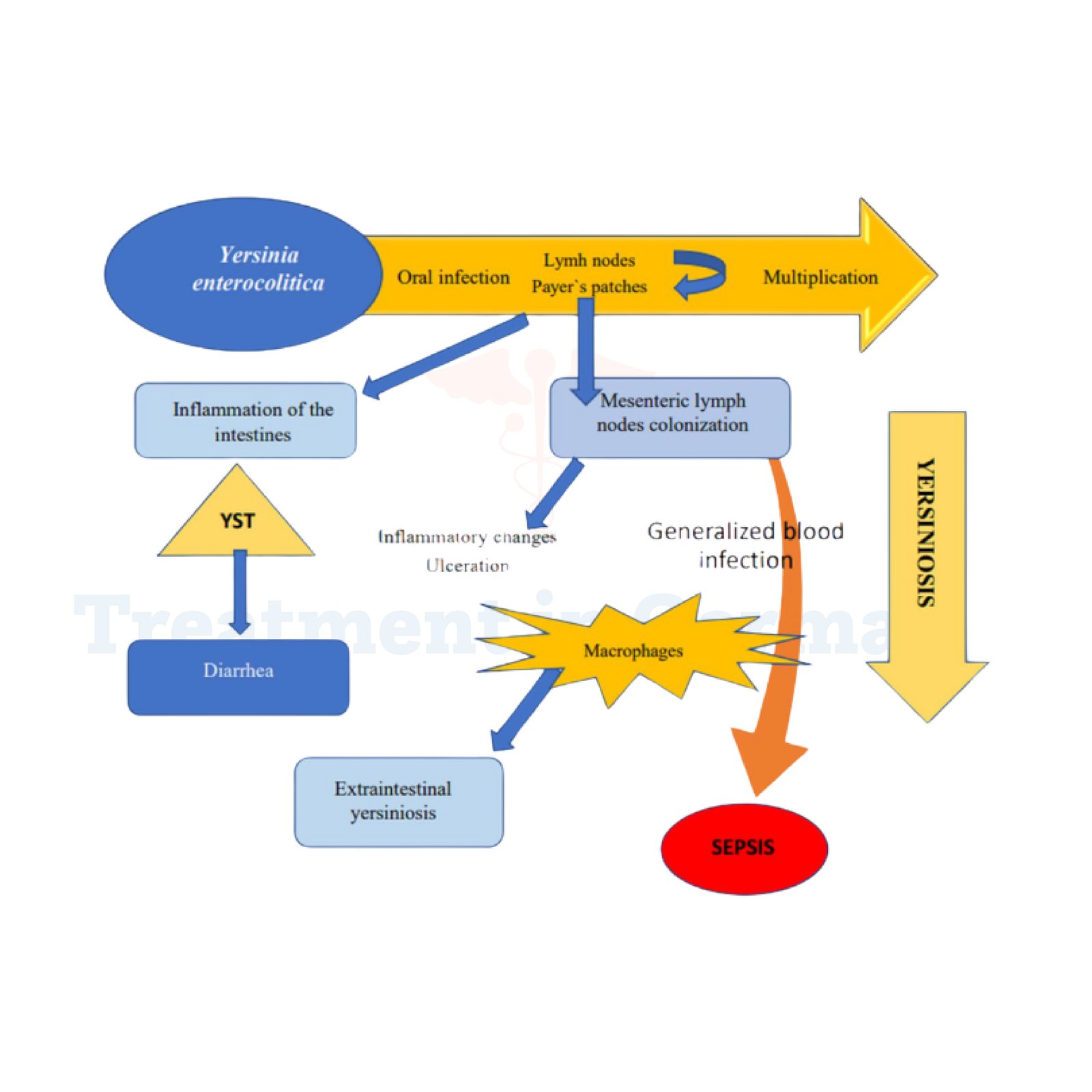
Yersinia enterocolitica is a type of bacteria that causes a gastrointestinal illness known as yersiniosis. This infection often manifests as abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, and sometimes vomiting.
While many cases are mild and resolve on their own, severe infections can occur, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
In rare, severe cases, the infection may lead to complications that require surgical intervention to address issues such as intestinal perforation or severe abscesses.
Side Effects of Yersinia enterocolitica Infection
The primary symptoms of Yersinia enterocolitica infection include:
In severe instances, complications can arise such as:
These severe complications may necessitate surgical procedures to manage or rectify the damage caused by the infection.
How is Yersinia enterocolitica Infection Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a Yersinia enterocolitica infection typically involves:
A combination of these diagnostic tools helps determine the presence and severity of the infection and any potential need for surgical intervention.
Potential Treatment for Yersinia enterocolitica Infection
Treatment for Yersinia enterocolitica infection varies based on the severity of the case:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
