Cholestasis, defined as the disease that affects bile channels, prevents the normal transport of bile out of the liver into the gallbladder or small intestine. Bile is crucial for food fat digestion and the elimination of waste by-products such as bilirubin. If the biliary obstruction is not dealt with, then one is likely to develop such complications as infection, liver failure, and malnutrition.
Germany has a well-developed medical industry, and it centers on promising diagnostic and treatment methods for biliary obstruction, which can provide patients with hope and good medical care in treating diseases.
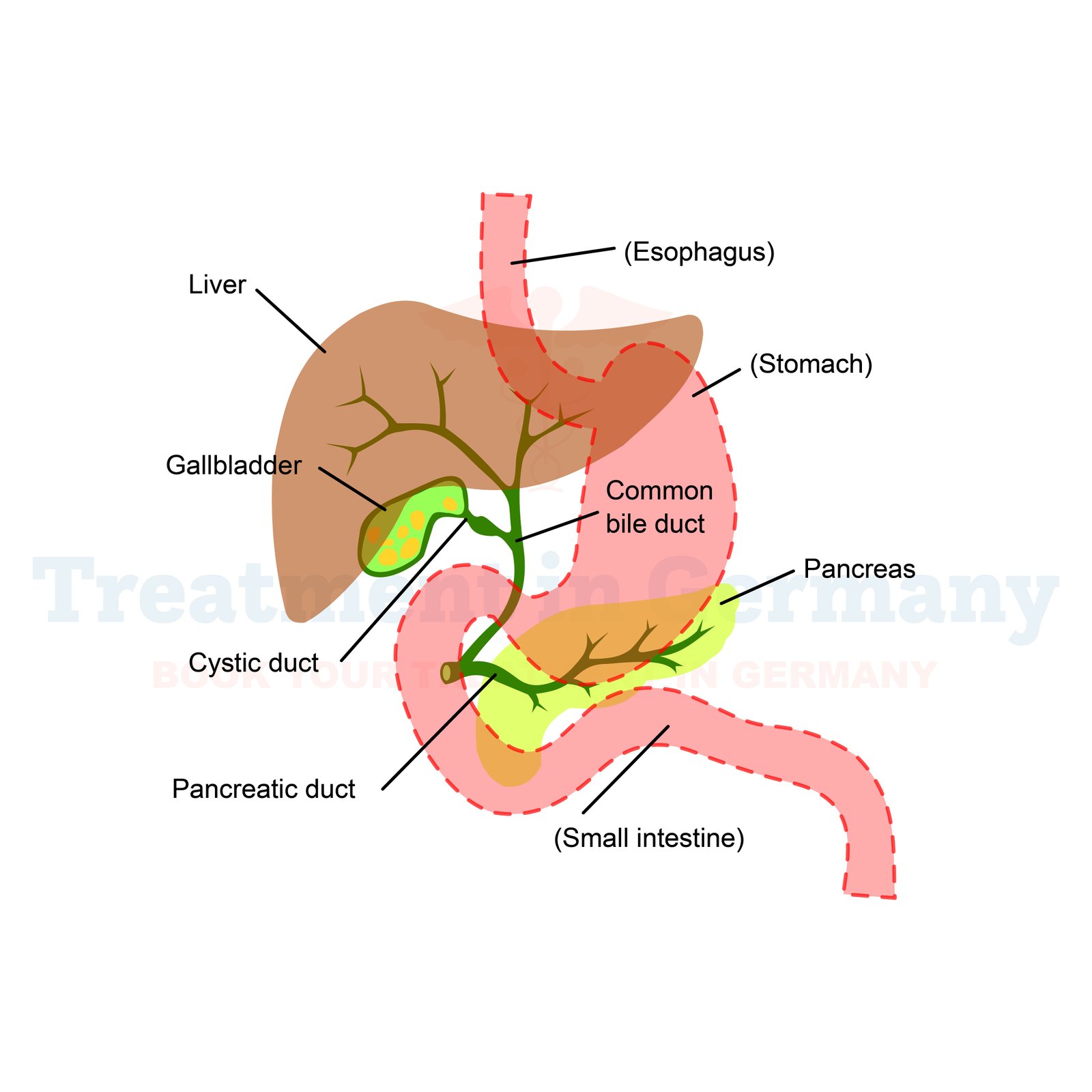
Biliary obstruction is a condition where there is partial or complete blockage of the bile ducts that carry bile, which is a product of the liver to the gall bladder and small intestine. This condition is a temporary stoppage of bile, and bile begins to puddle within the liver. It accumulates, which causes jaundice, delayed digestion, and many other system effects.
How common is It?
Obstructive jaundice occurs frequently, and the major cause worldwide is gallstones. It is universal, as anyone can get it; however, specific congenital diseases and lifestyles predispose someone to get the flu.
The causes of biliary obstruction are as follows:
Gallstones and Bile Duct Strictures
Cholelithiasis or the presence of stones in the common bile duct is an obstructive pathology commonly attributed to the formation of gallstones. These stones are not only dangerous, but they can sometimes fill the ducts, hence paving the way for bile to accumulate. Moreover, primary bile duct structures are due to scarring and surgery.
Congenital Anomalies and Hereditary Diseases
Some children develop diseases such as biliary atresia or Alagille syndrome in which bile ducts are either malformed or congenitally narrowed and get blocked. Such conditions may warrant either surgical treatment or other forms of radical therapy.
Cancer and Inflammation
Obstruction of the ducts may be due to tumors in the bile ducts, pancreas, or liver; bile duct cancer, pancreatic cancer, or metastatic cancer. There is also chronic active hepatitis from autoimmune pancreatitis and biliary cholangitis.
Symptoms of Biliary Obstruction
Biliary obstruction manifests through several symptoms, often worsening if left untreated:
Diagnosis of Biliary Obstruction
The diagnosis of biliary obstructionare as follows:
Clinical Evaluation
A physical examination is used in diagnosis to check for signs of blood jaundice and tenderness in the abdomen, among others. Risk factors are apparent in past medical complaints, particularly history of gallstones or operations.
Blood Tests
Imaging Studies
Treatment Options for Biliary Obstruction in Germany
A minimally invasive diagnostic approach and standard treatments for biliary obstruction are available at Germany's healthcare best facilities.
Surgical And Endoscopic Procedures
Cancer-Specific Treatments
Germany has specialized in cancers associated with biliary obstruction. They include accurate surgeries, chemotherapy, and several sorts of radiation therapy. Correct targeting is achievable due to the use of advanced imaging techniques that in turn improve the results.
Preventing Biliary Obstruction
While not all cases of biliary obstruction can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as:
Prognosis and Outlook
The general outcome of treating biliary obstruction depends more so on the initial cause and the time that the patient is diagnosed with the condition. Germany has modern diagnostic facilities, and advanced treatments dramatically enhance the results.
But simple cases for example, after ERCP, the majority of the patients are cured of their condition, but for other complex cases like cancer-related obstructions, the patients must continue to be managed. Failure to seek treatment for the obstruction can cause the following life-threatening complications liver failure, malnutrition, and severe infections.
What are the features of biliary obstruction?
Signs and symptoms include yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark-colored urine, upper abdominal pain and tiredness.
How is biliary obstruction diagnosed?
It is diagnosed through clinical assessment, biochemical tests, MRCP, CT and HIDA scans.
What therapies are utilizable in Germany?
The sophisticated treatments in Germany include endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, cholecystectomy, and radiation therapy in cases of biliary obstructive pathology and their complications.
Does it mean that biliary obstruction can be prevented by changing certain life styles?
Indeed, many aspects, like a healthy diet, exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol, contribute to a low risk of gallstones, which are the commonest cause of obstruction.
Is biliary obstruction lethal?
If not controlled or treated, cause other complications such as liver failure and infections. You need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
