Bone scintigraphy (bone scan) is the most basic diagnostic and monitoring tool for many bone-related conditions. Since they are the most non-invasive tests, they can check whether there is cancer, a fractured bone, infection, or unexplained pain in patients.
Advanced medical structures characterize Germany, which also includes innovative bone scan treatment solutions that provide accurate diagnoses, paving the way to appropriate treatment.
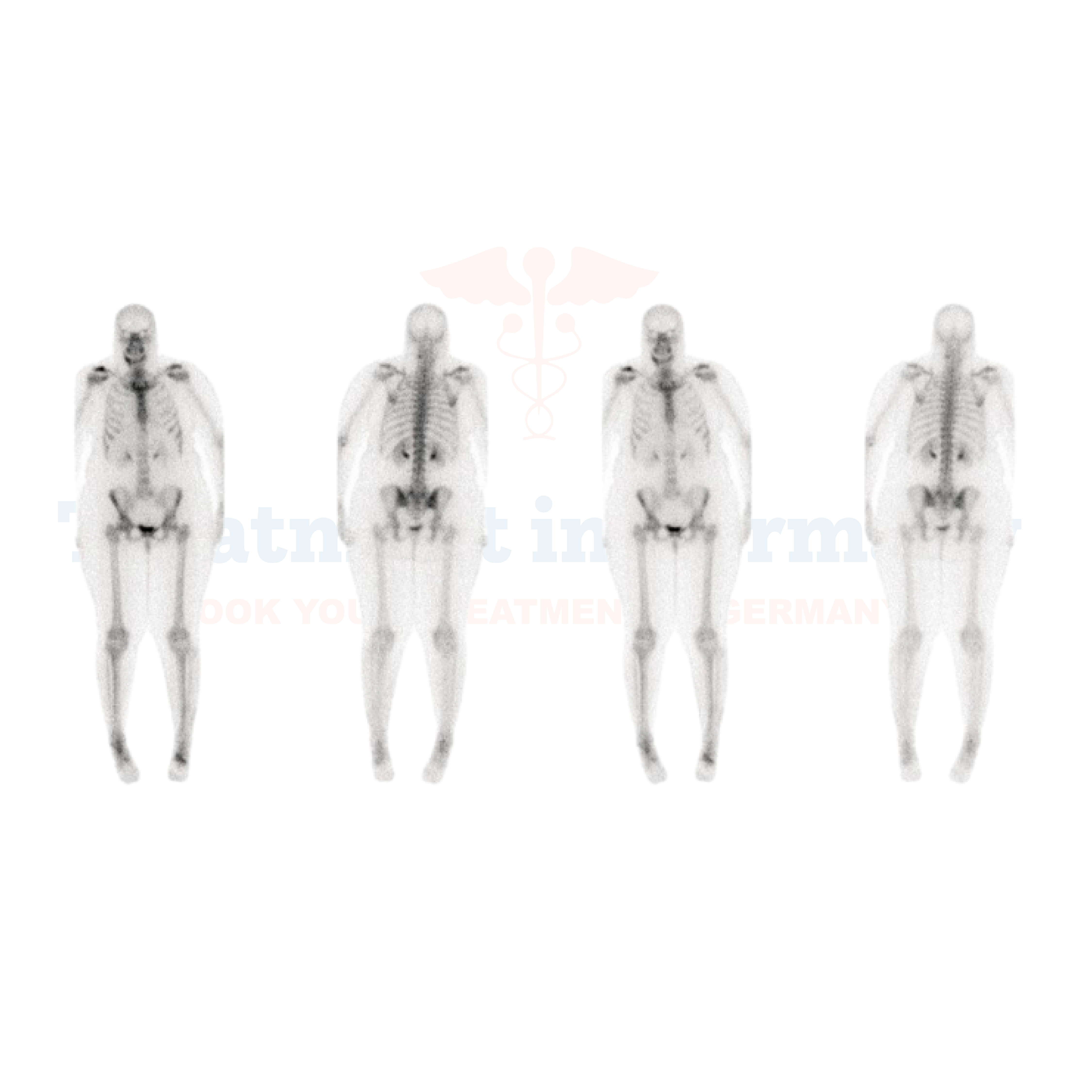
What is a Whole-Body Bone Scan?
Whole Body Bone Scan, also known as bone scintigraphy, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses a radiotracer to detect abnormal bone cell accumulation. The radiotracer accumulates in areas containing abnormal cells and thus serves as a potential indicator for problems.
Types of Bone Scans
Bone scans differ based on the variety of imaging techniques and different diagnostic purposes. Here is the list of the common types of bone scans.
Whole-Body Bone Scan
This helps to assess the whole skeleton for abnormalities. It is one of the recommended scans, which are used in order to diagnose metastatic cancer that has spread to bones, to determine the stages of cancer, or just to evaluate widespread bone disorders, such as Paget's disease (osteitis deformans) and fibrous dysplasia.
Three-Phase Bone Scan
A three-phase bone scan is an advanced technique in which images are captured at three different stages following the injection of the radiotracer:
This scan is extremely helpful in the detection of infections such as osteomyelitis, where it studies unexplained bone pain and locates degenerative foci in bones.
SPECT Bone Scan
A SPECT bone scan is a highly technical method because it combines bone scintigraphy with 3D imaging. It results in better, three-dimensional views of the bone. It will be especially advantageous in a case where there could be some abnormalities or lesions too deep in the bones for normal bone scans to identify in proper detail.
The technique is, therefore, used in various cases where bone would be evaluated in detail to make an accurate estimation of the extent of fractures, infections of bone, or other bone-specific cancers.
DEXA Scan (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry)
While not specifically a nuclear bone scan, the DEXA is sometimes considered in a separate category of bone imaging diagnostics. It evaluates osteoporosis by establishing the amount of bone loss or fragility that causes the fracture danger.
While the radiotracers of other forms of nuclear bone scans, this DEXA makes use of X-rays. Overall, this scan brings essential evidence to observe how much loss of bone will be there and whether that treatment for osteoporosis succeeded or not.
PET Bone Scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
PET scans can be combined with CT or MRI for more detailed imaging. PET bone scans use radiotracers that localize in metabolically active bone tissue, which helps spot abnormal cells in cases of bone cancer or metastasized cancers. The PET bone scan is particularly good at mapping cancerous growths and tracking how the treatment is going.
Why Do I Need a Bone Scan?
Indicated a bone scan for the following reasons:
Help patients suffering from any kind of metallic implant, dental implant, or pacemaker.
How Does a Bone Scan Work?
A bone scan is the process of administering a radiotracer, which is taken up by bones with heightened metabolic activity. Any bruises or fractures will show as "hot spots" on the scan.
Preparing for the Bone Scan
Patients typically do not need special preparation before the procedure is administered. However, the individual should inform the provider about any recent barium or DEXA scans done to avoid interference with the results of the scan.
Steps of Procedure for Bone Scan in Germany
Risks and Side Effects of Bone Scan
Although the bone scan requires radioactive material, the amount is minimal and is rarely dangerous to most patients. Some minor side effects could be bruising at the injection site.
Advanced Technology and Innovation Treatment in Germany
Germany has always established novel treatments in medical imaging. The country integrates new concepts in nuclear medicine to ensure accurate and safe diagnoses for bones. Patients who travel from other parts of the world to receive treatment from Germany have the benefit of bringing state of the art machinery with the best service providers at the clinics, which specialize strictly in accuracy with minimal intervention diagnostics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to do a bone scan in Germany?
This captures for about 30 to 60 minutes. Some other time is utilized as radiotracers circulate.
What are the precautions that I take when the patient has an implant-like dental implant and a pacemaker and can be given a bone scan?
Yes, it is safe because prior to informing the physician and according to his medical report, adjustments will be made regarding that implant by that physician.
How might the following diseases be diagnosed based on a bone scan?
A bone scan diagnoses avascular necrosis, osteoarthritis, infection within a bone, and any malignancy metastases.
Can a bone scan detect bone cancer?
Yes, a bone scan can point out abnormal cells that possibly indicate bone cancer or other malignancies.
What are the risks associated with a bone scan?
The amount of radiation exposure is typically minimal, and for most people, it is safe; however, pregnant or nursing individuals should consult their provider.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
