Germany is very famous all over the world for its well-developed medical service and especially for the intervention of hemorrhages in the brain. This is a life-threatening disease that is caused by hemorrhage in or around the brain and warrants emergency treatment.
Hospitals in Germany are equipped with the latest technology and perform state-of-the-art techniques in the management of the hospitals, hence enhancing survival, morbidity, and mortality in patients.
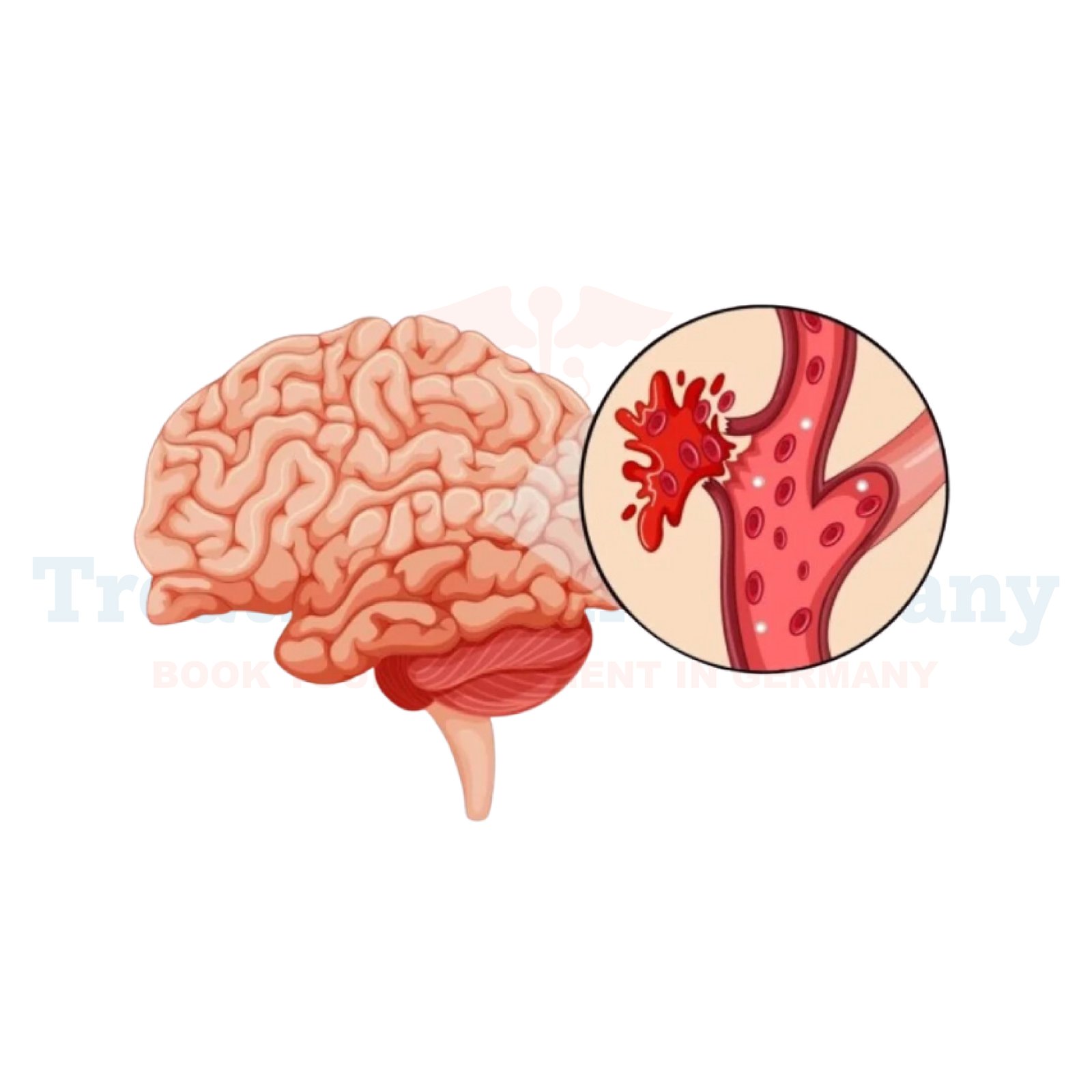
A brain hemorrhage, referred to as an intracranial hemorrhage, is a serious illness brought on by the rupture or leakage of blood vessels in the brain. This type of stroke results in blood collecting in or around the brain, putting pressure on cells and depriving them of oxygen and nutrients. If the situation is left unaddressed, it is possible to receive bad news of an accident, which is devastating.
How Brain Hemorrhages Occur
The human brain relies on a network of blood vessels to deliver nutrients and oxygen to one’s body. A trauma, high blood pressure, or conditions such as arteriovenous malformation may compromise the vessel walls and make them pop. Any hemorrhage that occurs within the confines of the skull is dangerous and calls for immediate medical intervention if ever there is one.
Types of Brain Hemorrhages
It’s important to know whether a hemorrhage happened due to a rupture of a cerebral vessel and where exactly this happened.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
There are several usual causes and risk elements of this condition. Some of their causes and risk factors are as follows:
Symptoms of a Brain Hemorrhage
Hemorrhagic stroke may present with one or multiple focal neurological signs or non-specific symptoms and can develop as a sudden onset or over several hours depending on the extent of the bleeding. Among the most typical symptoms are:
Nausea and vomiting.
Modern Diagnostic Methods of Brain Hemorrhage In Germany
Germany’s hospitals have advanced diagnostics to timely and adequately assess brain hemorrhages.
Initial Evaluations
The physical examination follows, and the neurological examination, includes reflexes, speech, and motor standard tests.
Imaging Tests
The imaging tests of the brain hemorrhage are as follows:
Treatment Options for Brain Hemorrhage in Germany
Hospitals provide comprehensive and state-of-the-art medical care to the patient and especially focus on the kind of treatment the patients need.
Medications
Depending on the diagnosis, doctors may prescribe:
Surgical Interventions
Supportive Care
In severe cases, patients may require:
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Low vision rehabilitation is important in improving the function of lost vision and also in avoiding other related complications. German healthcare facilities provide tailored programs, including:
Risk Factors for Prevention
To reduce the risk of recurrence, patients are encouraged to:
Why choose Germany for the treatment of brain hemorrhage?
Germany boasts one of the best medical systems in the world that provides specialized treatment for a brain hemorrhage condition. The cooks employ state-of-the-art technology that includes imaging and minimally invasive surgery to produce good results often in hospitals across the country.
Prevention Strategies
Why is Germany considered one of the best places to seek treatment for a brain hemorrhage?
The available techniques and experienced doctors of Germany focus on fast and accurate diagnosis and an individual approach to every patient.
What exactly are brain hemorrhages, and are they preventable?
However, not all intraoperative bleeding sources are preventable, but maintaining targeted blood pressure, avoiding anticoagulants, and adopting a healthy lifestyle will minimize it.
How does one recover from a brain hemorrhage?
It entails treatment including speaking, walking, eating, or moving exercises, besides adjusting one’s daily practices to decrease the possibility of relapse.
Which symptoms indicate a brain hemorrhage?
The warning signs are surely headache, dizziness, and vision changes, which may appear suddenly. In severe situations, it may cause a seizure or a possible loss of consciousness.
What are brain hemorrhages, and what are the primary causes of this condition?
Some of the most prevalent ones are traumatic, cerebral aneurysm, or atherosclerosis cases.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
