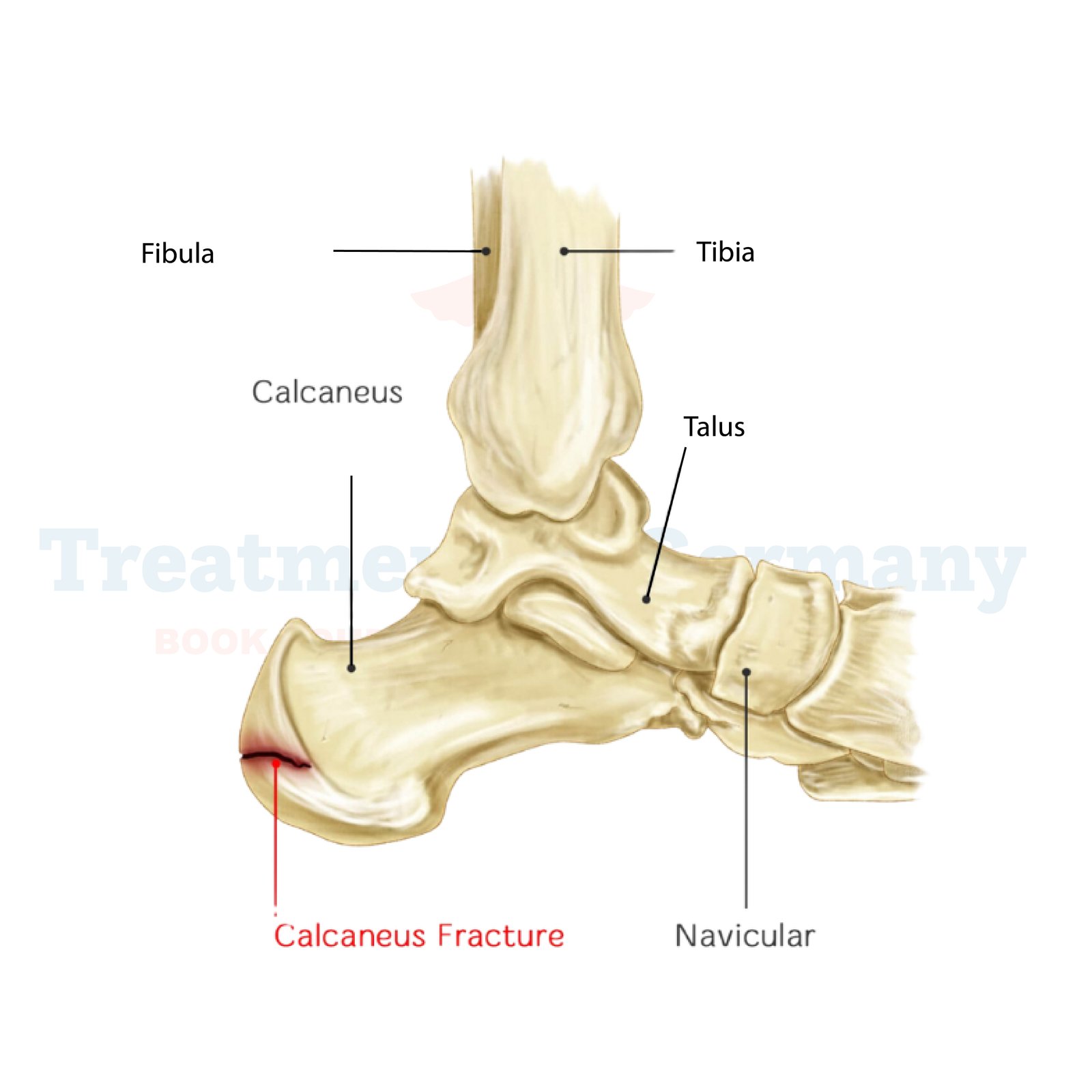
What is Calcaneal Fractures?
Calcaneal fractures, also known as heel fractures, occur when there is a break in the heel bone, which is the largest bone in the foot. These fractures are often the result of high-impact injuries, such as falls from heights or car accidents.
They can vary in severity from small cracks to complete breaks, and they may affect the shape and function of the foot.
Side effects of Calcaneal Fractures:
Calcaneal fractures can lead to several side effects, including severe pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot. Some patients may also experience deformity of the heel or difficulty walking normally.
In severe cases, complications such as nerve or blood vessel damage may occur, which can affect sensation and circulation in the foot.
How is Calcaneal Fractures diagnosed?
To Diagnose a Calcaneal Fracture, a healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination and order imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans. These tests help determine the location and severity of the fracture, as well as any associated injuries to nearby structures in the foot.
Potential treatments of Calcaneal Fractures:
The treatment of calcaneal fractures depends on various factors, including the severity of the fracture, the patient's overall health, and their activity level. In some cases, non-surgical approaches such as immobilization with a cast or boot, rest, and pain management may be sufficient for healing. However, for more severe fractures or those with complications, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Surgical options for calcaneal fractures may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
