Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) is an invalidating ocular vascular disorder that threatens vision. Germany is the most famous destination for the diagnosis and treatment of CRVO, having high medical technologies, skilled ophthalmologists, and tailored patient care. We provide detailed insight into the CRVO treatments in Germany and describe diagnostic methods and therapies.
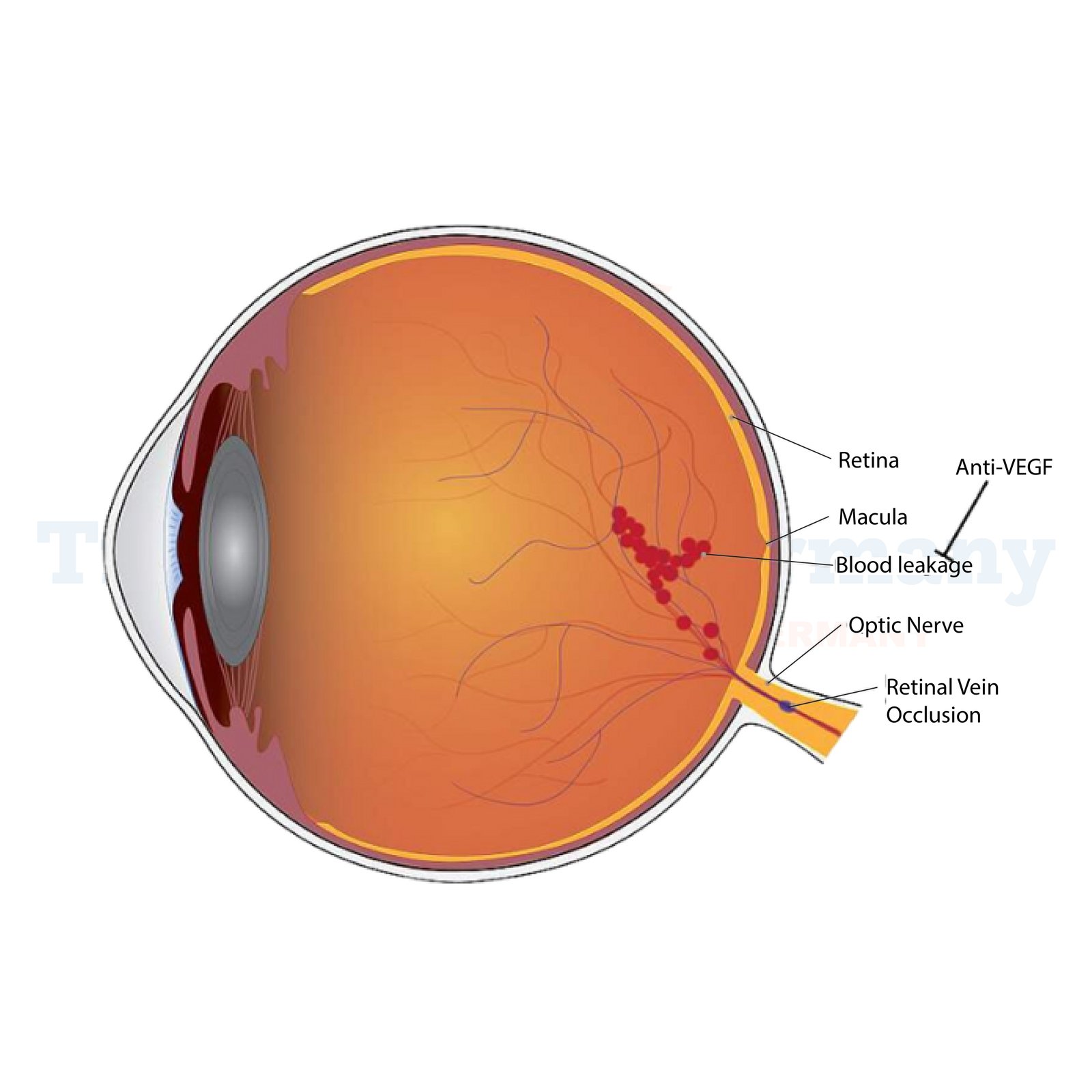
CRVO happens when there is blockage of the central retinal vein, through a clot or other different vascular problems. This blockage causes fluids and blood into the retina and lowers oxygen supply, leading to swelling of the cells. If not treated, CRVO has the potential of progressively eroding the quality and functions of vision.
Types of CRVO
The types of Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) are as follows:
Non-Ischemic CRVO
This type is usually less severe and is expressed as blood clot blockage that is partial, hence allowing the flow of blood. Symptoms are often mild for this type of pneumonia, and individuals who seek medical care have a good outcome.
Ischemic CRVO
Ischemic CRVO is a severe form of the condition that decreases or stops blood flow to the retina's blood vessels.
Why choose Germany for the treatment of CRVO?
Germany has one of the most effective treatments and diagnostics of CRVO in the world. Patients benefit from:
Diagnostic Methods in Germany
Germany has several leading-edge diagnostic procedures to facilitate proper detection and assessment of CRVO.
Comprehensive Eye Examination
The diagnostic process starts with a comprehensive eye checkup to determine the state of vision and retinal pictures of the rods and cones.
Fluorescein Angiography
The intraocular injection of a dye that circulates in the body’s bloodstream and the retina blood flow mapping can establish areas of blockage as well as oxygen deprivation.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography gives cross-sectional pictures of high resolution of the retina to assess the accumulation of swelling due to CRVO.
Treatment options for CRVO in Germany
Germany provides a range of treatments meant to regulate the illness and stop complications.
Anti-VEGF Injections
Current therapeutic options for maculars associated with CRVO are anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections, including Eylea and Lucentis.
Steroid Injections
A steroid is employed for clients who do not actively improve with anti-VEGF treatment.
Laser Therapy (Panretinal Photocoagulation)
Panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) is applied to ischemic CRVO due to the absence of adequate oxygen supply to the area.
Risk Factor Management
In Germany, patient care focuses on the prevention of complications that may arise due to recurrent CRVO, requiring aggressive treatment of associated diseases like hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia.
Best Hospitals for CRVO treatment in Germany
The best hospitals for CRVO treatment in Germany are as follows:
Follow-up care is an essential means of assessing and modifying treatments. Germany’s facilities are equipped with quality aftercare services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there options for CRVO treatment for patients coming from other countries to Germany?
Yes, Germany’s hospitals are ready to welcome and treat foreigners; starting with doctors and nurses and ending with coordinators, they speak different languages.
In Germany, what success rates apply for CRVO treatments?
Germany boasts excellent success rates, especially with anti-VEGF injections and laser treatment, therefore guaranteeing most patients better vision.
Are the costs covered by insurance?
Most of the international insurance plans avail the treatment of CRVO in Germany. Check with your provider before treatment because they may give different advice.
What is the duration of the recovery after CRVO while receiving treatment?
Recovery periods are different; injections do not demand any time off, but surgeries at least can take one to two weeks.
How may the recurrence of CRVO be avoided?
Optimal control of diabetes and hypertension by adopting a healthy lifestyle and periodic check- ups constitutes an important way of avoiding reoccurrence.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
