Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)is a lung disease that becomes worse, characterized by increased breathing difficulty. It includes diseases like emphysema or chronic bronchitis and develops from chronic offending gas or particulate matter. A large number of innovative treatment designs for COPD patients and the best doctors are available in Germany, and most of them enhance the effective quality of life of the patients.
This article focuses on the signs and signs, etiology, diagnosis, and new approaches to treating COPD in Germany.
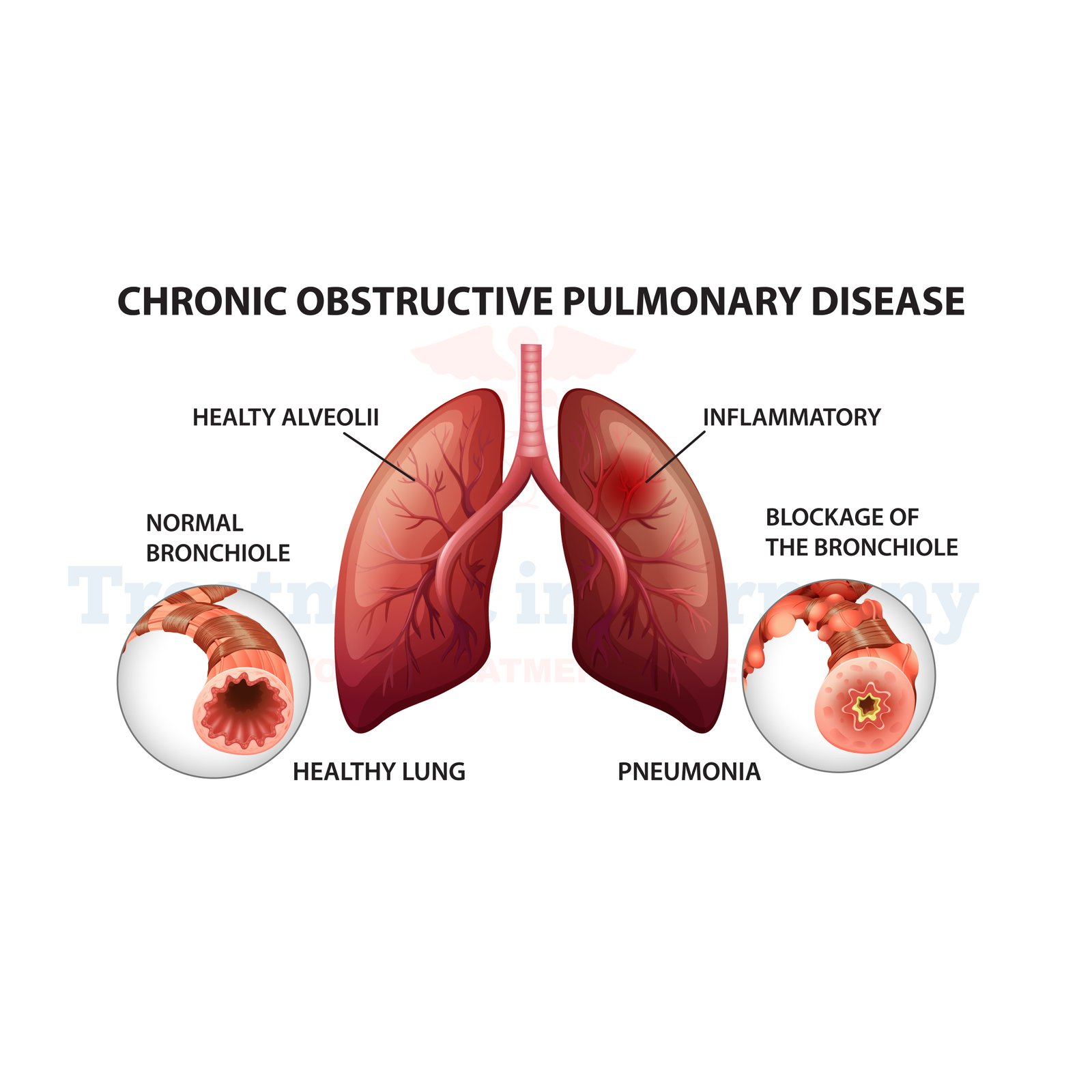
COPD is a term that covers emphysema or chronic bronchitis, conditions that cause difficulties in breathing. It comprises inflammation of the respiratory tract, alveolar injury, and production of tenacious sputum. This results in manifestations like wheezing, dyspnea or short breath, cough, and abnormal respiratory sounds.
Causes of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
The following are the causes of COPD:
Complications of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD can lead to severe complications, including:
Symptoms of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
The hallmark symptoms include:
Diagnosis of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Germany
Germany’s healthcare facilities diagnose COPD using sophisticated techniques to diagnose COPD early enough.
Diagnostic Procedures
Treatment options of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Germany
Germany is on the leading edge of COPD treatment, utilizing both traditional and innovative approaches. Currently, there is no cure for COPD; however, treatment is formulated to decrease patients’ symptoms and halt the condition’s progression.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Surgical Treatments
The following are the surgical treatments:
Preventive Measures for COPD
In the case of preventive measures, efforts are made in order not to aggravate the severity and not to develop high-risk factors.
New Models of COPD Management in Germany
This paper examines how Germany is applying innovation in treating COPD through modern treatments and technologies.
Daily Management
Frequently Asked Questions
How is COPD classified, and what are the main subtypes?
Tobacco is the biggest killer, but second-hand smoke and irritants play a significant part as well.
Can COPD be cured in Germany?
There is no known cure for this type of COPD, but in Germany, treatment options are applicable towards diminishing symptoms and increasing the quality of the lungs.
What new therapies are out there in Germany?
We have identified that Germany performs value-added procedures, has world-class rehabilitation and has access to the most research activities.
Do patients with COPD need to be vaccinated?
So then, immunization against flu, COVID-19, or pneumonia decreases one’s chances of getting the disease.
How does Germany overcome barriers to early diagnosis of COPD?
Preventive methods range from spirometry, computed tomography (CT), to even genetic tests to confirm the disease.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
