Deep vein thrombosis is a serious complication due to thrombus formation in the deep veins, frequently in the lower limbs. Germany is one of the leading medical innovators with outstanding medical technologies that are applied to treat DVT. This article highlights various aspects of DVT in Germany, including causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, risk reduction, and life management.
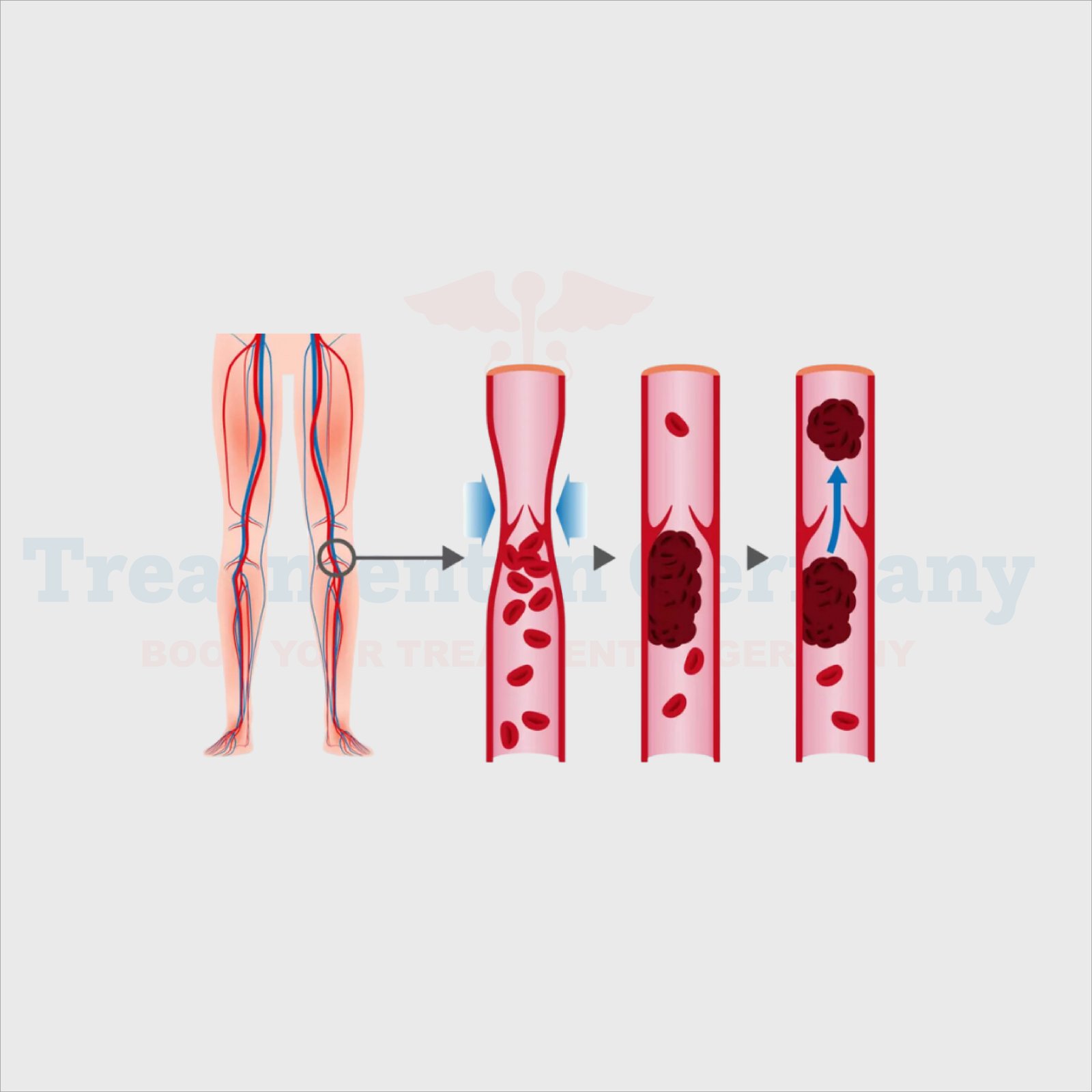
DVT develops when blood circulation is reduced, or blood vessels of the limbs are compromised, and blood clots start to form and thicken further. However, clots often form in the legs and can also occur in the pelvis, arms, and other deep veins throughout the body.
The risk of DVT is when the clots formed develop into severe complications like pulmonary embolism, where a clot goes to the lungs and threatens the supply of blood.
Symptoms of Deep vein thrombosis
All individuals not with DVT exhibit symptoms, but when they do, common signs include:
In some instances, the first clue to DVT is a pulmonary embolism sudden breathing difficulties, chest pains, or cough that produces blood.
Primary Causes of Deep vein thrombosis
The formation of blood clots can result from several factors, including:
Contributing Risk Factors
The following health and lifestyle factors raise the risk of DVT:
Diagnostic of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in Germany
Germany is renowned for its precision in diagnosing DVT using advanced techniques.
Duplex Venous Ultrasound
This is a less invasive imaging method that sends sound waves through the body tissue to discern the formation of clots and to estimate the conditions of blood circulation. It is the first choice of investigation in diagnosing DVT.
MRI and CT Scans
MRI also creates better images of the veins, specifically with clots in difficult scenarios. Computed tomography scans are invaluable while diagnosing clots in the pulmonary or abdominal veins critical in diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
Venography
While not very common, venography involves putting a contrast dye into the veins that can help pinpoint the location of a blood clot.
Medications
These drugs do not lyse existing clots but permit the kidney to lyse them.
Surgical and Mechanical Interventions
Minimal Invasive Procedures
Hospitals in Germany focus on using trends in catheter techniques for removing extensive or unrelenting clots to reduce downtime and danger.
Preventive Strategies
After initial treatment, the focus shifts to preventing recurrence:
Lifestyle Modifications
German healthcare emphasizes holistic care, encouraging patients to adopt healthier habits such as:
Why Choose Germany for DVT Treatment?
Germany has something special as it pays much attention to the innovativeness of the medical care delivery system. Its hospitals are well endowed with modern equipment as well as experienced health personnel who practice patient-oriented care. Other techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, as well as other minimally invasive procedures, show that German healthcare is keen to have the best return on investment for patients with DVT.
FAQs
Does COVID-19 make DVT a possibility?
Indeed, in response to an infection, COVID-19 can cause inflammation throughout the body that augments blood clot risk.
What part does warfarin play in treating DVT?
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that assists in preventing the formation of more clots and thus controls and alleviates the risks of DVT.
In other words, do compression devices work well to stop DVT?
Of course, compression garments facilitate the circulation of blood and prevent the formation of clots when worn after surgery.
What is the advantage of treating DVT in Germany?
The healthcare of Germany has the best diagnostic tools, various treatment techniques, and a careful treatment approach to DVT.
Does the genetic factor increase the risk of DVT in a person?
It is possible to argue that having certain hereditary conditions increases the probability of developing DVT.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
