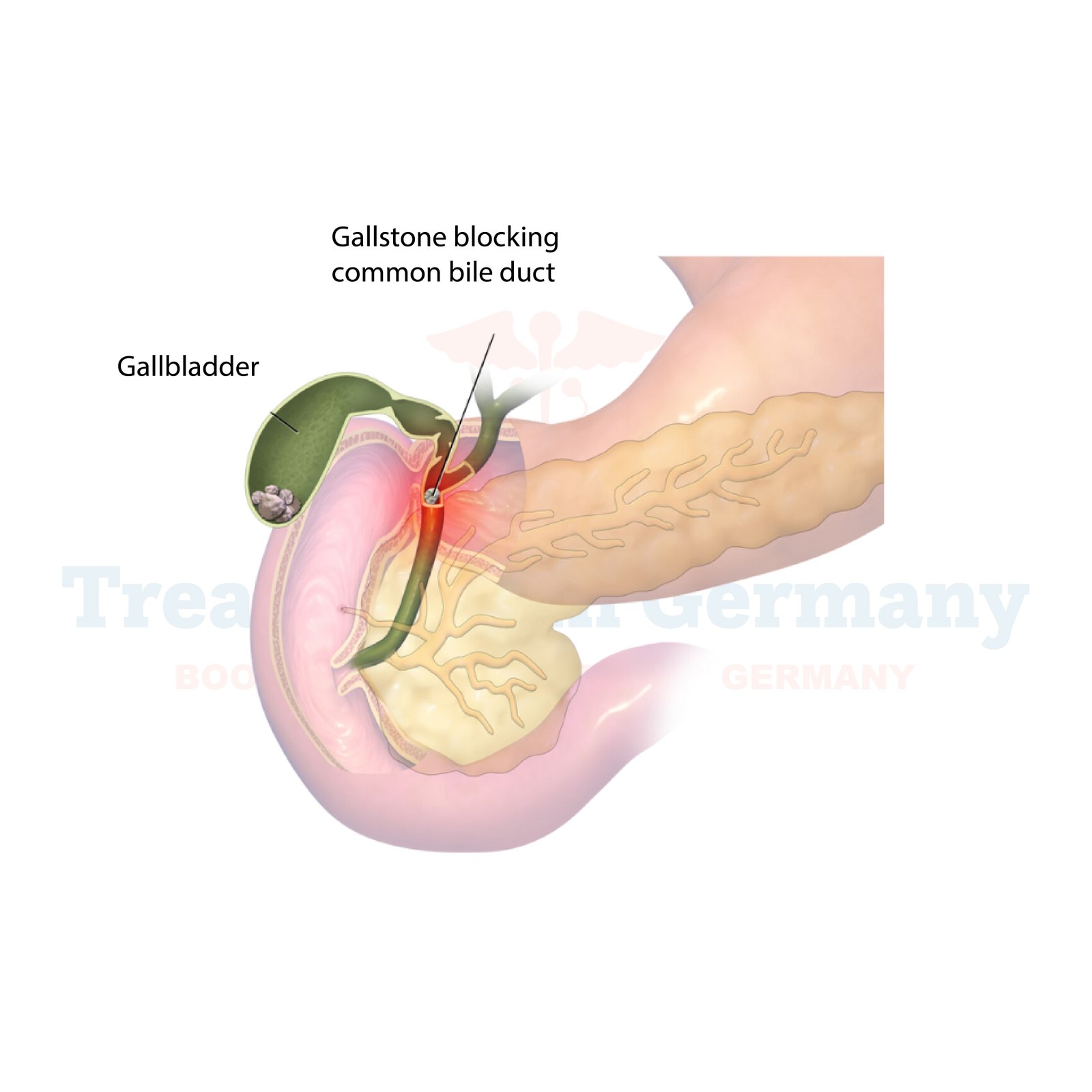
Gallstones are hardened deposits that may occur in the gallbladder transporting ducts as a result of abnormalities in the composition of bile. These stones are not rare and usually not symptomatic, but when they reside in the biliary duct, they can be a real source of pain and health issues.
Due to the advanced facilities and professional care available in Germany, innovative treatment procedures for gallstones have caught up with the reputation in the country. This article characterizes gallstones, their formation, signs, and treatment, as well as the advantages of treatment in Germany.
Gallstones are hard, morphologic formations that accumulate in the gallbladder or the bile ducts. They develop when there is more cholesterol and bilirubin of bile salts. The causes investigated are hormonal balance or imbalance as dictated by estrogen and progesterone or lack of appropriate body weight or fluctuations in the same, blood disorders, and obesity.
Types of Gallstones
Gallstones come in the following types:
Symptoms of Gallstones
A large number of gallstone sufferers show no symptoms.
However, they can cause pathophysiological manifestations in the biliary tract such as pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and biliary colic if they are stenosis.
Recognizing Gallstone Pain
Complications of Gallstones
Gallstones can cause serious health problems, such as:
Diagnosing Gallstones
Diagnosis forms the basis of treatment, and, therefore, accurate diagnosis is important to determine the kind of treatment that the patients need. Common diagnostic methods include:
Therapies for gallstones in Germany
Available opinions regarding the treatment of gallstones in Germany present an array of treatment options using advanced technology and patient-centered care.
Surgical Treatments
Non-Surgical Treatments
Why choose Germany for gallstone treatment?
Healthcare in Germany has posted great strides in handling biliary tract conditions. Key advantages include:
Prevention of Gallstones
Preventive measures can reduce the risk of gallstone formation, such as:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs you want to look out for to diagnose gallstones?
Thus, typical manifestations include upper abdominal pain, nausea, and biliary colic, the last being usually provoked by fatty meals.
How can gallstones be diagnosed in Germany?
Hence, MRCP and abdominal ultrasound are used to diagnose the condition in Germany.
Do gallstones keep on forming, and can they cause serious problems?
Indeed, complications may be cholecystitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis, jaundice, and septicemia.
Do we need to remove the gallbladder for every case of gallstones?
Not always. Gallstones require surgery when they result in symptoms such as pain or when they create obstruction. For minor forms, drugs and life alterations are options to consider.
What makes Germany’s healthcare system unique in the case of treating gallstones?
Due to professionalism and experienced medical personnel and the equipment accompanied by surgical enhancement, Germany has perhaps the best healthcare facilities needed for patients with gallstones.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
