What is Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis):
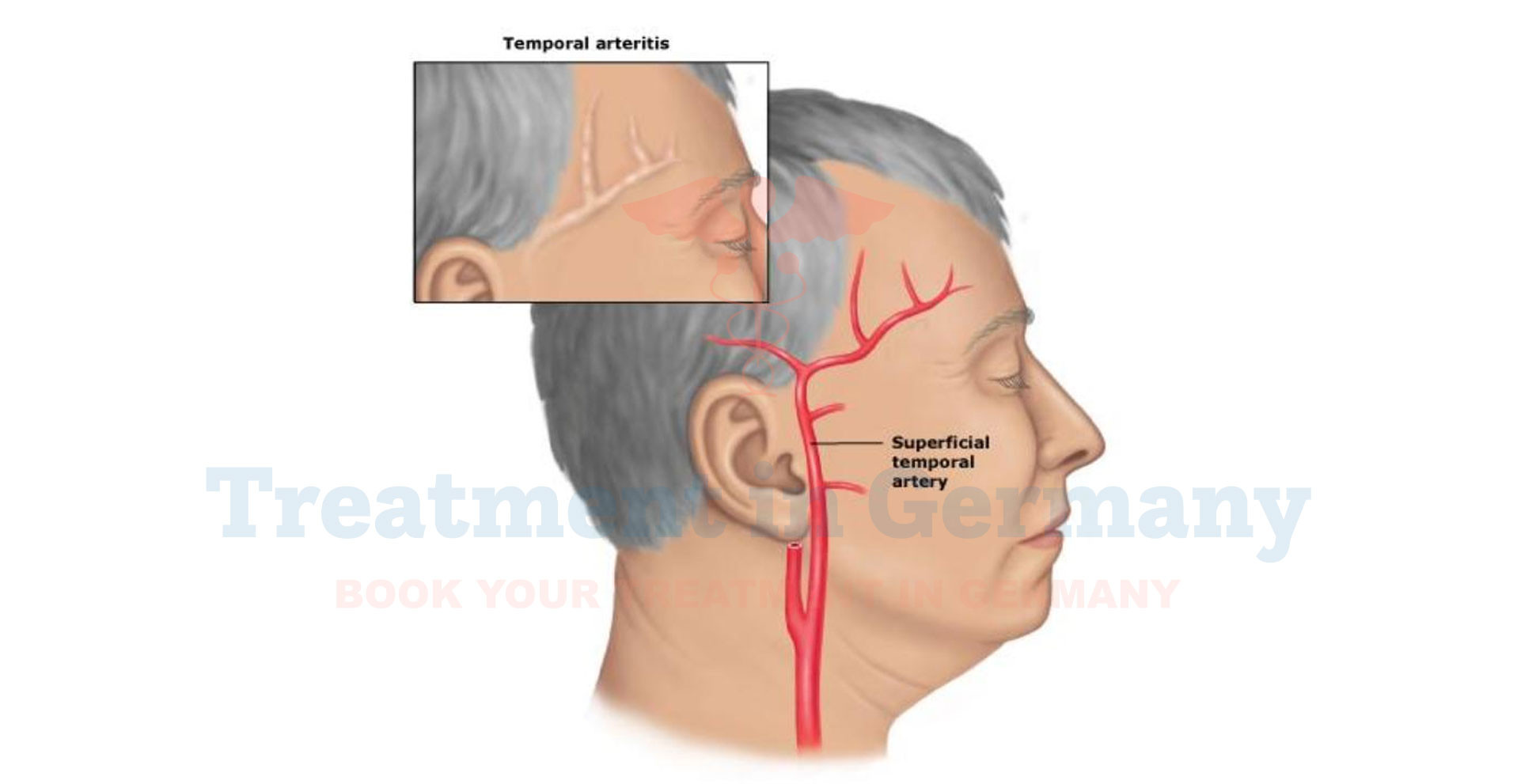
Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA), also known as Temporal Arteritis, is a type of vasculitis, a group of disorders involving inflammation of blood vessels.
In GCA, the medium and large arteries, particularly those around the temples and scalp, become inflamed.
This inflammation can lead to significant complications, including vision loss and stroke, if left untreated. GCA primarily affects individuals over the age of 50, with a higher incidence in women than men.
Side effects of Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis):
The symptoms of Giant Cell Arteritis can vary widely but commonly include:
How is Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis) diagnosed?:
Diagnosing Giant Cell Arteritis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider may:
1. Conduct a Physical Exam: Your doctor may look for signs of inflammation, such as tenderness or swelling over the temples, reduced pulse in the affected arteries, or visual changes.
2. Blood Tests: Blood tests can help detect markers of inflammation, such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
3. Imaging Tests: Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, may be used to visualize the affected arteries and assess the extent of inflammation.
4. Temporal Artery Biopsy: A biopsy of the temporal artery may be performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining the artery for characteristic inflammation.
Potential treatments of Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis):
The primary goal of treatment for GCA is to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
1. Corticosteroids: High-dose corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are the mainstay of treatment for GCA. These medications help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to significant side effects, so your doctor will work to taper the dosage gradually.
2. Immunosuppressive Therapy: In some cases, immunosuppressive medications, such as methotrexate or tocilizumab, may be prescribed alongside corticosteroids to help reduce reliance on steroids and prevent disease relapses.
3. Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your response to treatment, manage side effects, and adjust medications as needed.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco use, can help support overall health and well-being.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
