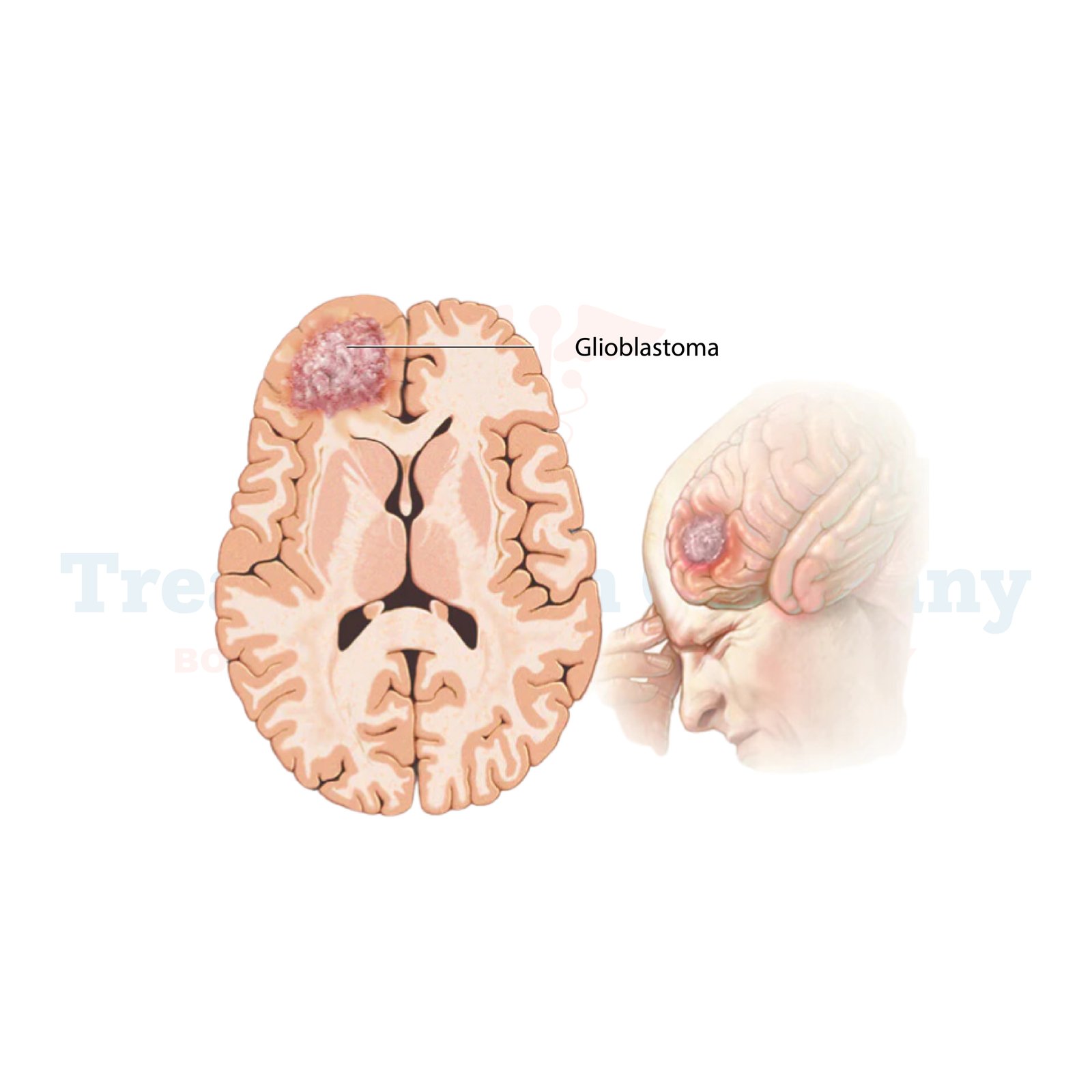
Glioblastoma, also referred to as glioblastoma multiform (GBM), is among the most invasive and challenging brain tumor types. This factor alone, together with the aggressive nature of its progression and the involvement of ostensibly ‘healthy’ brain tissue, makes GBM a difficult disease to manage, both for the patient and the clinician. Glioblastoma has been diagnosed in very early stages in Germany and it provides enhanced treatment procedures. The causes, symptoms, and therapies for glioblastoma in Germany are all explained in this article.
Glioblastoma is a subtype of glioma that is a tumor of glial cells that support the nervous system of the brain and spinal sequence. In particular, glioblastoma originates from astrocytes the multipotent cells involved in maintaining the function of neurons. These tumors are fast-growing and can easily penetrate adjacent brain tissue.
Characteristics of Glioblastoma
The glioblastoma has the following characteristics:
Glioblastoma Subtypes
The following are the subtypes of glioblastoma:
Symptoms and Causes
The following are the signs and reasons:
Symptoms of glioblastoma
Again, glioblastoma has an effect on the brain and as such, its signs and symptoms can manifest quickly. These include:
Headaches are chronic and can be worse in the morning.
Causes of Glioblastoma
The cause of glioblastoma is damage to the DNA of cells within the brain. These are usually random changes, which bring about some degree of abnormality in cell functions; cells divide in an uncontrolled manner. Factors contributing to these mutations include:
Is Glioblastoma Hereditary?
There are few inherited causes of glioblastoma. However, genetic predispositions do play a role; for instance, variations in gene profiles could lead to susceptibility—cancer-related genes for instance. Family dele and testing facilitate the evaluation of familial risks.
Diagnosis of Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma diagnosis involves a combination of advanced medical imaging and laboratory analysis, such as:
Importance of Genetic Testing
Mutations are identified to be an important cause of glioblastoma, and genetic testing is important in identifying them. The results from such tests can inform specific therapies, which would be more effective and specific.
Treatment Methods for Glioblastomas in Germany
The organization of healthcare in Germany offers or has been providing one of the most extensive and progressive frameworks for cancer treatment. For glioblastoma, mortality, and methods for its increased attempt to proceed with treatment and recovery with enhancing life expectancy and life quality.
Surgical Interventions
Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Cytotoxic medicines like temozolomide work by reaching cancer cells in blood bloodstream to eliminate or inhibit the growth of cells. It is mostly prescribed for use alongside radiation treatment.
Targeted Therapy
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are a relatively new class of drugs that inhibit only those proteins that are essential for the growth of malignant cells with a specific hereditary predisposition. Which are less toxic to the body than the traditional chemotherapy methods mentioned above.
Immunotherapy
Germany is on the leading edge of immunotherapy, which uses the body’s immune system to locate and kill glioblastoma cancer cells.
Tumor Treatment Fields (TTF)
This is a wearable technology that uses low electric current fields to interfere with the division of cancer cells and hence reduce tumor formation.
New Development in Glioblastoma Disease in Germany
Germany’s robust medical research infrastructure has led to significant advancements in glioblastoma treatment.
FAQs
Why is glioblastoma considered to be such a difficult tumor to manage?
Due to glioblastoma's rapid rate of proliferation and infiltration, the tumor cannot be completely removed. Due to its resistance to numerous treatments, this makes the problem worse.
What is glioblastoma treatment?
At present, glioblastoma cannot be prevented, as this sort of cancer is the result of spontaneous mutations of DNA. The cancers are comprised of screening detection and early diagnostic tests for those at risk of developing the disease through physical examination and imaging.
What are the symptoms of neurological assessment?
The symptoms are week-long headaches, seizures, memory loss, mood swings, vision or balance issues, etc.
What advantage of the German healthcare system is perceived by glioblastoma patients?
Germany has high-tech equipment, innovative therapies such as TTF and laser ablation, as well as an opportunity to participate in clinical trials all over the world which gives hope to patients from all over the world.
What part does genetic counseling play in the treatment of glioblastoma?
Genetic counselling is useful for a condition’s familiar predisposition and it influences the treatment process in diseases such as Li-Fraumeni.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
