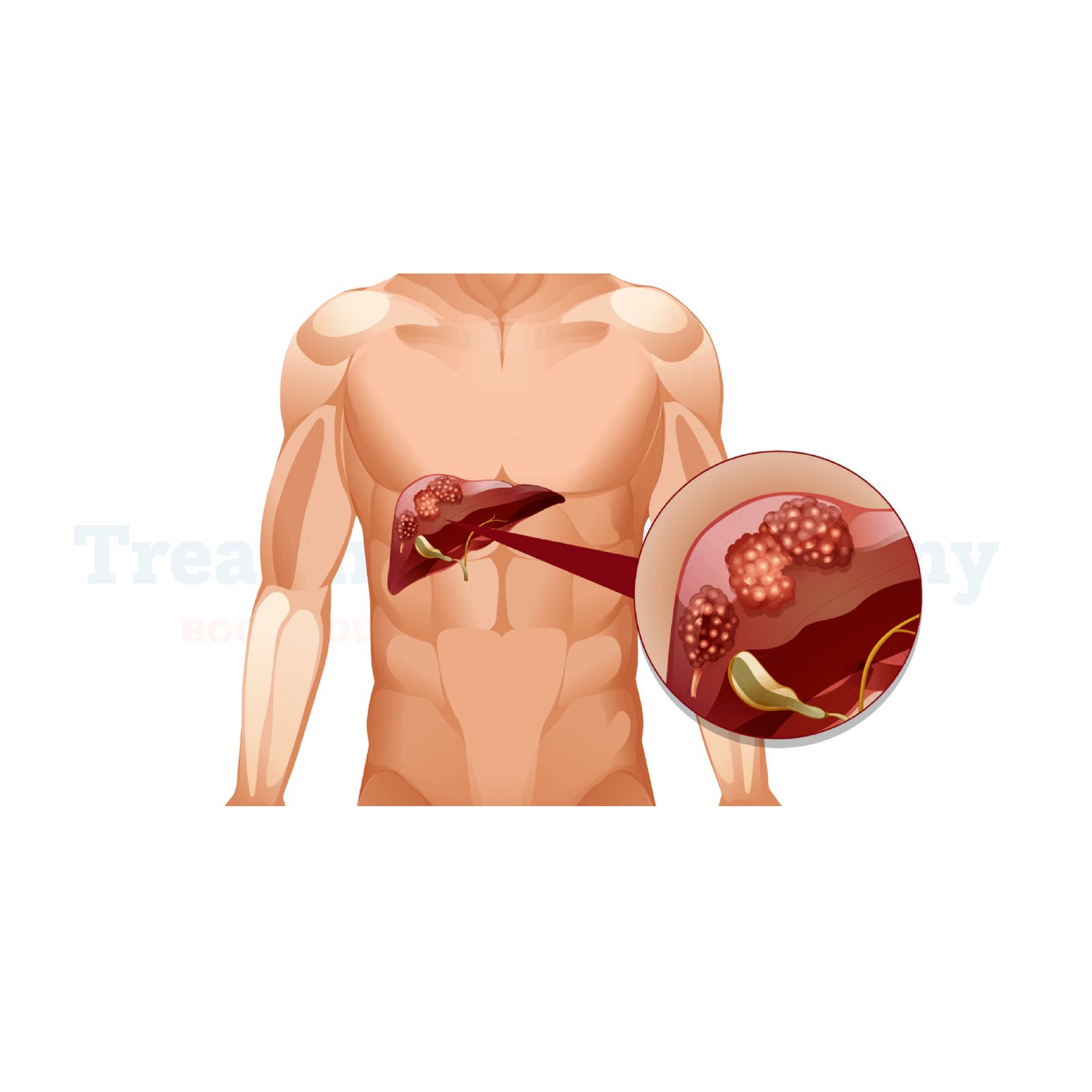
The most prevalent type of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, starts in the hepatocytes. These are the main cells making up the body organ called the liver.
This cancer condition is usually aggressive and mainly associated with chronic liver disorders like cirrhosis of the liver or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, MASLD. Among its contemporaries, Germany is one destination that leads to curing this dangerous form of HCC through advanced therapies and technologies.
HCC is the primary liver cancer, which is one originating from the liver itself and does not arise as metastatic cancer that spreads to the liver from other parts of the body. The early stages of HCC can be treated with surgery or a liver transplant. however, most patients are diagnosed later on, which makes treatment complicated. The most common outcome in cases of untreated or late-stage HCC is liver failure.
Who is at Risk?
HCC is most common among people with chronic liver diseases. It disproportionately affects males assigned at birth (AMAB) and those over 60 years of age. Risk factors include:
Identifying Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Early diagnosis is critical but challenging, as symptoms for HCC commonly overlap with other liver-related conditions. Common symptoms include:
If these symptoms last for more than two weeks, then it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Methods in Germany
Germany utilizes the advanced diagnostic tools in the diagnosis of HCC in a manner that there will be accuracy and precision.
Diagnostic Tests
Emerging HCC Treatments in Germany
Germany offers a wide range of advanced and high-specialty treatments based on the type of stage liver cancer has achieved and the general health of the patient.
Surgical Treatments
Local Therapies
Systemic Therapies
Radiation Therapy
Preventive measures and risk management
The risk of HCC can be reduced with preventable measures:
Supportive Care and Innovation in Germany
There is an emphasis on both curative and palliative care to treat the symptoms and improve the quality of life in Germany. The care is tailored with dietary recommendations, and therefore the patient is well nutritionally prepared during treatment by a nutritionist or a dietitian.
Why Choose Germany for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Liver Cancer) Treatment?
Germany is regarded as the leader in the world for the treatment of cancer, making all the latest innovations in medical technologyand therapies available. Specialists there are highly trained and practice multiple disciplines; each patient will be treated on an individual basis according to his or her specific condition and needs. Access to new, experimental treatments will also be gained by participating in clinical trials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the early symptoms of liver cancer?
Early symptoms include loss of appetite, unknown weight loss, nausea, and swelling in the abdominal regions.
What is the diagnosis of liver cancer?
The testing includes blood tests, CT or MRI imaging, and sometimes a biopsy to confirm cancer.
What is ablation therapy?
Ablation therapy is a new technique where, with minimal invasion, cancer cells are destroyed using heat, cold, or chemicals.
How can hepatitis infections lead to liver cancer?
Infection with hepatitis B leads to chronic liver inflammation that results in cirrhosis and cancer, while infection with hepatitis C also leads to chronic liver inflammation that causes cirrhosis and cancer.
What is prevention against liver cancer?
The main prevention measures are vaccination against hepatitis B, proper handling of Type 2 diabetes, and complete abstinence from alcohol.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
