An intracranial hemorrhage, often known as a brain bleed, is a hazardous and serious medical illness that can be fatal if left untreated. Germany is an ideal place to treat this complicated disease because of the country’s medical equipment and the skills of its professionals.
This article reviews the various forms of intracranial hemorrhage, the signs of the disease, its causes, diagnosis, and the latest treatment options in Germany.
Intracranial hemorrhage refers to a condition in which a blood vessel in the skull is broken or ruptured or is seeping and cracks, causing blood to accumulate and add pressure to the brain.
In essence, this can cause a diminution of blood flow and nutrient supply to the brain, which, if not corrected, can lead to a cavalcade of extensive losses by the tissues. Some of the signs include trauma to the head, hypertension, cerebral aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations.
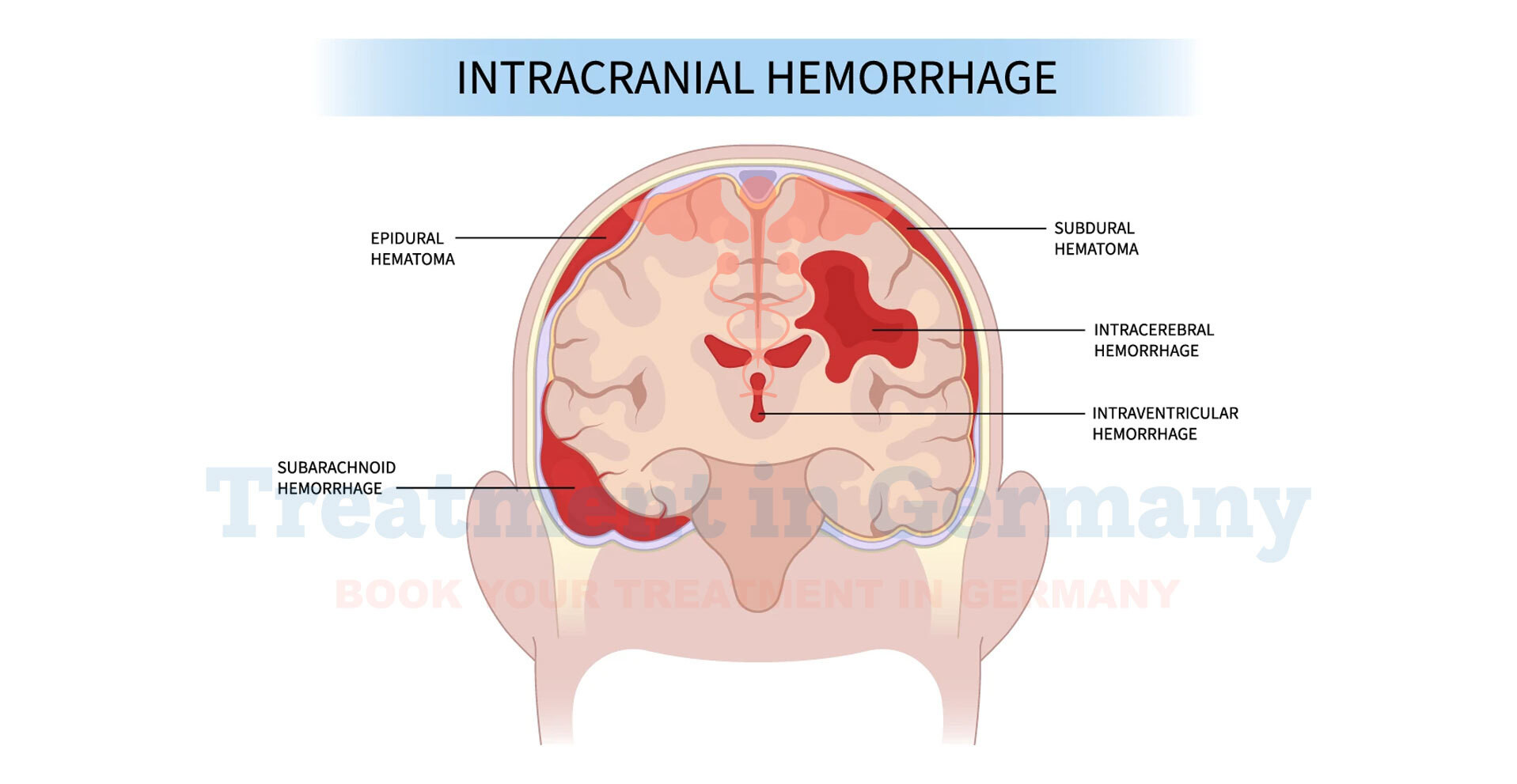
Types of intracranial hemorrhage
The following are the types of intracranial hemorrhage:
Epidural Bleed:
Subdural Bleed:
Subarachnoid Bleed:
Intracerebral Hemorrhage:
Intraventricular Hemorrhage:
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Symptoms of intracranial hemorrhage may include:
In their opinion, fear of light, confusion, or difficult speech may also be a sign of serious blood loss. Early signs of such symptoms are very crucial since they help save lives.
Causes and Risk Factors
Intracranial hemorrhage may result from:
The intensity is additionally influenced by age, habits, and the coexistence of such illnesses more often than not, including diabetes.
Diagnosis of Intracranial Hemorrhage
The place and intensity of the bleeding are ascertained by the healthcare facilities in Germany using the latest diagnostic technologies. These include:
Superior imaging brings accurate diagnosis, and hence proper treatment plans that can be adopted for everyone.
Innovative Treatment in Germany
Stopping the bleeding, controlling brain pressure, and determining the condition's etiology are some of the innovative methods of treatment that Germany has developed. Even complicated cases can be well handled in the various healthcare institutions within the country.
Surgical Interventions
Each procedure is carried out by specialized neurosurgeons using state-of-the-art instruments and equipment to avoid risks.
Medication Management
These drugs are only given to patients and are meant to alleviate symptoms and prevent a worsening of illness.
Supportive Care
Such a treatment concept guarantees integrated care adapted to the specific condition of the patient and the required rehabilitation outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Preventing intracranial hemorrhage involves addressing modifiable risk factors and adopting healthy habits:
Such changes must be included because, besides avoiding the development of intracranial hemorrhage, they’re also beneficial to the brain. The use of protective devices, including helmets and seat belts, reduces traumatic brain injury risks or impact force by a greater degree.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first sign of intracranial hemorrhage?
The early signs include a severe headache, nausea, and one-sided numbness.
How is intracranial hemorrhage diagnosed?
This entails clinical evaluation, including neurologic and motor examination, computerized tomography scans or magnetic resonance imaging, and angiography for vasculature definition.
What can be done in Germany for treating this disease?
It provides cutting-edge operations, the latest solutions in medicines, and complex rehabilitation services.
Does lifestyle change reduce the risk of intracranial hemorrhage?
Yes, controlling them, stopping the smoking habit, and taking a healthy diet make a big difference in the risk level.
Is it important to initiate the process of rehabilitation after the treatment?
Rehabilitation is typically necessary to bring back the necessary skills and enable the patients to live a more fulfilling life. It is designed to enhance the motion, communication, and functional activity of people with the disability.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
